Civil Engineering (CE) Exam > Civil Engineering (CE) Questions > Which of the following is a shear-thickening ...
Start Learning for Free
Which of the following is a shear-thickening fluid?
- a)Bingham plastic
- b)Thixotropic
- c)Dilatant
- d)Pseudoplastic
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
| FREE This question is part of | Download PDF Attempt this Test |
Verified Answer
Which of the following is a shear-thickening fluid?a)Bingham plasticb)...
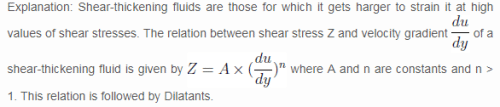
Most Upvoted Answer
Which of the following is a shear-thickening fluid?a)Bingham plasticb)...
Shear-thickening fluids are non-Newtonian fluids whose viscosity increases with an increase in shear rate or stress. Dilatant fluids are an example of shear-thickening fluids.
Explanation:
Dilatant fluids are those fluids whose viscosity increases with the increase in the shear rate. In such fluids, the particles within the fluid tend to form clusters or networks that resist deformation. As a result, the fluid becomes more viscous and resists flow. When the shear rate is low, these particles are not able to form a network and the fluid behaves like a Newtonian fluid. However, when the shear rate is increased, the particles start to form clusters, resulting in an increase in viscosity.
Examples of dilatant fluids include cornstarch suspended in water and quicksand. When these fluids are subjected to shear forces, they become more viscous and resist flow. This property makes dilatant fluids useful in certain applications, such as body armor and protective equipment.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, dilatant fluids are an example of shear-thickening fluids. They exhibit an increase in viscosity with an increase in shear rate or stress. This unique property makes them useful in several applications, including protective equipment and body armor.
Explanation:
Dilatant fluids are those fluids whose viscosity increases with the increase in the shear rate. In such fluids, the particles within the fluid tend to form clusters or networks that resist deformation. As a result, the fluid becomes more viscous and resists flow. When the shear rate is low, these particles are not able to form a network and the fluid behaves like a Newtonian fluid. However, when the shear rate is increased, the particles start to form clusters, resulting in an increase in viscosity.
Examples of dilatant fluids include cornstarch suspended in water and quicksand. When these fluids are subjected to shear forces, they become more viscous and resist flow. This property makes dilatant fluids useful in certain applications, such as body armor and protective equipment.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, dilatant fluids are an example of shear-thickening fluids. They exhibit an increase in viscosity with an increase in shear rate or stress. This unique property makes them useful in several applications, including protective equipment and body armor.
Free Test
FREE
| Start Free Test |
Community Answer
Which of the following is a shear-thickening fluid?a)Bingham plasticb)...
Explanation: Shear-thickening fluids are those for which it gets harger to strain it at high values of shear stresses. The relation between shear stress Z and velocity gradient of a shear-thickening fluid is given by where A and n are constants and n > 1. This relation is followed by Dilatants.
Attention Civil Engineering (CE) Students!
To make sure you are not studying endlessly, EduRev has designed Civil Engineering (CE) study material, with Structured Courses, Videos, & Test Series. Plus get personalized analysis, doubt solving and improvement plans to achieve a great score in Civil Engineering (CE).

|
Explore Courses for Civil Engineering (CE) exam
|

|
Similar Civil Engineering (CE) Doubts
Which of the following is a shear-thickening fluid?a)Bingham plasticb)Thixotropicc)Dilatantd)PseudoplasticCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
Which of the following is a shear-thickening fluid?a)Bingham plasticb)Thixotropicc)Dilatantd)PseudoplasticCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? for Civil Engineering (CE) 2024 is part of Civil Engineering (CE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Civil Engineering (CE) exam syllabus. Information about Which of the following is a shear-thickening fluid?a)Bingham plasticb)Thixotropicc)Dilatantd)PseudoplasticCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Civil Engineering (CE) 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Which of the following is a shear-thickening fluid?a)Bingham plasticb)Thixotropicc)Dilatantd)PseudoplasticCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?.
Which of the following is a shear-thickening fluid?a)Bingham plasticb)Thixotropicc)Dilatantd)PseudoplasticCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? for Civil Engineering (CE) 2024 is part of Civil Engineering (CE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Civil Engineering (CE) exam syllabus. Information about Which of the following is a shear-thickening fluid?a)Bingham plasticb)Thixotropicc)Dilatantd)PseudoplasticCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Civil Engineering (CE) 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Which of the following is a shear-thickening fluid?a)Bingham plasticb)Thixotropicc)Dilatantd)PseudoplasticCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for Which of the following is a shear-thickening fluid?a)Bingham plasticb)Thixotropicc)Dilatantd)PseudoplasticCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Civil Engineering (CE).
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Civil Engineering (CE) Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Which of the following is a shear-thickening fluid?a)Bingham plasticb)Thixotropicc)Dilatantd)PseudoplasticCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Which of the following is a shear-thickening fluid?a)Bingham plasticb)Thixotropicc)Dilatantd)PseudoplasticCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for Which of the following is a shear-thickening fluid?a)Bingham plasticb)Thixotropicc)Dilatantd)PseudoplasticCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of Which of the following is a shear-thickening fluid?a)Bingham plasticb)Thixotropicc)Dilatantd)PseudoplasticCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Which of the following is a shear-thickening fluid?a)Bingham plasticb)Thixotropicc)Dilatantd)PseudoplasticCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Civil Engineering (CE) tests.

|
Explore Courses for Civil Engineering (CE) exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
























