Civil Engineering (CE) Exam > Civil Engineering (CE) Questions > The neutral axis of the cross-section a beam ...
Start Learning for Free
The neutral axis of the cross-section a beam is that axis at which the bending stress is
- a)Zero
- b)minimum
- c)maximum
- d)infinity
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
| FREE This question is part of | Download PDF Attempt this Test |
Verified Answer
The neutral axis of the cross-section a beam is that axis at which the...
Ρ is the radius of curvature of the beam at its neutral axis. From statics, a moment (i.e. pure bending) consists of equal and opposite forces. Therefore, the total amount of force across the cross section must be 0. Therefore the first moment of the cross section about its neutral axis must be zero.
View all questions of this test
Most Upvoted Answer
The neutral axis of the cross-section a beam is that axis at which the...
The neutral axis of a beam refers to the axis at which the bending stress is zero. When a beam is subjected to bending, different parts of the beam experience different stresses. The top fibers of the beam are subjected to compressive stresses, while the bottom fibers are subjected to tensile stresses. The neutral axis is a line within the beam where the stress is neither tensile nor compressive, resulting in zero stress.
Explanation:
1. Introduction:
- A beam is a structural member that is designed to support loads and resist bending.
- Bending stress occurs when a beam is subjected to a bending moment.
- The neutral axis is an important concept in understanding the behavior of a beam under bending.
2. Definition of the neutral axis:
- The neutral axis is the line within the cross-section of a beam where the bending stress is zero.
- It is the axis that divides the cross-section into two regions: the compression zone and the tension zone.
3. Bending stress distribution:
- When a beam is subjected to a bending moment, the top fibers of the beam are compressed while the bottom fibers are stretched.
- The bending stress is maximum at the extreme fibers of the cross-section and decreases linearly towards the neutral axis.
- At the neutral axis, the bending stress is zero, as there is no compression or tension.
4. Determining the location of the neutral axis:
- The location of the neutral axis depends on the geometry of the cross-section and the loading conditions.
- For symmetric cross-sections, such as a rectangular or circular shape, the neutral axis is located at the centroid of the cross-section.
- For non-symmetric cross-sections, the neutral axis may not coincide with the centroid and needs to be determined using complex calculations.
5. Significance of the neutral axis:
- The neutral axis is crucial in the design of beams as it determines the distribution of stresses within the cross-section.
- Engineers need to ensure that the maximum stresses in the beam do not exceed the material's capacity to avoid failure.
- By positioning the neutral axis appropriately, engineers can optimize the design and minimize the overall weight and cost of the beam.
In conclusion, the neutral axis of a beam is the axis at which the bending stress is zero. It is an imaginary line within the cross-section that divides the beam into compression and tension zones. Understanding the location and behavior of the neutral axis is essential for designing safe and efficient beams.
Explanation:
1. Introduction:
- A beam is a structural member that is designed to support loads and resist bending.
- Bending stress occurs when a beam is subjected to a bending moment.
- The neutral axis is an important concept in understanding the behavior of a beam under bending.
2. Definition of the neutral axis:
- The neutral axis is the line within the cross-section of a beam where the bending stress is zero.
- It is the axis that divides the cross-section into two regions: the compression zone and the tension zone.
3. Bending stress distribution:
- When a beam is subjected to a bending moment, the top fibers of the beam are compressed while the bottom fibers are stretched.
- The bending stress is maximum at the extreme fibers of the cross-section and decreases linearly towards the neutral axis.
- At the neutral axis, the bending stress is zero, as there is no compression or tension.
4. Determining the location of the neutral axis:
- The location of the neutral axis depends on the geometry of the cross-section and the loading conditions.
- For symmetric cross-sections, such as a rectangular or circular shape, the neutral axis is located at the centroid of the cross-section.
- For non-symmetric cross-sections, the neutral axis may not coincide with the centroid and needs to be determined using complex calculations.
5. Significance of the neutral axis:
- The neutral axis is crucial in the design of beams as it determines the distribution of stresses within the cross-section.
- Engineers need to ensure that the maximum stresses in the beam do not exceed the material's capacity to avoid failure.
- By positioning the neutral axis appropriately, engineers can optimize the design and minimize the overall weight and cost of the beam.
In conclusion, the neutral axis of a beam is the axis at which the bending stress is zero. It is an imaginary line within the cross-section that divides the beam into compression and tension zones. Understanding the location and behavior of the neutral axis is essential for designing safe and efficient beams.
Free Test
FREE
| Start Free Test |
Community Answer
The neutral axis of the cross-section a beam is that axis at which the...
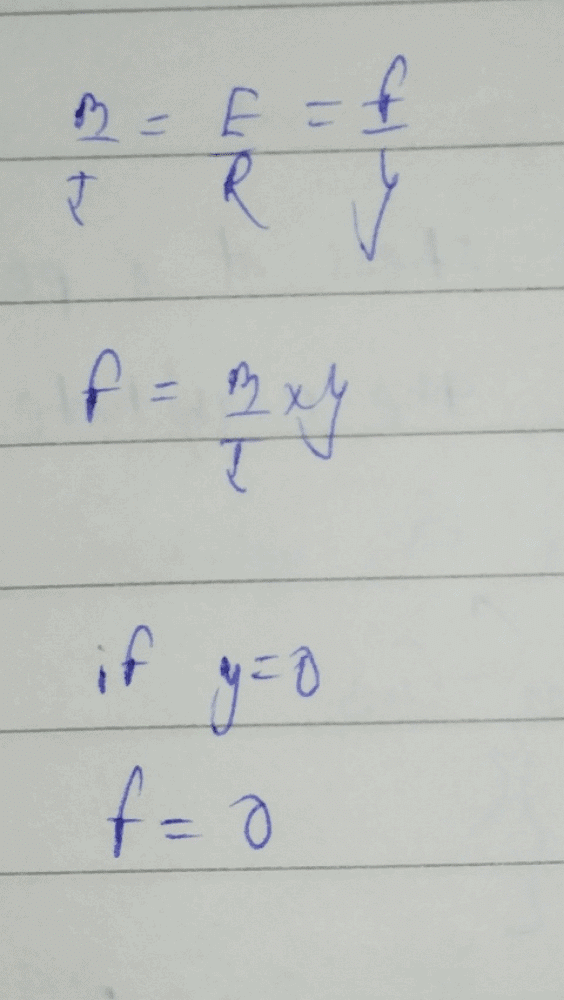
Attention Civil Engineering (CE) Students!
To make sure you are not studying endlessly, EduRev has designed Civil Engineering (CE) study material, with Structured Courses, Videos, & Test Series. Plus get personalized analysis, doubt solving and improvement plans to achieve a great score in Civil Engineering (CE).

|
Explore Courses for Civil Engineering (CE) exam
|

|
Similar Civil Engineering (CE) Doubts
The neutral axis of the cross-section a beam is that axis at which the bending stress isa)Zerob)minimumc)maximumd)infinityCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
The neutral axis of the cross-section a beam is that axis at which the bending stress isa)Zerob)minimumc)maximumd)infinityCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for Civil Engineering (CE) 2024 is part of Civil Engineering (CE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Civil Engineering (CE) exam syllabus. Information about The neutral axis of the cross-section a beam is that axis at which the bending stress isa)Zerob)minimumc)maximumd)infinityCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Civil Engineering (CE) 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for The neutral axis of the cross-section a beam is that axis at which the bending stress isa)Zerob)minimumc)maximumd)infinityCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
The neutral axis of the cross-section a beam is that axis at which the bending stress isa)Zerob)minimumc)maximumd)infinityCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for Civil Engineering (CE) 2024 is part of Civil Engineering (CE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Civil Engineering (CE) exam syllabus. Information about The neutral axis of the cross-section a beam is that axis at which the bending stress isa)Zerob)minimumc)maximumd)infinityCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Civil Engineering (CE) 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for The neutral axis of the cross-section a beam is that axis at which the bending stress isa)Zerob)minimumc)maximumd)infinityCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for The neutral axis of the cross-section a beam is that axis at which the bending stress isa)Zerob)minimumc)maximumd)infinityCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Civil Engineering (CE).
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Civil Engineering (CE) Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of The neutral axis of the cross-section a beam is that axis at which the bending stress isa)Zerob)minimumc)maximumd)infinityCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
The neutral axis of the cross-section a beam is that axis at which the bending stress isa)Zerob)minimumc)maximumd)infinityCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for The neutral axis of the cross-section a beam is that axis at which the bending stress isa)Zerob)minimumc)maximumd)infinityCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of The neutral axis of the cross-section a beam is that axis at which the bending stress isa)Zerob)minimumc)maximumd)infinityCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice The neutral axis of the cross-section a beam is that axis at which the bending stress isa)Zerob)minimumc)maximumd)infinityCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Civil Engineering (CE) tests.

|
Explore Courses for Civil Engineering (CE) exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
























