Adrenals | Animal Husbandry & Veterinary Science Optional for UPSC PDF Download
Adrenal Medulla
Hormones
- Derived from tyrosine.
- Two main hormones: norepinephrine and epinephrine.
- Tyrosine → Dihydroxyphenylalanine (DOPA) → Dopamine → Norepinephrine → Epinephrine.
- Epinephrine secretion mainly from the adrenal medulla.
- Norepinephrine secreted by adrenal medulla and postganglionic sympathetic neurons.
- Varies in ratio among species and age.
- Epinephrine predominates in adult mammals, while some mammals have mostly norepinephrine.
- Foetal adrenal tissue contains mainly norepinephrine.
- Adrenal cortex steroids may influence norepinephrine to epinephrine conversion.
Adrenal Cortex
Steroid Biosynthesis
- Complex process involving many steps.
- Cholesterol is the basic substrate.
- Cholesterol synthesized from acetyl fragments.
- ACTH (Adrenocorticotropic hormone) stimulation depletes adrenal cholesterol and ascorbic acid.
- ACTH activates glycogenolysis.
- ACTH crucial in 17-hydroxylation.
Sex Hormones
- Types:
- Androgens, estrogens, progestins, and relaxin.
- Placental and Testicular Estrogens:
- Similar to ovarian estrogen in most species.
- Sheep and goat placenta: Predominantly estradiol 17.
- Porcine placenta: Consists of estrone.
- Principal Sex Hormone:
- Progesterone with progestational activity.
- Central role in biosynthesis of steroid hormones.
- Influences various metabolic processes.
Testosterone Production
Source:
- Interstitial cells of testis (Leydig cells) are the main source.
- Responsible for male hormone (testosterone) secretion.
Estrogen and Progesterone Production
Sources:
- Theca interna cells: Secrete estrogen.
- Granulosa cells: Secrete progesterone and other progestins.
- Placenta in pregnant animals is a significant source of progestins and estrogens.
- Relaxin found in various reproductive tissues.
Prostaglandins
Sources:
- Isolated from multiple tissues.
- Principal substrates: Unsaturated fatty acids like arachidonic acid.
Mechanism and Control of Hormone Secretion
- Hormone Types:
- Two main classes: steroids and protein/protein derivatives.
- Adrenal cortex and gonads secrete steroids.
- Pituitary gland, thyroid, parathyroid, pancreas, and adrenal medulla secrete protein-type hormones.
- Some exceptions exist (e.g., ovary major source for relaxin, a protein-type hormone).
- General Hormone Characteristics:
- Regulate reactions rather than initiate.
- Effective in minute quantities.
- Not secreted at uniform rates, allowing diverse responses.
- Mechanism of Action:
- Proposed mechanism involves adenyl-cyclase activation.
- Results in increased cellular 3,5 AMP (cyclic AMP) in cytoplasm.
- cAMP acts as the second messenger, triggering various cellular changes.
- Specificity determined by binding proteins in target cell membranes.
- Steroid Hormones:
- Act differently, involving specific membrane proteins.
- Transported to the nucleus, exerting intranuclear effects like geno derepression.
- Protein binding crucial for transport, specificity, and mechanism of action.
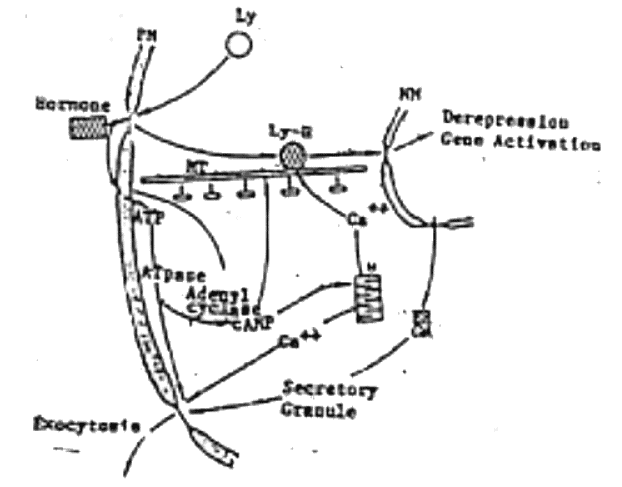
Fig. 13: Some elements of hormone mechanism of action. PM, plasma membrane; NM, nuclear membrane; ER, endoplasmic reticulum; Ly, lysosome; Ly-H, bound hormone-lysosome; MT, microtubule; M, mitochondrion; GA, Golgi apparatus
Importance of Endocrine Glands
Roles:
- Regulate crucial body activities such as growth, differentiation, reproduction, internal environment maintenance, and adaptation to external changes.
- Each activity, except growth and differentiation, is seen as a form of adaptation.
Adaptation in Reproduction
Significance: Reproduction is an adaptive process redirecting the entire body toward this goal.
Internal Regulatory Adjustments
Examples
- Pancreas controls blood sugar levels.
- Parathormone secretion maintains blood calcium.
- These are short-term adaptations responding to recurring internal changes.
Adaptation to External Environment
Nervous and Endocrine Systems:
- Both systems play crucial roles in adapting to external influences.
- Nerve impulses induce fast, short-term reactions to sudden environmental changes.
- Hormones are involved in longer-duration adaptive responses to prolonged environmental stimuli.
Emergency or Stress Response
Situation: Consider the body's reaction to an emergency or stress that threatens health.
Nervous System's Role
Response:
- Ultrashort responses (primarily motor) by the somatic or voluntary nervous system.
- Autonomic nerves quickly adjust internal functions, aided by adrenal medulla's release of epinephrine.
Endocrine System's Role
Response:
- Adrenocortical hormones bring about changes for prolonged stress endurance.
- Other endocrine glands align and coordinate body chemistry to meet new demands.
Long-Term Body Defense
Function:
- Endocrine activity contributes to long-term body defense mechanisms.
- Initiates recovery processes, showcasing the "wisdom of the body" as termed by Cannon.
Response to Temperature Change
Effect on Thyroid and Adrenal Medulla:
- Lower temperature leads to increased activity in thyroid and adrenal medulla.
- Results in heightened heat production.
- Autonomic nerve impulses cause peripheral blood vessels to constrict.
 |
Download the notes
Adrenals
|
Download as PDF |
Voluntary Adaptive Reactions
Example:
- Animal typically withdraws to a warmer location.
- Shows the inseparable connection between biology and change.
- Biological integrative systems are dynamic and constantly adapting.
Endocrine Glands and Nervous System Interaction
Function:
- Endocrine glands, along with the nervous system, redirect, coordinate, and unify various organ functions for optimal conditions.
- These changes represent adaptation to given circumstances.
Regulation of Endocrine Activity
Neuroendocrine Reflexes:
- Some cases involve both nervous and endocrine systems, termed neuroendocrine reflexes.
- Example in adrenal medulla where sympathetic nerve fibers direct endocrine secretion.
- Posterior pituitary secretion may also be influenced by peripheral afferent impulses, partly through blood vessels.
Anterior Pituitary Regulation
Control Mechanisms:
- Both neural and blood-vascular afferent inputs regulate anterior pituitary secretion.
- Central integrative pathways primarily neural, but "humoral regulating hormones" from the hypothalamus control anterior pituitary activity.
Posterior Pituitary Secretion
Unique Feature:
- Hormones from hypothalamus to posterior pituitary pass within axons before release into general circulation.
- Represents a distinctive aspect of efferent output from the posterior pituitary.
Chemical Sensitivity in Endocrine Glands
Pancreas and Parathyroid:
- Sensitive to concentrations of specific chemicals.
- Analogous to spinal reflex in the nervous system.
- Not isolated; influenced by other endocrine glands.
- Example: Adrenal medulla activation increases blood glucose, prompting insulin secretion from the pancreas.
Humoral Regulation
Interconnected Regulation:
- Efferent pathway of one endocrine gland influences another.
- Example: Anterior pituitary tropic hormones regulate other glands, forming a feedback loop.
- Feedback affects adenohypophysis or hypothalamic regulating hormones.
- Circulating hormones may influence higher CNS centers, impacting tropic hormone secretion.
Prostaglandins as Unique Control
Characteristics:
- Prostaglandins are compounds secreted in response to various stimuli.
- Have potent systemic effects.
- Regulatory influence likely localized when responding to specific stimuli.
- Rapidly deactivated by lung and liver, not extensively present in arterial circulation.
Hormonal Receptors: Classification and Role
- Steroids vs. Peptides:
- Steroids and peptides have distinct action mechanisms.
- Steroid and thyroid hormones are small (MW 300), freely diffuse into cells.
- Plasma membrane doesn't hinder their entry.
- Peptide hormones are large (MW 10,000+), can't pass through the plasma membrane.
- Hormone Action Location:
- Steroid and thyroid hormones: Act inside the cell.
- Steroids: In the cytoplasm.
- Thyroid: In the nuclear chromatin.
- Peptide hormones: Act on the cell surface, influencing internal processes indirectly.
- Target Cells and Receptors:
- Not all cells respond to hormones; specific ones do—called target cells.
- Target cells have specialized receptor sites for hormones.
- Receptors:
- Peptide hormones: On the cell surface.
- Thyroid hormones: In the nuclear chromatin.
- Steroid hormones: In the cytoplasm.
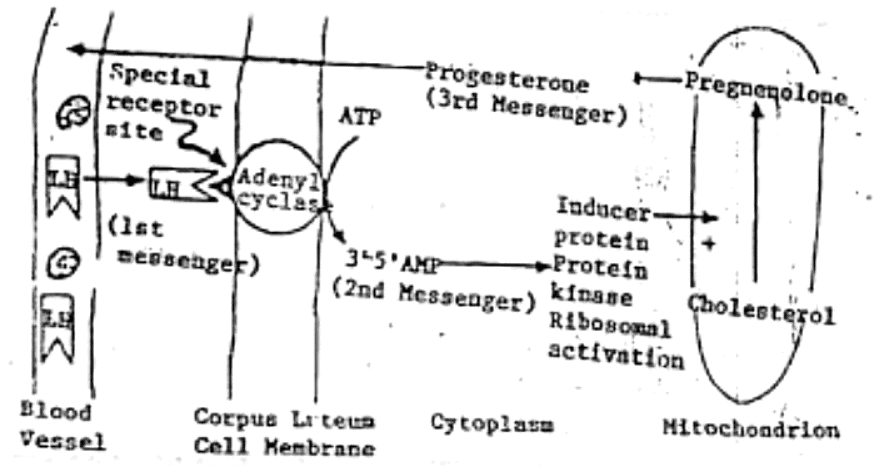
Fig. 14: Model to show how a specific receptor site binds a particular hormone (LH in this case). The target organ (corpus luteum cell membrane) contains a hormone-specific receptor protein as part of its adenyl cyclase system. Binding of LH results in activation of adenyl eyelase with resulting increase in production of 3, 5-AMP (CAMP) (second messenger). The cAMP then activates the protein kinase in that particular cell, which leads to progesterone (third mi ssenger) production by the mitochondrion.
Hormone Action in Target Cells: Steps and Significance
- Receptor Binding:
- Specific receptor sites in a target organ bind a particular hormone.
- This binding occurs at the cell membrane, initiating the action of peptide hormones.
- Second Step in Peptide Hormone Action (e.g., LH):
- After binding, the hormone stimulates adenyl cyclase enzyme in the cell membrane.
- Adenyl cyclase converts adenosine triphosphate (ATP) to cyclic AMP (cAMP), known as the second messenger.
- Significance of cAMP (Second Messenger):
- cAMP provides energy for protein synthesis inside the cell.
- Hormones like ACTH, FSH, TSH, and hCG use the cAMP route for their effects.
- cAMP influences protein synthesis, leading to the production of hormones within the mitochondria (third messenger).
- Regulation of Steroid Production:
- Steroid production by adrenal cortex and gonads is regulated by cAMP.
- Injecting cAMP can mimic effects of hormones like LH or ACTH to some extent.
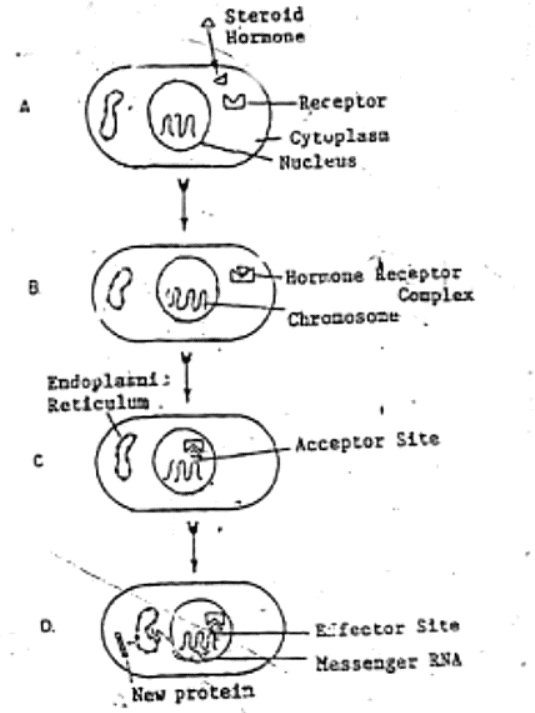
Fig. 15: Mechanism of action of steroid hormones. Steroids apparently can ent all cells, but only target cells contain the specific receptors (A) that bind t hormone (B). The receptor-hormone complex rasses into the cell nucleus (C) a attaches to an acceptor site on the chromosome that contains the cell genes (DN At the effector site the receptor-sterold complex causes synthesis of a messeng RNA, depending on the particular gene. Messenger RNA then migrates to t endoplasmic reticulum (D), where it dictates synthesis of a new protein.
Mechanisms of Hormone Action: Understanding the Basics
- Common Signaling Molecule:
- Cyclic AMP (cAMP) or cyclic guanosine 5-phosphoric acid could serve as a common factor in the action of peptide hormones.
- Different cells have various enzymes influenced by cAMP.
- Variety in Hormone Action:
- While many peptide hormones rely on cAMP for their action, some hormones (e.g., parathyroid hormone, insulin, glucagon, oxytocin, prolactin, angiotensin, somatotropin, epinephrine, vasopressin) don't require another hormone (third messenger).
- Certain hormones affect cell membrane permeability or transport, making substrates more available.
- Steroid and Thyroid Hormones:
- Act by intracellular mechanisms, controlling the synthesis of specific proteins.
- Target cells have specific receptors for these hormones.
- Hormone-receptor complex moves into the nucleus, where it binds to the chromosome.
- This binding activates genes to produce ribonucleic acid (RNA), which, in turn, triggers the endoplasmic reticulum to create specific proteins needed for the hormone's function.
- Thyroid Hormones' Distinct Mechanism:
- Thyroid hormones penetrate cell membranes and bind to specific receptors already present on the cell's nuclear chromatin.
- This differs from steroid receptors located in the cytoplasm, moving into the nucleus upon hormone binding.
FAQs on Adrenals - Animal Husbandry & Veterinary Science Optional for UPSC
| 1. What is the function of the adrenal medulla? |  |
| 2. What are the main hormones produced by the adrenal cortex? |  |
| 3. How are hormone secretion and control regulated in the endocrine glands? |  |
| 4. What is the role of hormonal receptors and how are they classified? |  |
| 5. What are the steps and significance of hormone action in target cells? |  |