Class 11 Exam > Class 11 Questions > What is the difference between cyclohexatrien...
Start Learning for Free
What is the difference between cyclohexatriene and benzene ? Chemistry?
Verified Answer
What is the difference between cyclohexatriene and benzene ? Chemistry...
The primary difference between benzene and the fictional compound 1,3,5-cyclohexatriene is the bond length. Cyclohexatriene has alternating single and double bonds, and one would expect that the double bonds would be significantly shorter than the single bonds. In benzene, however, all of the bonds are the same length.
 This question is part of UPSC exam. View all Class 11 courses
This question is part of UPSC exam. View all Class 11 courses
Most Upvoted Answer
What is the difference between cyclohexatriene and benzene ? Chemistry...
Community Answer
What is the difference between cyclohexatriene and benzene ? Chemistry...
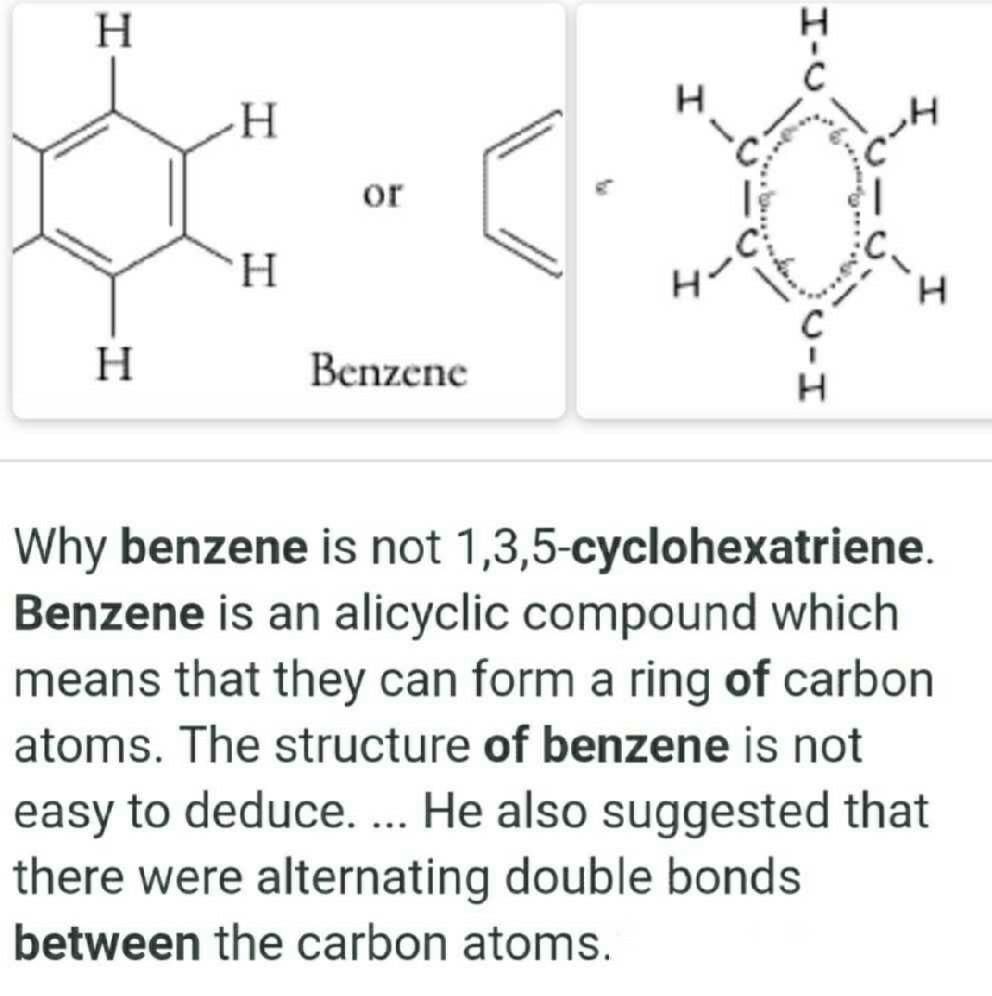
Difference between Cyclohexatriene and Benzene
Cyclohexatriene and benzene are both organic compounds that contain a ring of six carbon atoms. However, there are some key differences between these two compounds. Let's explore them in detail.
Structure:
- Cyclohexatriene: Cyclohexatriene is an unsaturated hydrocarbon with the molecular formula C6H6. It consists of a six-membered carbon ring with alternating single and double bonds. In cyclohexatriene, three of the carbon atoms in the ring have double bonds, while the other three have single bonds.
- Benzene: Benzene is also a six-membered carbon ring with the molecular formula C6H6. However, unlike cyclohexatriene, all the carbon atoms in benzene are bonded to each other by alternating single and double bonds. This unique structure is often represented by a hexagon with a circle inside, indicating that the double bonds are delocalized throughout the ring.
Bonding:
- Cyclohexatriene: In cyclohexatriene, the double bonds are localized, meaning the pi electrons are confined to specific carbon atoms. This results in a higher reactivity compared to benzene. Due to localized pi electrons, cyclohexatriene can undergo addition reactions more readily.
- Benzene: Benzene exhibits a special type of bonding called aromaticity. The pi electrons in the double bonds are delocalized over the entire ring, creating a stable and symmetric structure. This delocalization of electrons gives benzene its characteristic stability and resistance to addition reactions.
Stability:
- Cyclohexatriene: Cyclohexatriene is less stable compared to benzene due to the presence of localized double bonds. The localization of pi electrons leads to higher reactivity and susceptibility to reactions that break the double bonds.
- Benzene: Benzene is highly stable due to its delocalized electron system. The delocalization of pi electrons spreads the negative charge evenly over the ring, minimizing the repulsion between electrons. This stability makes benzene less reactive compared to cyclohexatriene.
Physical Properties:
- Cyclohexatriene: Cyclohexatriene is a colorless liquid with a boiling point of around 79-81°C. It has a characteristic aromatic odor.
- Benzene: Benzene is a colorless liquid with a lower boiling point of 80.1°C. It has a sweet, pleasant odor.
Applications:
- Cyclohexatriene: Cyclohexatriene is not commonly used in industrial applications. However, it is an important intermediate in the synthesis of various organic compounds.
- Benzene: Benzene has numerous industrial applications. It is widely used as a starting material in the production of plastics, resins, synthetic fibers, detergents, pharmaceuticals, and many other chemicals.
In conclusion, the main difference between cyclohexatriene and benzene lies in their structure, bonding, stability, physical properties, and applications. While cyclohexatriene has localized double bonds and higher reactivity, benzene exhibits delocalized bonding and higher stability. Benzene is also more widely used in industrial applications compared to cyclohexatriene.
Cyclohexatriene and benzene are both organic compounds that contain a ring of six carbon atoms. However, there are some key differences between these two compounds. Let's explore them in detail.
Structure:
- Cyclohexatriene: Cyclohexatriene is an unsaturated hydrocarbon with the molecular formula C6H6. It consists of a six-membered carbon ring with alternating single and double bonds. In cyclohexatriene, three of the carbon atoms in the ring have double bonds, while the other three have single bonds.
- Benzene: Benzene is also a six-membered carbon ring with the molecular formula C6H6. However, unlike cyclohexatriene, all the carbon atoms in benzene are bonded to each other by alternating single and double bonds. This unique structure is often represented by a hexagon with a circle inside, indicating that the double bonds are delocalized throughout the ring.
Bonding:
- Cyclohexatriene: In cyclohexatriene, the double bonds are localized, meaning the pi electrons are confined to specific carbon atoms. This results in a higher reactivity compared to benzene. Due to localized pi electrons, cyclohexatriene can undergo addition reactions more readily.
- Benzene: Benzene exhibits a special type of bonding called aromaticity. The pi electrons in the double bonds are delocalized over the entire ring, creating a stable and symmetric structure. This delocalization of electrons gives benzene its characteristic stability and resistance to addition reactions.
Stability:
- Cyclohexatriene: Cyclohexatriene is less stable compared to benzene due to the presence of localized double bonds. The localization of pi electrons leads to higher reactivity and susceptibility to reactions that break the double bonds.
- Benzene: Benzene is highly stable due to its delocalized electron system. The delocalization of pi electrons spreads the negative charge evenly over the ring, minimizing the repulsion between electrons. This stability makes benzene less reactive compared to cyclohexatriene.
Physical Properties:
- Cyclohexatriene: Cyclohexatriene is a colorless liquid with a boiling point of around 79-81°C. It has a characteristic aromatic odor.
- Benzene: Benzene is a colorless liquid with a lower boiling point of 80.1°C. It has a sweet, pleasant odor.
Applications:
- Cyclohexatriene: Cyclohexatriene is not commonly used in industrial applications. However, it is an important intermediate in the synthesis of various organic compounds.
- Benzene: Benzene has numerous industrial applications. It is widely used as a starting material in the production of plastics, resins, synthetic fibers, detergents, pharmaceuticals, and many other chemicals.
In conclusion, the main difference between cyclohexatriene and benzene lies in their structure, bonding, stability, physical properties, and applications. While cyclohexatriene has localized double bonds and higher reactivity, benzene exhibits delocalized bonding and higher stability. Benzene is also more widely used in industrial applications compared to cyclohexatriene.
Attention Class 11 Students!
To make sure you are not studying endlessly, EduRev has designed Class 11 study material, with Structured Courses, Videos, & Test Series. Plus get personalized analysis, doubt solving and improvement plans to achieve a great score in Class 11.

|
Explore Courses for Class 11 exam
|

|
Similar Class 11 Doubts
What is the difference between cyclohexatriene and benzene ? Chemistry?
Question Description
What is the difference between cyclohexatriene and benzene ? Chemistry? for Class 11 2024 is part of Class 11 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 11 exam syllabus. Information about What is the difference between cyclohexatriene and benzene ? Chemistry? covers all topics & solutions for Class 11 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for What is the difference between cyclohexatriene and benzene ? Chemistry?.
What is the difference between cyclohexatriene and benzene ? Chemistry? for Class 11 2024 is part of Class 11 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 11 exam syllabus. Information about What is the difference between cyclohexatriene and benzene ? Chemistry? covers all topics & solutions for Class 11 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for What is the difference between cyclohexatriene and benzene ? Chemistry?.
Solutions for What is the difference between cyclohexatriene and benzene ? Chemistry? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Class 11.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Class 11 Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of What is the difference between cyclohexatriene and benzene ? Chemistry? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
What is the difference between cyclohexatriene and benzene ? Chemistry?, a detailed solution for What is the difference between cyclohexatriene and benzene ? Chemistry? has been provided alongside types of What is the difference between cyclohexatriene and benzene ? Chemistry? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice What is the difference between cyclohexatriene and benzene ? Chemistry? tests, examples and also practice Class 11 tests.

|
Explore Courses for Class 11 exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.

























