JEE Exam > JEE Questions > In the figure shown, a ball of mass m collide...
Start Learning for Free
In the figure shown, a ball of mass m collides perpendicularly on a smooth stationary wedge of mass M, kept on a smooth horizontal plane. If the coefficient of restitution of collison is e, then determine the velocity of the wedge after collision.?
Verified Answer
In the figure shown, a ball of mass m collides perpendicularly on a sm...
Mass m stikes with velocity v0 perpendicularly to M
Coefficient of restitution,e
Coefficient of restitution,e
v is the velocity of wedge after collision and v' is the velocity of m after collisionwedge is at rest before collision and m is moving wuth v0 before collisione v
0=v−v'
Law of conservation of momentum
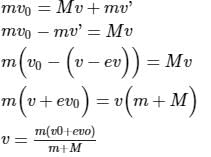
0=v−v'
Law of conservation of momentum
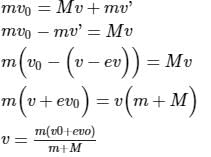
 This question is part of UPSC exam. View all JEE courses
This question is part of UPSC exam. View all JEE courses
Most Upvoted Answer
In the figure shown, a ball of mass m collides perpendicularly on a sm...
Introduction:
In this scenario, a ball of mass m collides perpendicularly with a smooth stationary wedge of mass M, which is placed on a smooth horizontal plane. We are given the coefficient of restitution (e), and we need to determine the velocity of the wedge after the collision.
Understanding the Problem:
To solve this problem, we need to analyze the collision between the ball and the wedge. The coefficient of restitution (e) is a measure of how elastic the collision is. It represents the ratio of the final relative velocity of separation to the initial relative velocity of approach.
Applying Conservation of Momentum:
To determine the velocity of the wedge after the collision, we can apply the principle of conservation of momentum. According to this principle, the total momentum before the collision should be equal to the total momentum after the collision.
Initial Momentum:
The initial momentum of the system can be calculated as the sum of the momentum of the ball and the momentum of the wedge before the collision. Since the wedge is stationary, its initial momentum is zero. The initial momentum of the ball can be calculated using the equation:
Initial momentum of the ball = mass of the ball (m) * velocity of the ball before the collision (u)
Final Momentum:
After the collision, the ball will rebound off the wedge and move in the opposite direction. The wedge will acquire a certain velocity in the direction opposite to the ball's initial velocity. Let's denote the final velocity of the ball as v and the final velocity of the wedge as V.
The final momentum of the system can be calculated as the sum of the momentum of the ball and the momentum of the wedge after the collision.
Final momentum of the system = (mass of the ball * velocity of the ball after the collision) + (mass of the wedge * velocity of the wedge after the collision)
Applying Coefficient of Restitution:
The coefficient of restitution (e) can be used to relate the velocities of separation and approach. According to the definition of the coefficient of restitution, we have:
e = (velocity of separation) / (velocity of approach)
For a collision perpendicular to the surface, the velocity of approach is the initial velocity of the ball (u), and the velocity of separation is the final velocity of the ball (v) minus the final velocity of the wedge (V).
e = (v - V) / u
Simplifying this equation, we can express the final velocity of the ball (v) in terms of the initial velocity of the ball (u), the final velocity of the wedge (V), and the coefficient of restitution (e):
v = e * u + V
Using Conservation of Momentum:
Now, we can substitute the values of the initial and final momenta into the conservation of momentum equation:
m * u = m * v + M * V
Substituting the expression for v derived from the coefficient of restitution equation:
m * u = m * (e * u + V) + M * V
Simplifying this equation will give us the value of V, the velocity of the wedge after the collision.
Conclusion:
By applying the principles of conservation of momentum and using the equation derived from the coefficient of restitution, we can determine the velocity of the wedge after the collision. The final equation obtained can be solved to find
In this scenario, a ball of mass m collides perpendicularly with a smooth stationary wedge of mass M, which is placed on a smooth horizontal plane. We are given the coefficient of restitution (e), and we need to determine the velocity of the wedge after the collision.
Understanding the Problem:
To solve this problem, we need to analyze the collision between the ball and the wedge. The coefficient of restitution (e) is a measure of how elastic the collision is. It represents the ratio of the final relative velocity of separation to the initial relative velocity of approach.
Applying Conservation of Momentum:
To determine the velocity of the wedge after the collision, we can apply the principle of conservation of momentum. According to this principle, the total momentum before the collision should be equal to the total momentum after the collision.
Initial Momentum:
The initial momentum of the system can be calculated as the sum of the momentum of the ball and the momentum of the wedge before the collision. Since the wedge is stationary, its initial momentum is zero. The initial momentum of the ball can be calculated using the equation:
Initial momentum of the ball = mass of the ball (m) * velocity of the ball before the collision (u)
Final Momentum:
After the collision, the ball will rebound off the wedge and move in the opposite direction. The wedge will acquire a certain velocity in the direction opposite to the ball's initial velocity. Let's denote the final velocity of the ball as v and the final velocity of the wedge as V.
The final momentum of the system can be calculated as the sum of the momentum of the ball and the momentum of the wedge after the collision.
Final momentum of the system = (mass of the ball * velocity of the ball after the collision) + (mass of the wedge * velocity of the wedge after the collision)
Applying Coefficient of Restitution:
The coefficient of restitution (e) can be used to relate the velocities of separation and approach. According to the definition of the coefficient of restitution, we have:
e = (velocity of separation) / (velocity of approach)
For a collision perpendicular to the surface, the velocity of approach is the initial velocity of the ball (u), and the velocity of separation is the final velocity of the ball (v) minus the final velocity of the wedge (V).
e = (v - V) / u
Simplifying this equation, we can express the final velocity of the ball (v) in terms of the initial velocity of the ball (u), the final velocity of the wedge (V), and the coefficient of restitution (e):
v = e * u + V
Using Conservation of Momentum:
Now, we can substitute the values of the initial and final momenta into the conservation of momentum equation:
m * u = m * v + M * V
Substituting the expression for v derived from the coefficient of restitution equation:
m * u = m * (e * u + V) + M * V
Simplifying this equation will give us the value of V, the velocity of the wedge after the collision.
Conclusion:
By applying the principles of conservation of momentum and using the equation derived from the coefficient of restitution, we can determine the velocity of the wedge after the collision. The final equation obtained can be solved to find
Attention JEE Students!
To make sure you are not studying endlessly, EduRev has designed JEE study material, with Structured Courses, Videos, & Test Series. Plus get personalized analysis, doubt solving and improvement plans to achieve a great score in JEE.

|
Explore Courses for JEE exam
|

|
Similar JEE Doubts
In the figure shown, a ball of mass m collides perpendicularly on a smooth stationary wedge of mass M, kept on a smooth horizontal plane. If the coefficient of restitution of collison is e, then determine the velocity of the wedge after collision.?
Question Description
In the figure shown, a ball of mass m collides perpendicularly on a smooth stationary wedge of mass M, kept on a smooth horizontal plane. If the coefficient of restitution of collison is e, then determine the velocity of the wedge after collision.? for JEE 2024 is part of JEE preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the JEE exam syllabus. Information about In the figure shown, a ball of mass m collides perpendicularly on a smooth stationary wedge of mass M, kept on a smooth horizontal plane. If the coefficient of restitution of collison is e, then determine the velocity of the wedge after collision.? covers all topics & solutions for JEE 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for In the figure shown, a ball of mass m collides perpendicularly on a smooth stationary wedge of mass M, kept on a smooth horizontal plane. If the coefficient of restitution of collison is e, then determine the velocity of the wedge after collision.?.
In the figure shown, a ball of mass m collides perpendicularly on a smooth stationary wedge of mass M, kept on a smooth horizontal plane. If the coefficient of restitution of collison is e, then determine the velocity of the wedge after collision.? for JEE 2024 is part of JEE preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the JEE exam syllabus. Information about In the figure shown, a ball of mass m collides perpendicularly on a smooth stationary wedge of mass M, kept on a smooth horizontal plane. If the coefficient of restitution of collison is e, then determine the velocity of the wedge after collision.? covers all topics & solutions for JEE 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for In the figure shown, a ball of mass m collides perpendicularly on a smooth stationary wedge of mass M, kept on a smooth horizontal plane. If the coefficient of restitution of collison is e, then determine the velocity of the wedge after collision.?.
Solutions for In the figure shown, a ball of mass m collides perpendicularly on a smooth stationary wedge of mass M, kept on a smooth horizontal plane. If the coefficient of restitution of collison is e, then determine the velocity of the wedge after collision.? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for JEE.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for JEE Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of In the figure shown, a ball of mass m collides perpendicularly on a smooth stationary wedge of mass M, kept on a smooth horizontal plane. If the coefficient of restitution of collison is e, then determine the velocity of the wedge after collision.? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
In the figure shown, a ball of mass m collides perpendicularly on a smooth stationary wedge of mass M, kept on a smooth horizontal plane. If the coefficient of restitution of collison is e, then determine the velocity of the wedge after collision.?, a detailed solution for In the figure shown, a ball of mass m collides perpendicularly on a smooth stationary wedge of mass M, kept on a smooth horizontal plane. If the coefficient of restitution of collison is e, then determine the velocity of the wedge after collision.? has been provided alongside types of In the figure shown, a ball of mass m collides perpendicularly on a smooth stationary wedge of mass M, kept on a smooth horizontal plane. If the coefficient of restitution of collison is e, then determine the velocity of the wedge after collision.? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice In the figure shown, a ball of mass m collides perpendicularly on a smooth stationary wedge of mass M, kept on a smooth horizontal plane. If the coefficient of restitution of collison is e, then determine the velocity of the wedge after collision.? tests, examples and also practice JEE tests.

|
Explore Courses for JEE exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.




















