IIT JAM Exam > IIT JAM Questions > What is the difference between pitch and plun...
Start Learning for Free
What is the difference between pitch and plunge?
Verified Answer
What is the difference between pitch and plunge?
While plunge is the amount by which a line element departs from horizontality, usually therefore measured in a vertical plane containing the line element or linear feature, pitch or rake is that a line elemet makes with the strike of the plane in which it is contained and measured in this plane. A pitch is always acute angle unless the line element is oriented in the direction of true dip of the containing plane. As an example, hornblende grains in an amphibolite may form a distinct lineation in a plane which is a plane of schistosity. The angle that the linear hornblende crystals make with the strike of the schist within the plane of schistosity is Rake or Pitch. But the plunge of the lineation of these hornblende crystals will be measured in a vertical plane containing the dominant trend of hornblende grains.
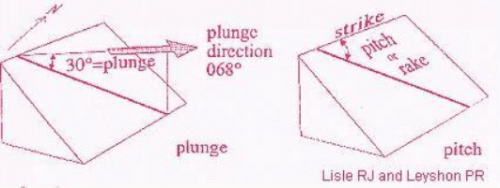

 This question is part of UPSC exam. View all IIT JAM courses
This question is part of UPSC exam. View all IIT JAM courses
Most Upvoted Answer
What is the difference between pitch and plunge?
Introduction
Pitch and plunge are two terms that are commonly used in the field of geology and structural geology. While they are related to the orientation of geological features, they have distinct meanings and applications. In this explanation, we will explore the difference between pitch and plunge in detail.
Pitch
Pitch refers to the angle between a geological feature and a horizontal plane. It is used to describe the inclination or slope of a planar feature, such as a bedding plane or a fault plane. The pitch angle is measured perpendicular to the strike direction, which is the horizontal line on the plane. Pitch angles can vary from 0° (horizontal) to 90° (vertical).
Plunge
On the other hand, plunge is the angle between a geological feature and a vertical plane. It is used to describe the inclination or dip of a linear feature, such as a fold axis or a lineation. Plunge angles can vary from 0° (horizontal) to 90° (vertical). Unlike pitch, plunge is measured parallel to the strike direction.
Key Differences
1. Orientation: Pitch is used to describe the orientation of planar features, while plunge is used for linear features.
2. Measurement Direction: Pitch is measured perpendicular to the strike direction, while plunge is measured parallel to the strike direction.
3. Angle Range: Pitch angles can range from 0° to 90°, while plunge angles can also range from 0° to 90°.
4. Application: Pitch is commonly used in describing bedding planes, fault planes, or any planar geological feature, whereas plunge is used to describe fold axes, lineations, or any linear geological feature.
Example
To better understand the difference, consider a folded rock layer. The fold axis is a linear feature that represents the hinge line of the fold. If we measure the angle between the fold axis and a horizontal plane, we are measuring the plunge of the fold axis. However, if we measure the angle between the bedding plane and a horizontal plane, we are measuring the pitch of the bedding plane.
Conclusion
In summary, pitch and plunge are terms used in geology to describe the orientation of geological features. Pitch refers to the angle between a planar feature and a horizontal plane, while plunge refers to the angle between a linear feature and a vertical plane. Understanding these concepts is crucial for accurately describing and interpreting geological structures.
Pitch and plunge are two terms that are commonly used in the field of geology and structural geology. While they are related to the orientation of geological features, they have distinct meanings and applications. In this explanation, we will explore the difference between pitch and plunge in detail.
Pitch
Pitch refers to the angle between a geological feature and a horizontal plane. It is used to describe the inclination or slope of a planar feature, such as a bedding plane or a fault plane. The pitch angle is measured perpendicular to the strike direction, which is the horizontal line on the plane. Pitch angles can vary from 0° (horizontal) to 90° (vertical).
Plunge
On the other hand, plunge is the angle between a geological feature and a vertical plane. It is used to describe the inclination or dip of a linear feature, such as a fold axis or a lineation. Plunge angles can vary from 0° (horizontal) to 90° (vertical). Unlike pitch, plunge is measured parallel to the strike direction.
Key Differences
1. Orientation: Pitch is used to describe the orientation of planar features, while plunge is used for linear features.
2. Measurement Direction: Pitch is measured perpendicular to the strike direction, while plunge is measured parallel to the strike direction.
3. Angle Range: Pitch angles can range from 0° to 90°, while plunge angles can also range from 0° to 90°.
4. Application: Pitch is commonly used in describing bedding planes, fault planes, or any planar geological feature, whereas plunge is used to describe fold axes, lineations, or any linear geological feature.
Example
To better understand the difference, consider a folded rock layer. The fold axis is a linear feature that represents the hinge line of the fold. If we measure the angle between the fold axis and a horizontal plane, we are measuring the plunge of the fold axis. However, if we measure the angle between the bedding plane and a horizontal plane, we are measuring the pitch of the bedding plane.
Conclusion
In summary, pitch and plunge are terms used in geology to describe the orientation of geological features. Pitch refers to the angle between a planar feature and a horizontal plane, while plunge refers to the angle between a linear feature and a vertical plane. Understanding these concepts is crucial for accurately describing and interpreting geological structures.

|
Explore Courses for IIT JAM exam
|

|
Similar IIT JAM Doubts
What is the difference between pitch and plunge?
Question Description
What is the difference between pitch and plunge? for IIT JAM 2025 is part of IIT JAM preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the IIT JAM exam syllabus. Information about What is the difference between pitch and plunge? covers all topics & solutions for IIT JAM 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for What is the difference between pitch and plunge?.
What is the difference between pitch and plunge? for IIT JAM 2025 is part of IIT JAM preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the IIT JAM exam syllabus. Information about What is the difference between pitch and plunge? covers all topics & solutions for IIT JAM 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for What is the difference between pitch and plunge?.
Solutions for What is the difference between pitch and plunge? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for IIT JAM.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for IIT JAM Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of What is the difference between pitch and plunge? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
What is the difference between pitch and plunge?, a detailed solution for What is the difference between pitch and plunge? has been provided alongside types of What is the difference between pitch and plunge? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice What is the difference between pitch and plunge? tests, examples and also practice IIT JAM tests.

|
Explore Courses for IIT JAM exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.





















