Commerce Exam > Commerce Questions > Explain the rationale behind the conditions o...
Start Learning for Free
Explain the rationale behind the conditions of equilibrium of a producer?
Verified Answer
Explain the rationale behind the conditions of equilibrium of a produc...
Equilibrium refers to a state of rest when no change is required. A producer is said to be in equilibrium when it has no inclination to expand or to contract its output. This state either reflects maximum profits or minimum losses. The conditions of producer's equilibrium can be explained through the MR-MC approach. In this approach, the producer attains equilibrium where the following two conditions are fulfilled.
(i) MR = MC:
As long as MC is less than MR, it is profitable for the producer to go on producing more because it adds to its profits. He stops producing more only when MC becomes equal to MR.
(ii) MC is greater than MR after MC = MR output level:
When MC is greater than MR after equilibrium, it means producing more will lead to decline in profits.
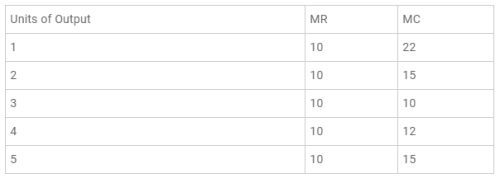

According to the schedule, at 3 units of output, both the conditions of producer’s equilibrium are satisfied. That is, at this level, both MR and MC are equal to 10 and MC is rising. Thus, the producer’s equilibrium is 3 units of output.
 This question is part of UPSC exam. View all Commerce courses
This question is part of UPSC exam. View all Commerce courses
Most Upvoted Answer
Explain the rationale behind the conditions of equilibrium of a produc...
Conditions of Equilibrium of a Producer:
The conditions of equilibrium of a producer refer to the factors that determine the optimal level of production and profit for a producer in a competitive market. These conditions are based on the principles of profit maximization and cost minimization, and they ensure that the producer is operating at a point where marginal cost equals marginal revenue.
1. Marginal Cost equals Marginal Revenue:
The first condition of equilibrium for a producer is that the marginal cost (MC) should be equal to the marginal revenue (MR) generated from selling an additional unit of output. This is because a producer will continue to increase production as long as the marginal revenue exceeds the marginal cost, as it indicates that producing one more unit will add to the overall profit. However, once the marginal cost exceeds the marginal revenue, the producer would be better off reducing production.
2. Optimal Level of Output:
The second condition of equilibrium is to determine the optimal level of output that maximizes profit. This is achieved by producing up to the point where the marginal cost equals the marginal revenue. At this level, the producer is neither overproducing nor underproducing, ensuring efficiency in resource allocation.
3. Price equals Marginal Cost:
The third condition of equilibrium involves setting the price of the product equal to the marginal cost. In a competitive market, the price is determined by the market forces of supply and demand. By setting the price equal to the marginal cost, the producer ensures that each unit produced generates a profit equal to the cost of producing that unit.
4. Cost Minimization:
The fourth condition of equilibrium is cost minimization. A producer aims to minimize costs by efficiently allocating resources and optimizing the production process. This involves reducing wastage, improving productivity, and utilizing the most cost-effective inputs. By minimizing costs, the producer can maximize profit and achieve equilibrium.
5. Long-Run Equilibrium:
The final condition of equilibrium is achieving long-run equilibrium. In the long run, a producer adjusts its inputs, such as labor and capital, to optimize production. This involves making long-term decisions regarding investment, technology adoption, and expansion. In long-run equilibrium, the producer operates at the most efficient scale of production, maximizing profit and ensuring sustainability.
In conclusion, the conditions of equilibrium for a producer involve the equalization of marginal cost and marginal revenue, determination of the optimal level of output, setting the price equal to marginal cost, cost minimization, and achieving long-run equilibrium. These conditions enable a producer to maximize profit, allocate resources efficiently, and operate in a competitive market.
The conditions of equilibrium of a producer refer to the factors that determine the optimal level of production and profit for a producer in a competitive market. These conditions are based on the principles of profit maximization and cost minimization, and they ensure that the producer is operating at a point where marginal cost equals marginal revenue.
1. Marginal Cost equals Marginal Revenue:
The first condition of equilibrium for a producer is that the marginal cost (MC) should be equal to the marginal revenue (MR) generated from selling an additional unit of output. This is because a producer will continue to increase production as long as the marginal revenue exceeds the marginal cost, as it indicates that producing one more unit will add to the overall profit. However, once the marginal cost exceeds the marginal revenue, the producer would be better off reducing production.
2. Optimal Level of Output:
The second condition of equilibrium is to determine the optimal level of output that maximizes profit. This is achieved by producing up to the point where the marginal cost equals the marginal revenue. At this level, the producer is neither overproducing nor underproducing, ensuring efficiency in resource allocation.
3. Price equals Marginal Cost:
The third condition of equilibrium involves setting the price of the product equal to the marginal cost. In a competitive market, the price is determined by the market forces of supply and demand. By setting the price equal to the marginal cost, the producer ensures that each unit produced generates a profit equal to the cost of producing that unit.
4. Cost Minimization:
The fourth condition of equilibrium is cost minimization. A producer aims to minimize costs by efficiently allocating resources and optimizing the production process. This involves reducing wastage, improving productivity, and utilizing the most cost-effective inputs. By minimizing costs, the producer can maximize profit and achieve equilibrium.
5. Long-Run Equilibrium:
The final condition of equilibrium is achieving long-run equilibrium. In the long run, a producer adjusts its inputs, such as labor and capital, to optimize production. This involves making long-term decisions regarding investment, technology adoption, and expansion. In long-run equilibrium, the producer operates at the most efficient scale of production, maximizing profit and ensuring sustainability.
In conclusion, the conditions of equilibrium for a producer involve the equalization of marginal cost and marginal revenue, determination of the optimal level of output, setting the price equal to marginal cost, cost minimization, and achieving long-run equilibrium. These conditions enable a producer to maximize profit, allocate resources efficiently, and operate in a competitive market.
Attention Commerce Students!
To make sure you are not studying endlessly, EduRev has designed Commerce study material, with Structured Courses, Videos, & Test Series. Plus get personalized analysis, doubt solving and improvement plans to achieve a great score in Commerce.

|
Explore Courses for Commerce exam
|

|
Similar Commerce Doubts
Explain the rationale behind the conditions of equilibrium of a producer?
Question Description
Explain the rationale behind the conditions of equilibrium of a producer? for Commerce 2024 is part of Commerce preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Commerce exam syllabus. Information about Explain the rationale behind the conditions of equilibrium of a producer? covers all topics & solutions for Commerce 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Explain the rationale behind the conditions of equilibrium of a producer?.
Explain the rationale behind the conditions of equilibrium of a producer? for Commerce 2024 is part of Commerce preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Commerce exam syllabus. Information about Explain the rationale behind the conditions of equilibrium of a producer? covers all topics & solutions for Commerce 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Explain the rationale behind the conditions of equilibrium of a producer?.
Solutions for Explain the rationale behind the conditions of equilibrium of a producer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Commerce.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Commerce Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Explain the rationale behind the conditions of equilibrium of a producer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Explain the rationale behind the conditions of equilibrium of a producer?, a detailed solution for Explain the rationale behind the conditions of equilibrium of a producer? has been provided alongside types of Explain the rationale behind the conditions of equilibrium of a producer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Explain the rationale behind the conditions of equilibrium of a producer? tests, examples and also practice Commerce tests.

|
Explore Courses for Commerce exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.

























