Electrical Engineering (EE) Exam > Electrical Engineering (EE) Questions > The transformer that does not provide electri...
Start Learning for Free
The transformer that does not provide electric isolation is
- a)power transformer
- b)autotransformer
- c)current transformer
- d)potential transformer
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
| FREE This question is part of | Download PDF Attempt this Test |
Verified Answer
The transformer that does not provide electric isolation isa)power tra...
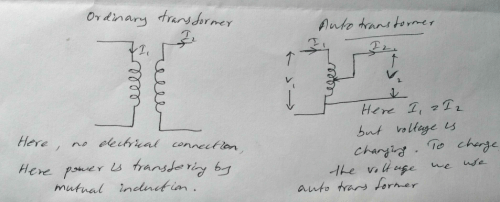
An autotransformer does not provide electrical isolation between its windings as an ordinary transformer does; if the neutral side of the input is not at ground voltage, the neutral side of the output will not be either.
View all questions of this test
Most Upvoted Answer
The transformer that does not provide electric isolation isa)power tra...
Free Test
FREE
| Start Free Test |
Community Answer
The transformer that does not provide electric isolation isa)power tra...
The transformer that does not provide electric isolation is an autotransformer.
Explanation:
An autotransformer is a type of transformer that has only one winding, which serves as both the primary and secondary winding. It is different from a traditional transformer that has separate primary and secondary windings.
No Galvanic Isolation:
The main reason why an autotransformer does not provide electric isolation is that there is no galvanic isolation between the primary and secondary circuits. Galvanic isolation is the separation of two electric circuits to prevent the flow of electrical current between them. In a traditional transformer, the primary and secondary windings are physically separated, providing galvanic isolation. However, in an autotransformer, the primary and secondary winding are interconnected, resulting in the absence of galvanic isolation.
Tap Connections:
An autotransformer has multiple tap connections along the winding, which allows for a variable voltage output. By tapping at different points along the winding, the output voltage can be adjusted accordingly. This feature makes autotransformers suitable for applications where voltage regulation is required.
Advantages:
Despite not providing electric isolation, autotransformers offer several advantages over traditional transformers, such as:
1. Compact Size: Autotransformers are smaller and lighter compared to traditional transformers with similar power ratings. This can be attributed to the shared winding design, which reduces the amount of copper and iron required.
2. Cost-Effectiveness: Due to the reduced material requirements, autotransformers are generally less expensive to manufacture than traditional transformers.
3. Improved Efficiency: The absence of galvanic isolation results in lower losses, leading to higher efficiency.
4. Voltage Regulation: Autotransformers can provide variable output voltages by tapping at different points along the winding. This makes them suitable for applications where precise voltage control is required.
Applications:
Autotransformers are commonly used in various electrical systems and devices, including:
1. Voltage Regulators: Autotransformers are often employed in voltage regulation circuits to adjust the output voltage as per the desired requirements.
2. Power Supplies: Autotransformers can be used in power supply circuits to step up or step down the voltage levels.
3. Motor Starters: Autotransformers are utilized in motor starter circuits to reduce the starting current and provide a smooth start to the motor.
In conclusion, while autotransformers offer several advantages such as compact size, cost-effectiveness, and voltage regulation, they do not provide galvanic isolation between the primary and secondary circuits. Therefore, they are not suitable for applications where electrical isolation is required.
Explanation:
An autotransformer is a type of transformer that has only one winding, which serves as both the primary and secondary winding. It is different from a traditional transformer that has separate primary and secondary windings.
No Galvanic Isolation:
The main reason why an autotransformer does not provide electric isolation is that there is no galvanic isolation between the primary and secondary circuits. Galvanic isolation is the separation of two electric circuits to prevent the flow of electrical current between them. In a traditional transformer, the primary and secondary windings are physically separated, providing galvanic isolation. However, in an autotransformer, the primary and secondary winding are interconnected, resulting in the absence of galvanic isolation.
Tap Connections:
An autotransformer has multiple tap connections along the winding, which allows for a variable voltage output. By tapping at different points along the winding, the output voltage can be adjusted accordingly. This feature makes autotransformers suitable for applications where voltage regulation is required.
Advantages:
Despite not providing electric isolation, autotransformers offer several advantages over traditional transformers, such as:
1. Compact Size: Autotransformers are smaller and lighter compared to traditional transformers with similar power ratings. This can be attributed to the shared winding design, which reduces the amount of copper and iron required.
2. Cost-Effectiveness: Due to the reduced material requirements, autotransformers are generally less expensive to manufacture than traditional transformers.
3. Improved Efficiency: The absence of galvanic isolation results in lower losses, leading to higher efficiency.
4. Voltage Regulation: Autotransformers can provide variable output voltages by tapping at different points along the winding. This makes them suitable for applications where precise voltage control is required.
Applications:
Autotransformers are commonly used in various electrical systems and devices, including:
1. Voltage Regulators: Autotransformers are often employed in voltage regulation circuits to adjust the output voltage as per the desired requirements.
2. Power Supplies: Autotransformers can be used in power supply circuits to step up or step down the voltage levels.
3. Motor Starters: Autotransformers are utilized in motor starter circuits to reduce the starting current and provide a smooth start to the motor.
In conclusion, while autotransformers offer several advantages such as compact size, cost-effectiveness, and voltage regulation, they do not provide galvanic isolation between the primary and secondary circuits. Therefore, they are not suitable for applications where electrical isolation is required.
Attention Electrical Engineering (EE) Students!
To make sure you are not studying endlessly, EduRev has designed Electrical Engineering (EE) study material, with Structured Courses, Videos, & Test Series. Plus get personalized analysis, doubt solving and improvement plans to achieve a great score in Electrical Engineering (EE).

|
Explore Courses for Electrical Engineering (EE) exam
|

|
Similar Electrical Engineering (EE) Doubts
The transformer that does not provide electric isolation isa)power transformerb)autotransformerc)current transformerd)potential transformerCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
The transformer that does not provide electric isolation isa)power transformerb)autotransformerc)current transformerd)potential transformerCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? for Electrical Engineering (EE) 2024 is part of Electrical Engineering (EE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Electrical Engineering (EE) exam syllabus. Information about The transformer that does not provide electric isolation isa)power transformerb)autotransformerc)current transformerd)potential transformerCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Electrical Engineering (EE) 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for The transformer that does not provide electric isolation isa)power transformerb)autotransformerc)current transformerd)potential transformerCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?.
The transformer that does not provide electric isolation isa)power transformerb)autotransformerc)current transformerd)potential transformerCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? for Electrical Engineering (EE) 2024 is part of Electrical Engineering (EE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Electrical Engineering (EE) exam syllabus. Information about The transformer that does not provide electric isolation isa)power transformerb)autotransformerc)current transformerd)potential transformerCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Electrical Engineering (EE) 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for The transformer that does not provide electric isolation isa)power transformerb)autotransformerc)current transformerd)potential transformerCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for The transformer that does not provide electric isolation isa)power transformerb)autotransformerc)current transformerd)potential transformerCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Electrical Engineering (EE).
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Electrical Engineering (EE) Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of The transformer that does not provide electric isolation isa)power transformerb)autotransformerc)current transformerd)potential transformerCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
The transformer that does not provide electric isolation isa)power transformerb)autotransformerc)current transformerd)potential transformerCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for The transformer that does not provide electric isolation isa)power transformerb)autotransformerc)current transformerd)potential transformerCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of The transformer that does not provide electric isolation isa)power transformerb)autotransformerc)current transformerd)potential transformerCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice The transformer that does not provide electric isolation isa)power transformerb)autotransformerc)current transformerd)potential transformerCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Electrical Engineering (EE) tests.

|
Explore Courses for Electrical Engineering (EE) exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
























