Chemistry Exam > Chemistry Questions > Which of the following compound do/es not sho...
Start Learning for Free
Which of the following compound do/es not show/s mutarotation?
- a)Glucose
- b)Fructose
- c)Maltose
- d)Sucrose
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
| FREE This question is part of | Download PDF Attempt this Test |
Verified Answer
Which of the following compound do/es not show/s mutarotation?a)Glucos...
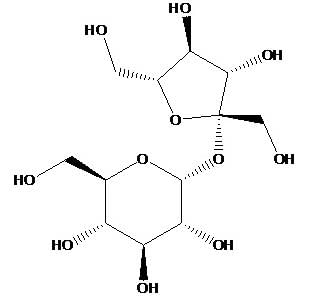
Muta rotation is the process involving gradual change in optical rotation of either form of carbohydrate in aqueous solution to that of equilibrium mixture the structure of sucrose shows that it does not have free CHO and CO groups.
View all questions of this test

Most Upvoted Answer
Which of the following compound do/es not show/s mutarotation?a)Glucos...
Mutarotation:
Mutarotation is the spontaneous change in the specific rotation of an optically active compound when it is dissolved in a solvent or when it is heated. It occurs due to the interconversion between different anomers of a compound.
a) Glucose:
Glucose is a sugar molecule that exists in a cyclic form in solution. It can exist in two different forms known as anomers: α-glucose and β-glucose. These anomers interconvert in solution, resulting in mutarotation. The specific rotation of glucose changes over time when dissolved in a solvent.
b) Fructose:
Fructose is another sugar molecule that exists in a cyclic form in solution. Similar to glucose, it can exist in two different forms: α-fructose and β-fructose. These anomers can also interconvert in solution, leading to mutarotation.
c) Maltose:
Maltose is a disaccharide composed of two glucose molecules. Each glucose molecule in maltose can exist in its cyclic form and exhibit mutarotation. Therefore, maltose undergoes mutarotation.
d) Sucrose:
Sucrose is a disaccharide composed of glucose and fructose molecules. Unlike glucose and fructose, sucrose does not have a free anomeric carbon, which is necessary for mutarotation. Thus, sucrose does not undergo mutarotation.
Conclusion:
The compound that does not show mutarotation is sucrose (option D). Sucrose lacks a free anomeric carbon and therefore cannot interconvert between different anomers, resulting in a constant specific rotation over time in a solvent.
Mutarotation is the spontaneous change in the specific rotation of an optically active compound when it is dissolved in a solvent or when it is heated. It occurs due to the interconversion between different anomers of a compound.
a) Glucose:
Glucose is a sugar molecule that exists in a cyclic form in solution. It can exist in two different forms known as anomers: α-glucose and β-glucose. These anomers interconvert in solution, resulting in mutarotation. The specific rotation of glucose changes over time when dissolved in a solvent.
b) Fructose:
Fructose is another sugar molecule that exists in a cyclic form in solution. Similar to glucose, it can exist in two different forms: α-fructose and β-fructose. These anomers can also interconvert in solution, leading to mutarotation.
c) Maltose:
Maltose is a disaccharide composed of two glucose molecules. Each glucose molecule in maltose can exist in its cyclic form and exhibit mutarotation. Therefore, maltose undergoes mutarotation.
d) Sucrose:
Sucrose is a disaccharide composed of glucose and fructose molecules. Unlike glucose and fructose, sucrose does not have a free anomeric carbon, which is necessary for mutarotation. Thus, sucrose does not undergo mutarotation.
Conclusion:
The compound that does not show mutarotation is sucrose (option D). Sucrose lacks a free anomeric carbon and therefore cannot interconvert between different anomers, resulting in a constant specific rotation over time in a solvent.

|
Explore Courses for Chemistry exam
|

|
Similar Chemistry Doubts
Which of the following compound do/es not show/s mutarotation?a)Glucoseb)Fructosec)Maltosed)SucroseCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
Which of the following compound do/es not show/s mutarotation?a)Glucoseb)Fructosec)Maltosed)SucroseCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? for Chemistry 2024 is part of Chemistry preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Chemistry exam syllabus. Information about Which of the following compound do/es not show/s mutarotation?a)Glucoseb)Fructosec)Maltosed)SucroseCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Chemistry 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Which of the following compound do/es not show/s mutarotation?a)Glucoseb)Fructosec)Maltosed)SucroseCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?.
Which of the following compound do/es not show/s mutarotation?a)Glucoseb)Fructosec)Maltosed)SucroseCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? for Chemistry 2024 is part of Chemistry preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Chemistry exam syllabus. Information about Which of the following compound do/es not show/s mutarotation?a)Glucoseb)Fructosec)Maltosed)SucroseCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Chemistry 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Which of the following compound do/es not show/s mutarotation?a)Glucoseb)Fructosec)Maltosed)SucroseCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for Which of the following compound do/es not show/s mutarotation?a)Glucoseb)Fructosec)Maltosed)SucroseCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Chemistry.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Chemistry Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Which of the following compound do/es not show/s mutarotation?a)Glucoseb)Fructosec)Maltosed)SucroseCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Which of the following compound do/es not show/s mutarotation?a)Glucoseb)Fructosec)Maltosed)SucroseCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for Which of the following compound do/es not show/s mutarotation?a)Glucoseb)Fructosec)Maltosed)SucroseCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of Which of the following compound do/es not show/s mutarotation?a)Glucoseb)Fructosec)Maltosed)SucroseCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Which of the following compound do/es not show/s mutarotation?a)Glucoseb)Fructosec)Maltosed)SucroseCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Chemistry tests.

|
Explore Courses for Chemistry exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


















