Alcohols and Phenols: Properties | Chemistry Class 12 - NEET PDF Download
Alcohol and phenols are two important chemical compounds that play significant roles in our daily lives and in various industries. Both contain a hydroxyl (-OH) group, which gives them certain properties and uses. Alcohols are commonly used as solvents, disinfectants, fuels, and in the production of various chemicals and consumer products and phenols are used in the manufacturing of plastics, pharmaceuticals, and antiseptics in personal care products.
What are Alcohols?
Alcohols are a class of organic compounds characterized by the presence of one or more hydroxyl (-OH) functional groups attached to a carbon atom. They are commonly used as solvents, fuels, and beverages.
 Alcohol as Stove Fuels
Alcohol as Stove Fuels
In the chemical structure of alcohol, the hydroxyl group (-OH) is attached to a carbon atom, which may be part of a larger hydrocarbon chain or a ring structure.
The general formula for an alcohol is R-OH, where R represents the hydrocarbon group.
The major simple forms of alcohol include methanol (CH3OH), ethanol (C2H5OH), propanol (C3H7OH), and butanol (C4H9OH).
What is Phenol?
Phenol is an aromatic compound. The chemical formula of this organic compound is C₆H₅OH. It consists of a hydroxyl group and a phenyl group attached.
It is sparingly soluble in cold water (solubility increases with temperature; forms phenoxide in alkali). Earlier, it was used as carbolic soap. It is mildly acidic and is corrosive to the respiratory tract, eyes, and skin.
 Phenol Crystal
Phenol Crystal
Phenol is a crystalline solid, white, and needs to be handled with care as it can cause chemical burns. Friedlieb Ferdinand Runge discovered Phenol in the year 1834. It was extracted from coal tar. It is also known as phenolic acid. If a compound consists of a six-membered aromatic ring and is bonded to a hydroxyl group directly, then it can be referred to as phenol.
Natural Sources of Phenols
Phenol is a constituent of coal tar and is formed during the decomposition of organic materials. Increased environmental levels of phenol may result from forest fires. It has been detected among the volatile components of liquid manure.
- Industrial sources of phenols and other related aromatics from petroleum refineries, petrochemicals, basic organic chemical manufacture, coal refining, pharmaceuticals, tannery and pulp, and paper mills.
Phenol Structure – C6H5OH
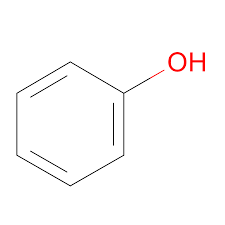 Phenol Structure
Phenol StructureTypes of Alcohols: Classification
Alcohols can be classified into different types based on various factors such as the structure of the hydrocarbon group, the number of hydroxyl groups, and the position of the hydroxyl group in the carbon chain.
Classification based on the number of Carbon Atoms attached to Carbon bonded with the -OH group
Depending on the number of carbon atoms that are directly attached to the carbon that is bonded with the -OH group, alcohols can be classified into three types.
(a) Primary Alcohols: These alcohols have one hydroxyl group (-OH) attached to a primary carbon atom (a carbon atom directly bonded to only one other carbon atom). Example: Ethanol 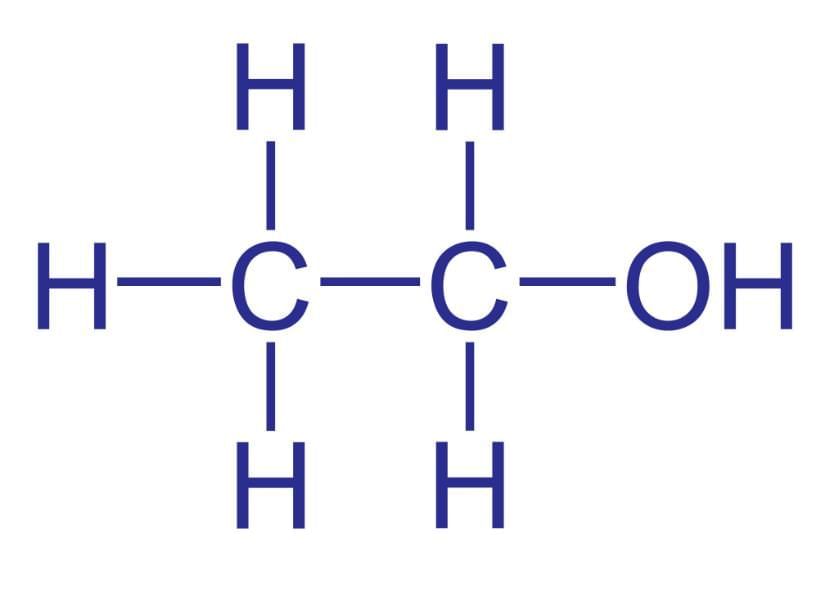 Ethanol
Ethanol
(b) Secondary alcohols: These alcohols have one hydroxyl group (-OH) attached to a secondary carbon atom (a carbon atom directly bonded to two other carbon atoms). Example: Isopropanol 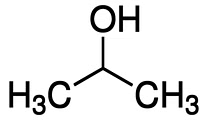 Isopropanol
Isopropanol
(c) Tertiary alcohols: These alcohols have one hydroxyl group (-OH) attached to a tertiary carbon atom (a carbon atom directly bonded to three other carbon atoms). Example: tert-Butanol  tert-Butanol
tert-Butanol
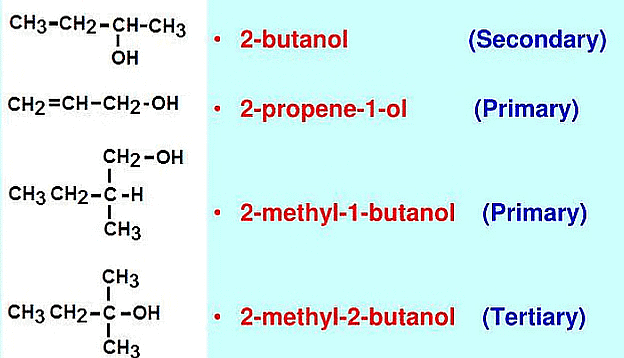 Classification Based on the Number of Carbon Atoms Attached
Classification Based on the Number of Carbon Atoms Attached
Classification on the number of hydroxyl groups attached
(a) Monohydric alcohols: They contain one -OH group. Example, Ethanol.
(b) Dihydric alcohols: They contain two -OH groups. Example, Ethane-1,2-diol.
(c) Trihydric alcohols: They contain three -OH groups. Example, Propane-1,2,3-triol.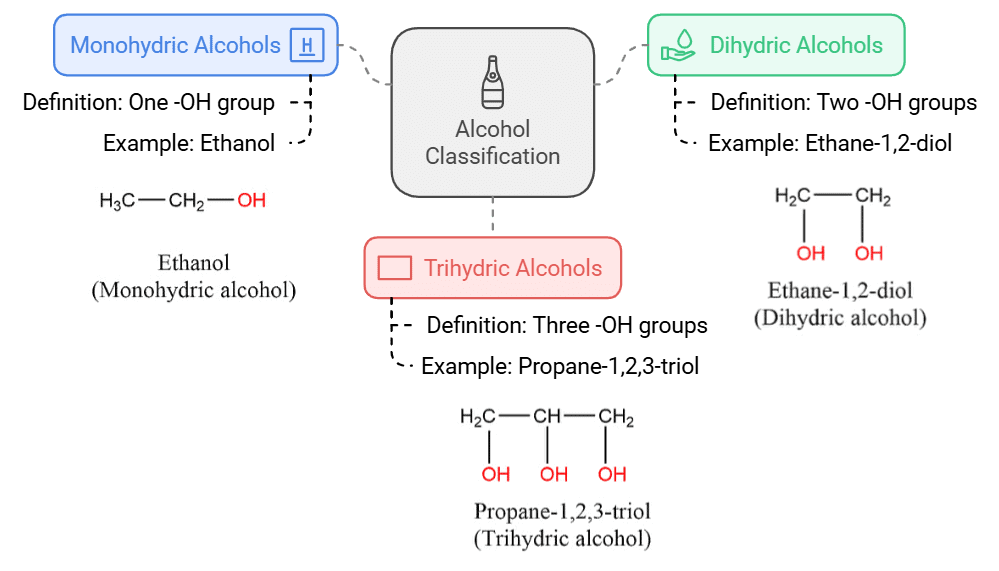
Aromatic Alcohols
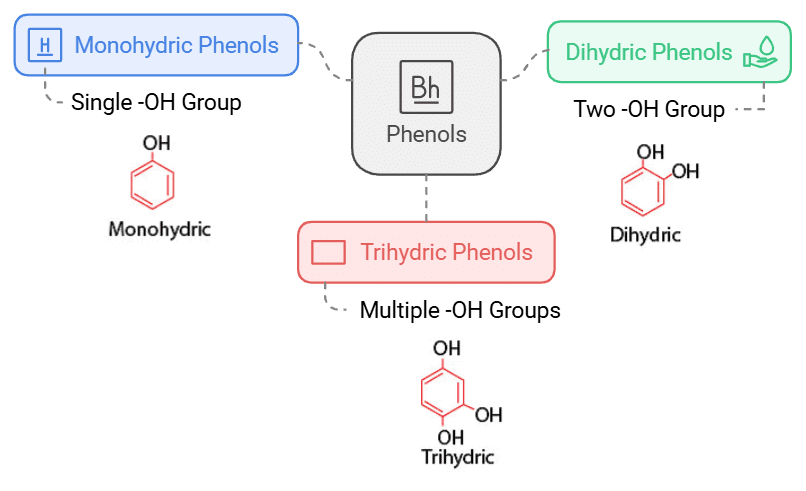
These alcohols contain a hydroxyl group (-OH) attached to an aromatic ring. Example: Phenol (C6H5OH). Depending on the number of hydroxyl groups attached, phenols can be classified into three types.
Monohydric phenols: They contain one -OH group.
Dihydric phenols: They contain two -OH groups. They may be ortho-, meta- or para-derivative.
Trihydric phenols: They contain three -OH groups.
Allylic Alcohols
These alcohols have a hydroxyl group (-OH) attached to an allylic carbon (a carbon adjacent to a carbon-carbon double bond).
Example: Allyl alcohol (CH2=CHCH2OH). Allyl Alcohol
Allyl Alcohol
Benzyl Alcohols
These alcohols have a hydroxyl group (-OH) attached to a benzyl group (a phenyl group attached to a methylene group).
Example: Benzyl alcohol (C6H5CH2OH). Benzyl Alcohol
Benzyl Alcohol
Nomenclature of Alcohols
1. Alcohols provide the first example of how the parent alkane was the starting point for the nomenclature of all families of compounds. The -ane suffix is modified systematically to indicate the presence of a functional group. Alcohol is named by identifying the longest straight carbon chain containing the -OH group. The -ane suffix is replaced with -anol and the location of the -OH group on the chain is designed by a number.
2. The generic IUPAC name for alcohol is alkanols, and they are represented in reactions by the general formula R-H. The presence of other substituents in alcohol is indicated by their names and numerical positions, always keeping the lowest possible number for the hydroxyl group.
IUPAC Nomenclature for Alcohols
The following procedure should be followed in giving alcohol IUPAC substitutive names.
Select the longest continuous chain to which the hydroxyl group is directly attached. Change the name of the alkane corresponding to the chain by dropping the final -e and adding the suffix -ol.
Number the longest continuous carbon chain to give the carbon atom bearing the hydroxyl group the lower number. Indicate the position of the hydroxyl group by using this number as a locant.
Indicate the position of another substituent as a prefix by using the numbers corresponding to their positions along the carbon chain as locants.
The following example shows how the rules are applied. IUPAC Nomenclature for Alcohols
IUPAC Nomenclature for Alcohols
Types of Nomenclature in Alcohols
There are three systems of naming alcohols
Common or trivial system
Carbinol system and
IUPAC system
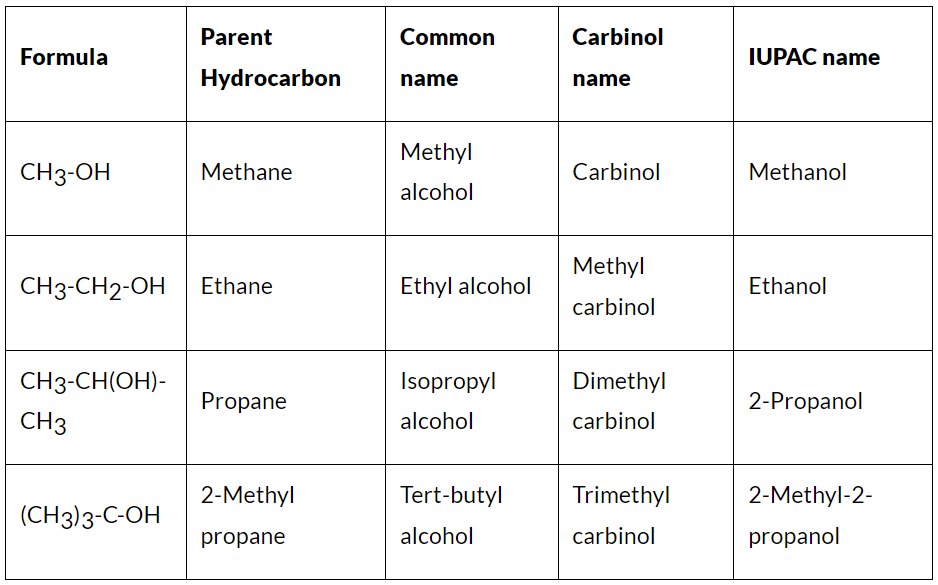 Common Names of Alcohols
Common Names of Alcohols
Ethanol is known as ethyl alcohol, grain alcohol, and the spirit of wine. The first system of nomenclature for alcohol which was based on the use of the term “carbinol” for methanol was originated by a 19th-century German chemist Harmann Kolbe. The presently accepted systematic nomenclature for alcohol was adopted by the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry in Paris in 1957.
Solved Example
Q1: Name the following compound.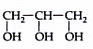
Ans: This compound has a three-carbon chain, so the parent alkane name is propane. Because the compound contains three hydroxyl groups, the suffix must be -triol. Therefore, the name is 1,2,3-propanetriol.
The common name of this compound is glycerol also called glycerin and it is an important by-product in the manufacture of soaps.
Nomenclature of Phenols
Phenols are organic compounds containing a benzene ring bonded to a hydroxyl group. They are also known as carbolic acids. Thus, a phenol molecule consists of two parts one aryl group part and the other hydroxyl group part. Based on the number of hydroxyl groups attached to the aryl group, it can be classified into mono-, di-, tri-, or polyhydric phenols.
Nomenclature of Phenols
(a) Earlier, most of the compounds with the same structural formula were known by different names depending on the regions where they were synthesized. This naming system was very trivial since it raised a lot of confusion. Finally, a common naming system enlisting standard rules was set up by IUPAC for the naming of compounds.
(b) It is both a common name and an IUPAC name for the compounds containing a benzene ring attached to a hydroxyl group. Structurally phenols are the simplest hydroxy derivative of the benzene ring. IUPAC nomenclature of phenols follows a set of rules.
Rules underlying the Nomenclature of Phenols
1. Locate the position of a hydroxyl group attached to the benzene ring.
2. Benzene rings attached to more than one hydroxyl group are labeled with the Greek numerical prefixes such as di, tri, and tetra to denote the number of similar hydroxyl groups attached to the benzene ring. If two hydroxyl groups are attached to the adjacent carbon atoms of the benzene ring, it is named as benzene1,2-diol
3. In the case of substituted phenols, we start locating the positions of the other functional groups concerning the position where the hydroxyl group is attached. For example, if a methyl group is attached to the fourth carbon atom concerning the hydroxy group, the compound is named 4-Methyl phenol.
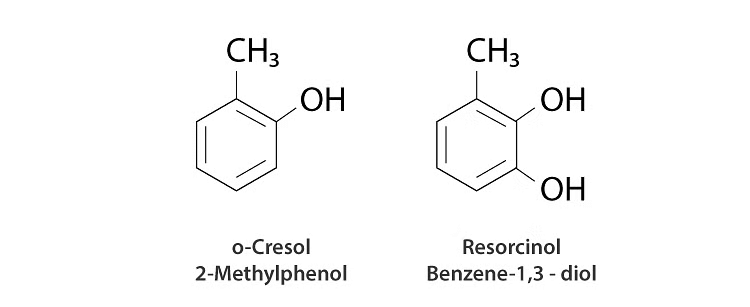
4. Depending on the position of the substituted functional group concerning the hydroxyl group, words like ortho (when the functional group is attached to the adjacent carbon atom), para (when the functional group is attached to the third carbon atom from the hydroxyl group), meta (when the functional group is attached to the second carbon atom from the hydroxyl group) are also used for the nomenclature of phenols.
Physical Properties of Alcohols and Phenols
The physical properties of alcohols are mainly due to the presence of hydroxyl group.
1. Boiling Point
Alcohols and Phenols generally have higher boiling points in comparison to other hydrocarbons having equal molecular masses due to various factors: 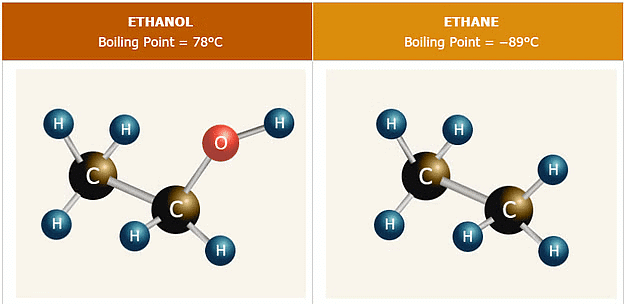
- Intermolecular Hydrogen Bonding: Alcohols and Phenols have higher boiling points due to intermolecular hydrogen bonding between hydroxyl groups.
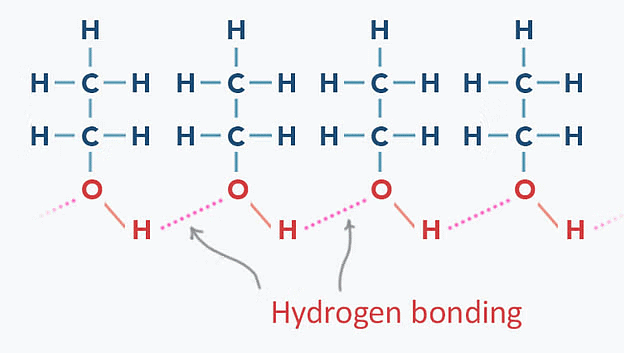 Hydrogen Bonding in Ethanol
Hydrogen Bonding in Ethanol - Carbon Chain Length: Boiling points of alcohols and phenols increase with longer aliphatic carbon chains (increase in van der Waals forces).
- Branching in Carbon Chains: Increased branching leads to lower boiling points in alcohols.
- Primary Alcohols: Primary alcohols have higher boiling points compared to other types.
More branching ⇒ lower bp; often 1° > 2° > 3° due to least branching, but this is a trend, not a universal rule across different carbon counts.
2. Solubility in Water
The solubility of alcohols and phenols in water is governed by the hydroxyl group present. The hydroxyl group is involved in the formation of intermolecular hydrogen bonding.
- Thus, hydrogen bonds are formed between water and alcohol molecules which make alcohol soluble in water.
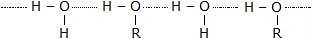 Intermolecular Hydrogen Bonding
Intermolecular Hydrogen Bonding - Phenols are similar to alcohol, but they form stronger hydrogen bonds. Therefore, they are more soluble in water than alcohols.
- However, the alkyl group attached to the hydroxyl group is hydrophobic. Thus, the solubility decreases with the increase in the size of the alkyl group.
3. Density
Alcohols have densities lower than that of water, meaning they float on water. The density of alcohols increases with an increase in carbon chain length and molecular mass.
 Alcohols Float on Water
Alcohols Float on Water
- Phenols have more density than water, hence phenol sinks in water.
4. Odor
- Many alcohols have distinct odors. For example, ethanol has a characteristic alcoholic smell.
- The odor of alcohols can vary depending on the carbon chain length and any additional functional groups present.
- Phenol has a distinct odor that is sickeningly sweet and tarry.
5. Volatility
- Alcohols and phenols generally have higher volatility compared to water and many other compounds.
- The volatility decreases as the carbon chain length increases, resulting in longer evaporation times.
6. Flammability
- Alcohols and phenols are flammable substances with varying degrees of flammability depending on their molecular structure.
 Alcohols are Flammable
Alcohols are Flammable - Lower-molecular-weight alcohols, such as methanol and ethanol, are highly flammable and can be used as fuel sources.
Chemical Properties of Alcohols and Phenols
Alcohols exhibit a wide range of spontaneous chemical properties due to the cleavage of the C-O bond and O-H bond.
1. Oxidation
Alcohols can undergo oxidation reactions to form various functional groups.
Primary alcohols can be oxidized to aldehydes and further to carboxylic acids.
Secondary alcohols can be oxidized to ketones.
Tertiary alcohols, lacking a hydrogen atom attached to the carbon bearing the hydroxyl group, are resistant to oxidation.
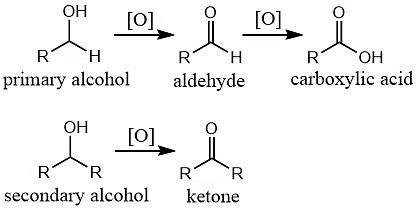 Oxidation Reaction of Alcohols
Oxidation Reaction of Alcohols
2. Acidity of alcohols and their ability to undergo acid-base reactions
Alcohols, in their pure form, are considered weak acids compared to strong mineral acids such as hydrochloric acid or sulfuric acid. The acidity of alcohols arises from the hydroxyl (-OH) group, which can donate a proton (H+) in acid-base reactions.
Acid-Base Reaction: Alcohols can undergo acid-base reactions by donating a proton (H+) from the hydroxyl group. In this reaction, the alcohol acts as an acid, and the species accepting the proton acts as a base. The base can be another molecule or an ion, such as water (H2O) or a hydroxide ion (OH-).
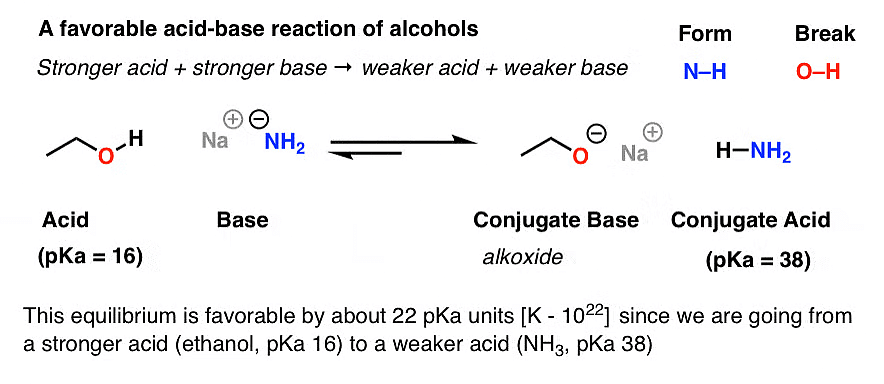
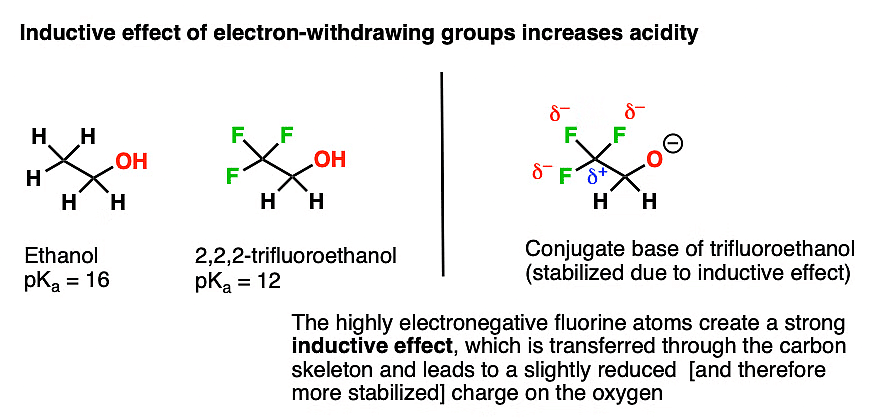
Acidic Character: The acidity of alcohols is influenced by factors such as the nature of the alcohol, the structure of the molecule, and the stability of the resulting ion. Factors such as electron-withdrawing groups (-COOH, -NO2) or resonance effects can enhance the acidity of alcohols.
Acidic Strength: Alcohols exhibit a range of acidic strengths, with phenols being more acidic than aliphatic alcohols. Phenols (aromatic alcohols) are more acidic due to the stabilization of the resulting phenoxide ion through resonance within the aromatic ring.
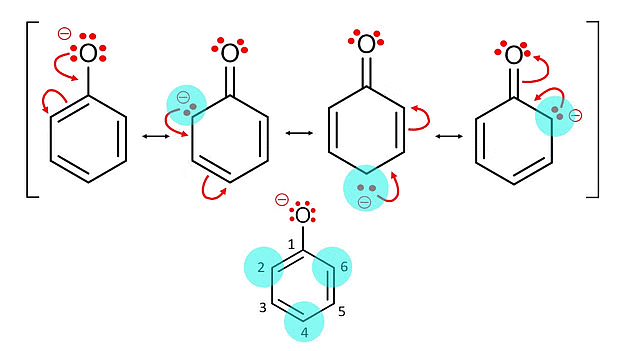 Phenol more Acidic due to Resonance
Phenol more Acidic due to ResonanceReaction with Strong Bases: Alcohols can react with strong bases, such as alkali metal hydroxides (e.g., sodium hydroxide, NaOH), to form alkoxide ions.
The reaction involves the deprotonation of the alcohol's hydroxyl group, resulting in the formation of an alkoxide ion and water.
3. Acidity of Phenols
- Phenols exhibit acidity as they generate phenoxides and release hydrogen ions. Due to the higher electronegativity of sp2 hybridized carbon of phenol to which –OH is attached, electron density decreases on oxygen. This increases the polarity of the O–H bond and results in an increase in ionization of phenols than that of alcohols.
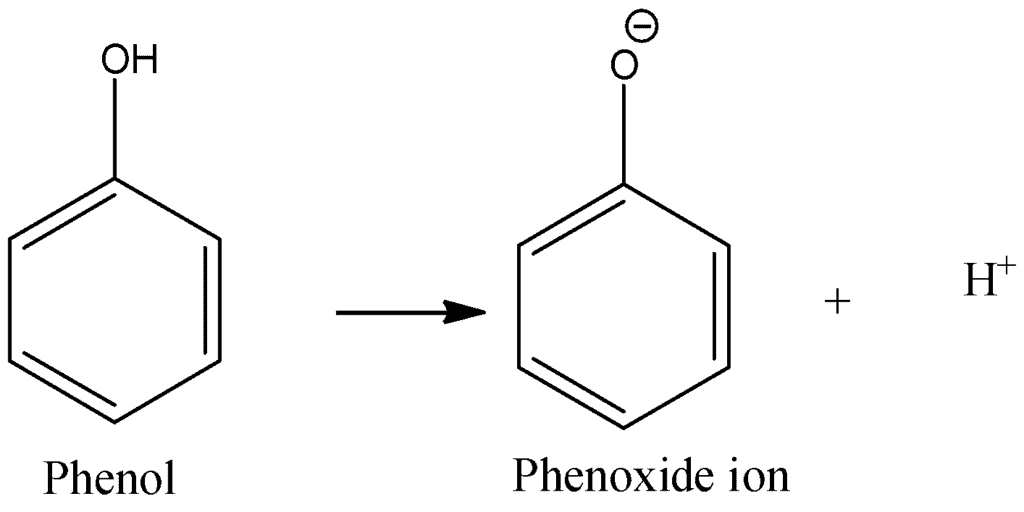 Phenol Generating Phenoxide and Hydrogen Ion
Phenol Generating Phenoxide and Hydrogen Ion
- The delocalization of the negative charge in phenoxide ions is clarified by their resonance structures. The introduction of an electron-withdrawing group in substituted phenols enhances their acidity, attributed to the increased stability of the resulting phenoxide ion. Phenols exhibit a substantial boost in acidity when these groups are positioned at ortho and para locations.
4. Dehydration of Alcohols
- Alcohols can undergo dehydration reactions, eliminating a molecule of water.
- This typically occurs in the presence of heat and a dehydrating agent, such as concentrated sulfuric acid or phosphoric acid.
- Dehydration of alcohols leads to the formation of alkenes, resulting in the loss of the hydroxyl group.
 Dehydration of Alcohols
Dehydration of Alcohols
- Unlike alcohols, phenols resist dehydration. Their formation doesn't involve adding water to an alkene, a process characteristic of alcohol synthesis.
5. Esterification Reaction
Esterification is the process of combining an organic acid (RCOOH) with an alcohol (ROH) to form an ester (RCOOR) and water; or a chemical reaction resulting in the formation of at least one ester product.
- Alcohols and Phenols can also undergo esterification reactions, where they react with carboxylic acids in the presence of an acid catalyst.
- In this reaction, the hydroxyl group of the alcohol combines with the carboxylic acid, resulting in the formation of an ester and water.
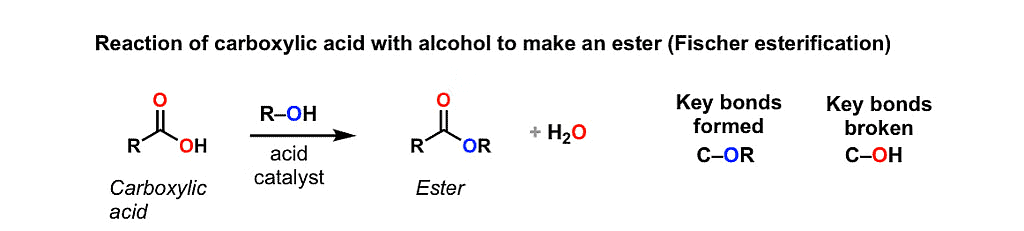
6. Reaction with Metals
- Alcohols and Phenols can react with highly reactive metals, such as sodium or potassium, to produce alkoxides and hydrogen gas.
This reaction is often used in organic synthesis to convert alcohols into alkoxide salts, which can participate in further reactions.
 Alcohols with Metals
Alcohols with Metals
 Phenol Reaction with Na
Phenol Reaction with Na
- In addition to this, phenols react with aqueous sodium hydroxide to form sodium phenoxides.
 Phenol reacting with NaOH
Phenol reacting with NaOH
7. Reaction with Acid Chlorides
Alcohols and Phenols can react with acid chlorides to form esters.
This reaction, known as the Fischer esterification, involves the substitution of the chloride group in the acid chloride with the alkoxyl group of the alcohol.
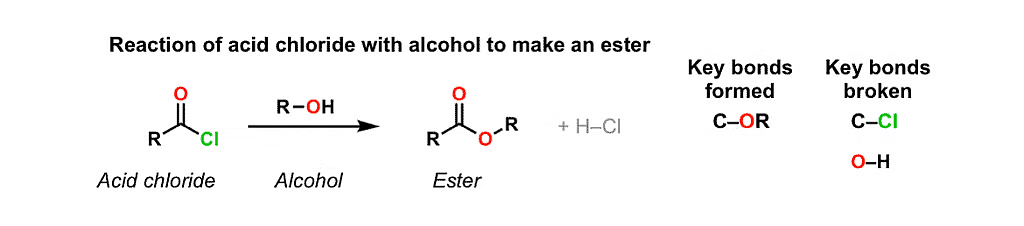
8. Nucleophilic Substitution
In nucleophilic substitution reactions in organic chemistry, a nucleophile (an electron-rich species) replaces a leaving group in a molecule. This typically occurs in molecules with a leaving group (often a halide or similar group) attached to a carbon atom, where the nucleophile attacks the carbon, leading to the departure of the leaving group.
- Alcohols can act as nucleophiles in substitution reactions.
- They can undergo nucleophilic substitution with various electrophiles, such as alkyl halides or acyl chlorides, to form new organic compounds.
 Alcohols as Nucleophiles
Alcohols as Nucleophiles
- Phenols typically do not undergo nucleophilic substitution reactions due to the repulsion of nucleophiles. The hydroxyl (OH) group in phenols acts as a potent electron donor, leading to a substantial increase in electron density on the benzene ring. Consequently, the benzene ring becomes resistant to nucleophiles, preventing their attack.
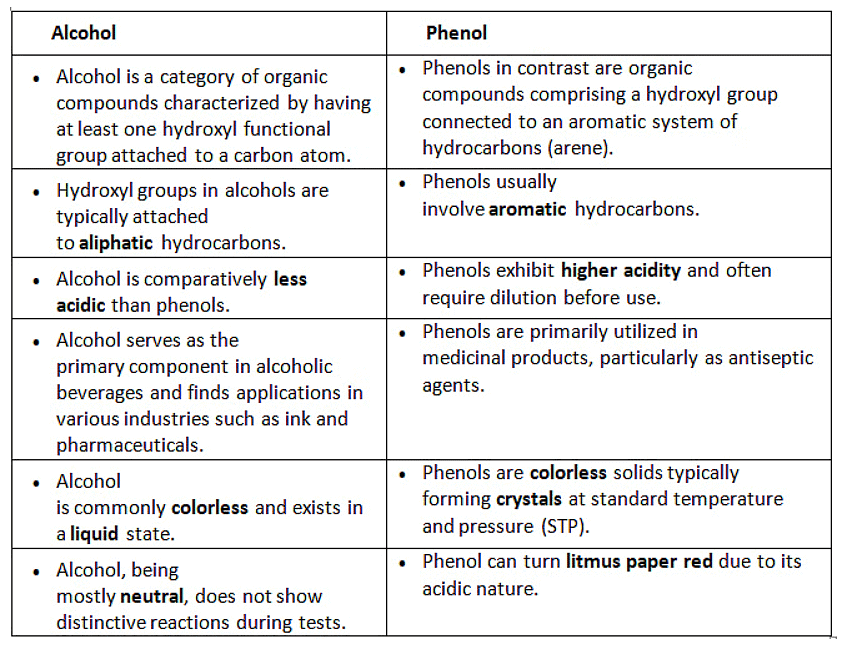
Difference between Alcohols and Phenols
Some Important Questions
Q1: Given below are two statements: One is labelled as Assertion A and the other is labelled as Reason R.
Assertion A: Butan -1- ol has higher boiling point than ethoxyethane.
Reason R: Extensive hydrogen bonding leads to stronger association of molecules.
In the light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A is false but R is true
(b) Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A
(c) Both A and R are true but R is the correct explanation of A
(d) A is true but R is false
Ans: (c)
The boiling point of a substance is dependent on the strength of the intermolecular forces between its molecules. Stronger intermolecular forces require more energy to overcome, thus resulting in a higher boiling point.
In the case of butan-1-ol and ethoxyethane (diethyl ether), they are both composed of similar numbers of similar atoms, but the type of intermolecular force between the molecules differs due to their functional groups.
Butan-1-ol is an alcohol and has a -OH group, which allows for hydrogen bonding, a strong type of dipole-dipole interaction. This happens when the hydrogen atom in a polar bond (especially -OH, -NH, -HF) is attracted to some electronegative atom (like O, N, or F) in another molecule. Because of this, butan-1-ol molecules "stick together" more strongly, requiring more heat energy to separate them and thus exhibiting a higher boiling point.
On the other hand, ethoxyethane, being an ether, does not have the ability to form hydrogen bonds since it lacks the -OH group. The primary intermolecular forces in ethers are relatively weaker van der Waals forces. Therefore, it requires less heat energy to break these forces, resulting in a lower boiling point compared to butan-1-ol. So, both A and R are true and R is indeed the correct explanation for A.
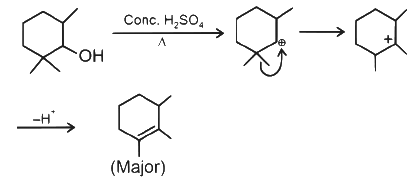
Q2: Find out the major product from the following reaction.
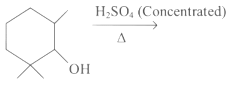 (a)
(a) 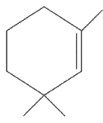
(b) 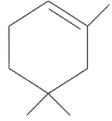
(c) 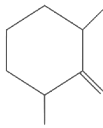
(d) 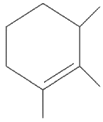
Ans: (d)
Q3: Which one of the following statements is not correct?
(a) Alcohols are weaker acids than water
(b) Acid strength of alcohols decreases in the following: RCH2OH> R2CHOH > R3COH
(c) Carbon-oxygen bond length in methanol, CH3OH is shorter than that of C - O bond length in phenol.
(d) The bond angle 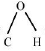 in methanol is 108.9°.
in methanol is 108.9°.
Ans: (c)
The C - O bond length in alcohols is 142 pm and in Phenol it is 136 pm. The C O bond length in phenol is shorter than that in methanol due to the conjugation of unshared pair of electrons on oxygen with the ring, which imparts double bond character to the C - O bond.
|
75 videos|278 docs|78 tests
|
FAQs on Alcohols and Phenols: Properties - Chemistry Class 12 - NEET
| 1. What are the main differences between alcohols and phenols? |  |
| 2. How are alcohols classified? |  |
| 3. What is the nomenclature system for naming alcohols? |  |
| 4. What are the physical properties of alcohols and phenols? |  |
| 5. What are some common chemical reactions involving alcohols and phenols? |  |