Class 10 Exam > Class 10 Questions > Describes the structure and functional of Nep...
Start Learning for Free
Describes the structure and functional of Nephron ?
Most Upvoted Answer
Describes the structure and functional of Nephron ?
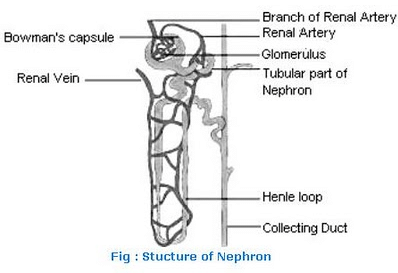
Nephron is the filtration unit of kidney. It consists of a tubule which is connected with collecting duct at one end and a cup – shaped structure at the other end.
This cup-shaped structure is called ‘Bowman’s capsule’. Every Bowman’s capsule contains a cluster of capillaries, called ‘Glomerulus’, within the cup – shaped structure. The blood enters into Glomerulus through afferent arteriole of renal artery and leaves it through efferent arteriole.
Functioning of Nephron
1. Filtration: Filtration of blood takes place in Bowman’s capsule from the capillaries of glomerulus. The filtrate passes into the tubular part of the nephron. This filtrate contains glucose, amino acids, urea, uric acid, salts and a major amount of water.
2. Re-absorption: As the filtrate flows along the tubule useful substances such as glucose, amino acids, salts and water are selectively re-absorbed into the blood by capillaries surrounding the nephron tubule.
The amount of water re-absorbed depends on the need of the body and also on the amount of wastes to be excreted.
3. Urine: The filtrate which remains after re-absorption is called urine. Urine contains dissolved nitrogenous waste, i.e. urea and uric acid, excess salts and water. Urine is collected from nephrons by the collecting duct to carry it to the ureter.
Community Answer
Describes the structure and functional of Nephron ?
Nephron :1)ultra absorption:: the process in which the dirty blood (contain: amino acids, urea water ,salt, glucose etc.) is transfer or passes into the Bowman's capsule through glomerulars from afferent artery is called ulta absorption.
2) selective reabsorption:: the process in which the waste present in the body require water at that time the water present in nephron gives out the water this process called as selective reabsorption.
3)tabular secretion :: the process , in which the extra urea present in the blood passes into the tube through renal vein is called tabular secretion.
2) selective reabsorption:: the process in which the waste present in the body require water at that time the water present in nephron gives out the water this process called as selective reabsorption.
3)tabular secretion :: the process , in which the extra urea present in the blood passes into the tube through renal vein is called tabular secretion.

|
Explore Courses for Class 10 exam
|

|
Similar Class 10 Doubts
Question Description
Describes the structure and functional of Nephron ? for Class 10 2025 is part of Class 10 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 10 exam syllabus. Information about Describes the structure and functional of Nephron ? covers all topics & solutions for Class 10 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Describes the structure and functional of Nephron ?.
Describes the structure and functional of Nephron ? for Class 10 2025 is part of Class 10 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 10 exam syllabus. Information about Describes the structure and functional of Nephron ? covers all topics & solutions for Class 10 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Describes the structure and functional of Nephron ?.
Solutions for Describes the structure and functional of Nephron ? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Class 10.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Class 10 Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Describes the structure and functional of Nephron ? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Describes the structure and functional of Nephron ?, a detailed solution for Describes the structure and functional of Nephron ? has been provided alongside types of Describes the structure and functional of Nephron ? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Describes the structure and functional of Nephron ? tests, examples and also practice Class 10 tests.

|
Explore Courses for Class 10 exam
|

|
Signup to solve all Doubts
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.





















