Alcohols and Phenols: Preparation and Synthesis | Chemistry Class 12 - NEET PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| What is Preparation of Alcohols? |

|
| Methods of Preparation of Alcohols |

|
| Preparation of Phenols |

|
| Solved Examples |

|
Alcohols and phenols are important types of chemicals used in many areas like medicine, perfumes, makeup, and making things. Alcohols have a special group called hydroxyl (-OH) attached to a carbon atom, and they can do many different chemical reactions. Phenols have a similar hydroxyl group, but it's attached to a special type of ring, making them react in unique ways.
Understanding how to make alcohols and phenols is really important for chemists because it lets them create lots of different chemicals with specific features and shapes.
What is Preparation of Alcohols?
The preparation of alcohols refers to the methods or processes used to produce alcohol compounds. There are several common methods for the preparation of alcohols, each with its own specific conditions and reagents. Another term often used to describe the preparation of alcohols is "alcohol synthesis" or "alcohol formation."
 Synthesis of Alcohols
Synthesis of Alcohols
Here are some common methods for the preparation of alcohols:
Methods of Preparation of Alcohols
1. From Alkenes
(i) By acid-catalyzed hydration of alkenes
One method to prepare alcohols from alkenes is through acid-catalyzed hydration. This process involves the addition of water to the double bond of the alkene in the presence of an acid catalyst. During the reaction, a carbocation intermediate is formed.
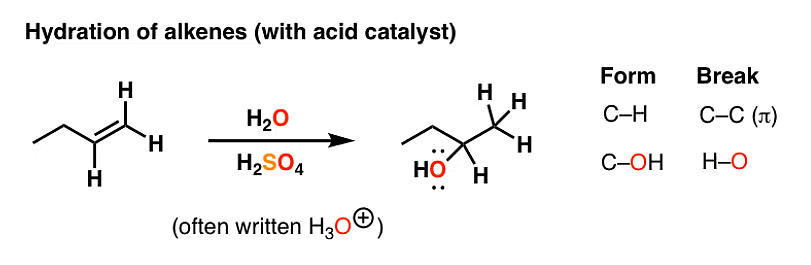 Hydration of Alkenes with Acid Catalyst
Hydration of Alkenes with Acid Catalyst
Note: The addition of water follows Markovnikov's rule, where the hydrogen atom attaches to the carbon atom with a greater number of hydrogen atoms already attached.
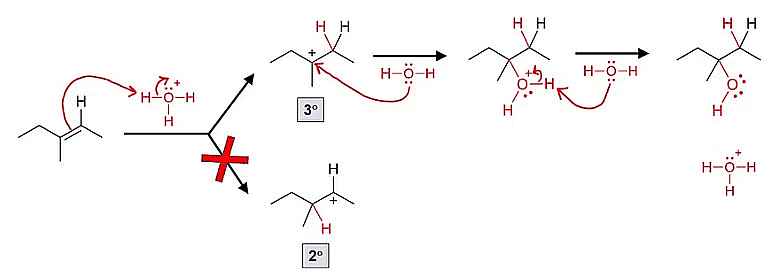 Mechanism of Addition of Water to Alkenes to Form Alcohols
Mechanism of Addition of Water to Alkenes to Form Alcohols
It's important to note that rearrangement of the carbocation can occur, leading to the formation of different alcohol products.
(ii) By Oxymercuration - Demercuration Process
Alkenes react with mercuric acetate in the presence of H2O and tetrahydrofuran to give alkyl mercury compounds. This is one of the most common types of methods to prepare alcohol. This method always leads to Markovnikov’s addition of water to alkenes.
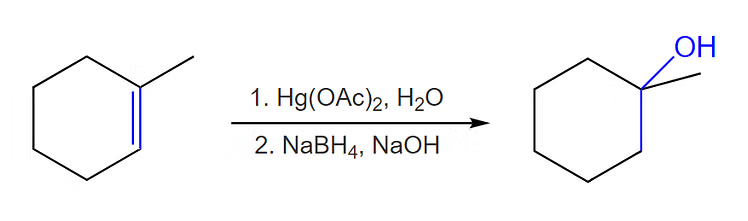 Oxymercuration - Demercuration Process
Oxymercuration - Demercuration Process
(iii) By Hydroboration-oxidation process
Alkenes, when treated with diborane, give alkyl boranes, R3B. Alkylboranes on oxidation with alkaline hydrogen peroxide give alcohol. It is significant to note that this method always leads to anti-Markovnikov’s addition of water to alkenes.
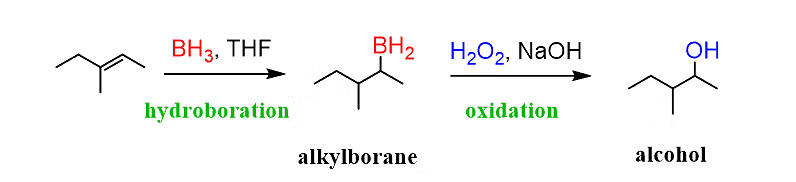
Formation of Alcohol by Hydroboration-Oxidation Process
(iv) Hydroformylation of Alkenes (Oxo Reaction)
Lower molecular weight alkenes react with carbon monoxide and hydrogen in the presence of a catalyst in a reaction called hydroformylation or the oxo reaction. The resulting aldehyde is subsequently hydrogenated to form an alcohol.
 Hydroformylation of Alkenes
Hydroformylation of Alkenes
2. From Alkyl Halides
(i) Hydrolysis of Halides
The hydrolysis of alkyl halides involves the reaction of the alkyl halide with an aqueous solution of an alkali hydroxide, typically sodium hydroxide (NaOH) or potassium hydroxide (KOH). This reaction is a nucleophilic substitution mechanism, where the halide ion (X-) is replaced by the hydroxide ion (OH-), resulting in the formation of an alcohol.
The general reaction equation for the hydrolysis of alkyl halides is:
R-X + KOH → R-OH + KX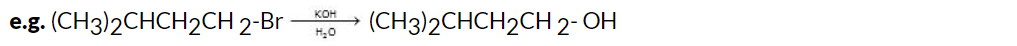 Here, R represents the alkyl group, and X represents the halide (such as chloride, bromide, or iodide).
Here, R represents the alkyl group, and X represents the halide (such as chloride, bromide, or iodide).
Nucleophilic substitution reactions for the formation of alcohols can take place through 2 mechanisms:
1. By SN2 Mechanism (Second-Order Substitution)
2. By SN1 mechanism (first-order substitution)
Here is a brief explanation of both of these:
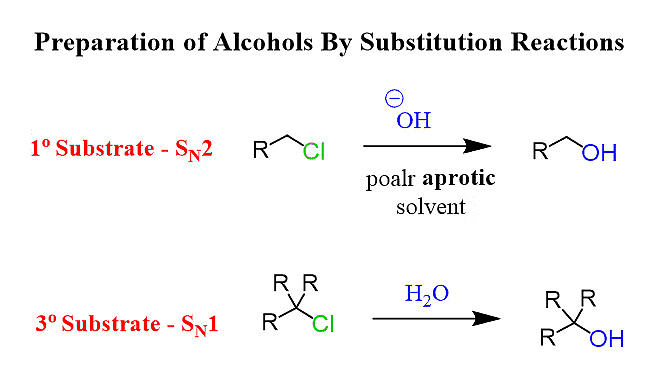
SN1 Mechanism: It's a two-step process observed in reactions with tertiary and some secondary alkyl halides. First, the alkyl halide forms a carbocation intermediate. Then, a nucleophile attacks the carbocation, resulting in a mixture of stereoisomers. Below is a detailed explanation:
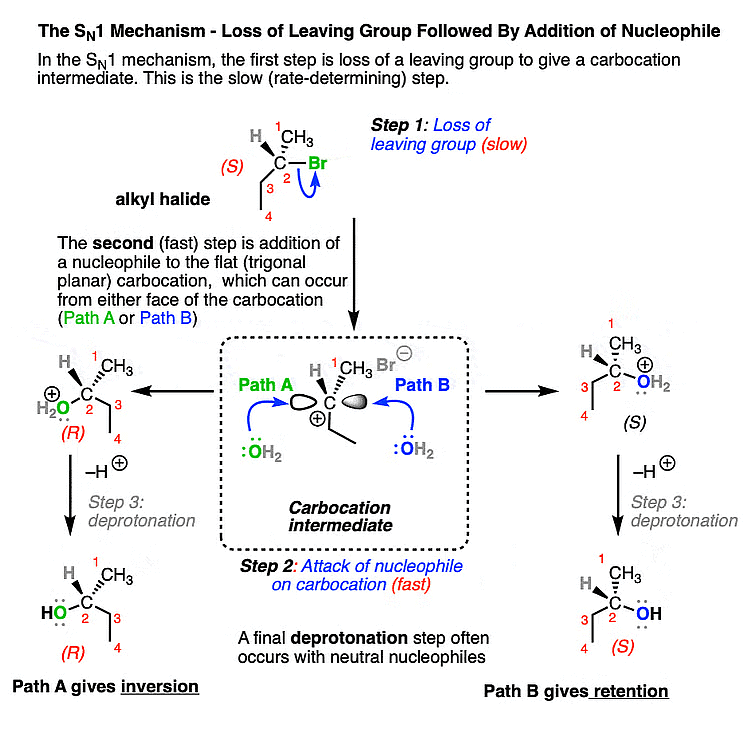 SN1 Mechanism
SN1 Mechanism
SN2 Mechanism: It's a single-step process observed in reactions with primary and some secondary alkyl halides. The nucleophile simultaneously attacks the electrophilic carbon and displaces the leaving group, causing an inversion of configuration at the chiral center.
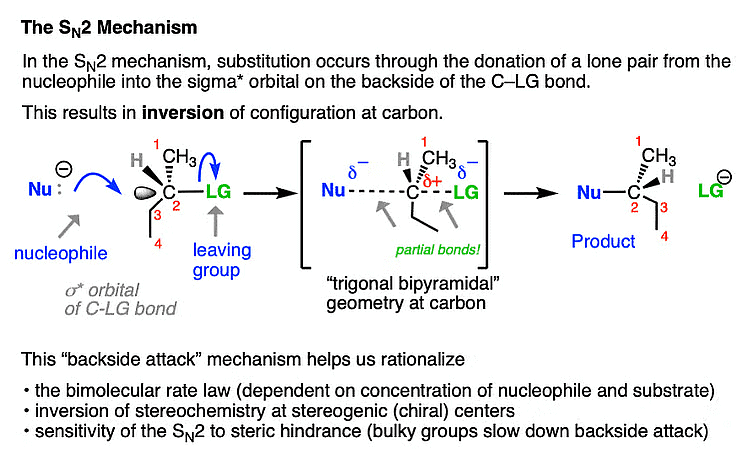 SN2 Mechanism
SN2 Mechanism
3. Preparation of Alcohols From Grignard Reagent
(i) From air
A Grignard reagent may be used to synthesize alcohol by treating it with dry oxygen and decomposing the product with acid :
General reaction:
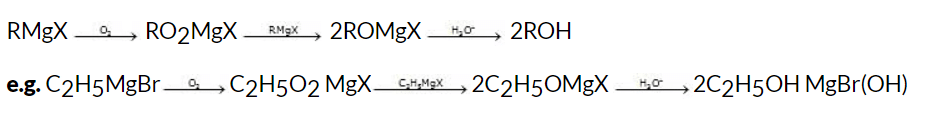
(ii) From ethylene oxide
The addition of Grignard reagent to ethylene oxide gives primary alcohol (with two carbon atoms added).
General reaction:
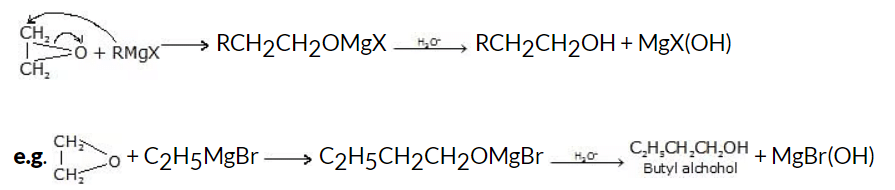
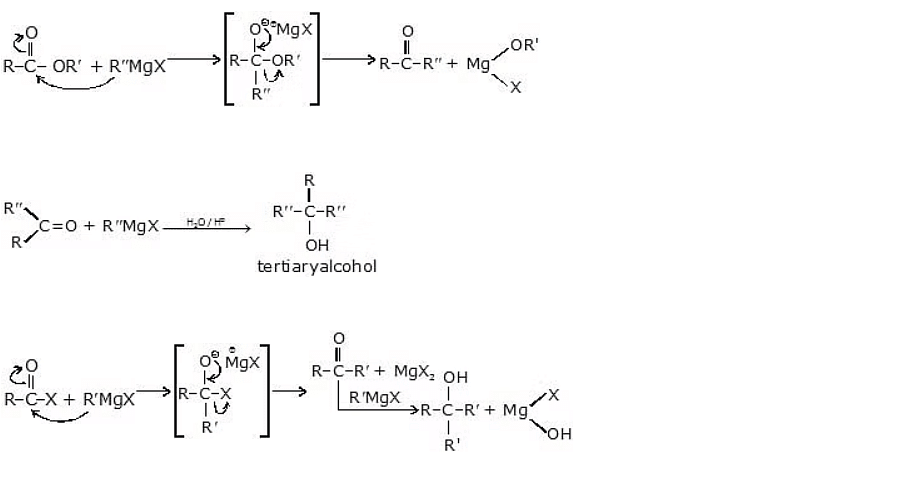
(iii) From carbonyl compounds
Alcohols can be synthesized from carbonyl compounds through nucleophilic addition reactions using Grignard's reagent. Grignard's reagent is an organometallic compound consisting of a carbon-metal bond, commonly formed by reacting an alkyl or aryl halide with magnesium metal.
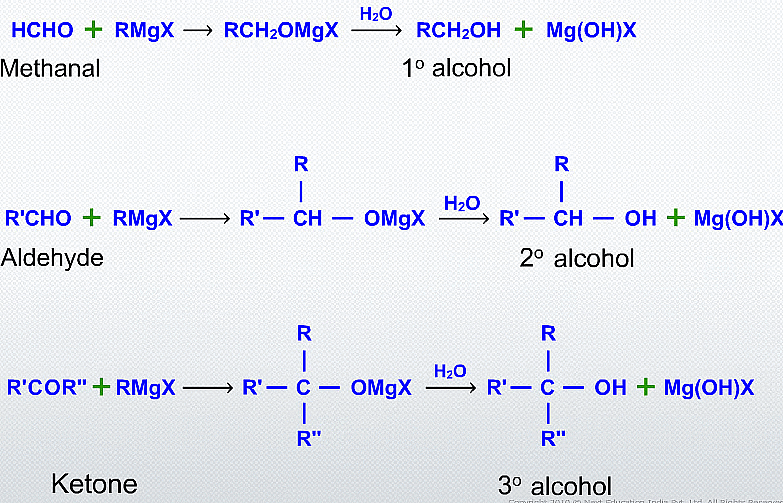 Alcohol Synthesis from Carbonyl Compounds
Alcohol Synthesis from Carbonyl Compounds
(iv) Addition of formaldehyde gives primary alcohol
General reaction:
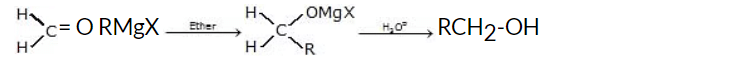
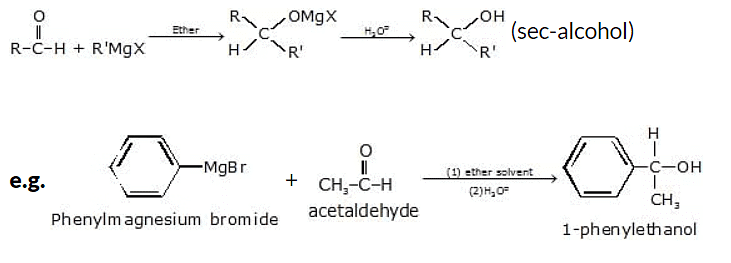
(v) Addition to an aldehyde (other than formaldehyde) gives secondary alcohol
General reaction:
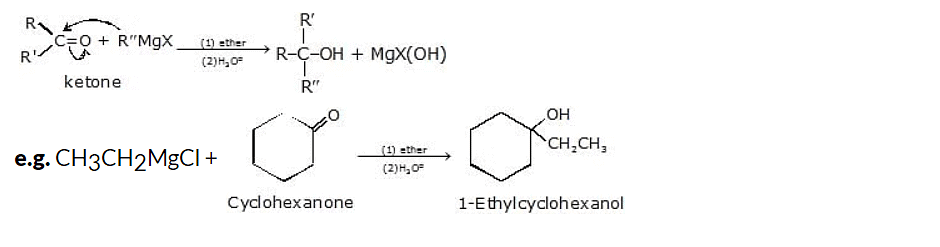
(vi) Addition to a ketone gives tertiary alcohol.
General reaction:
(vii) Addition to an acid halide or an ester gives tertiary alcohol.
Esters on treatment with Grignard's reagent first form ketones which then react with the second molecule of Grignard's reagent and form tertiary alcohol.
General reaction:
4. By Reduction of Carbonyl Compounds
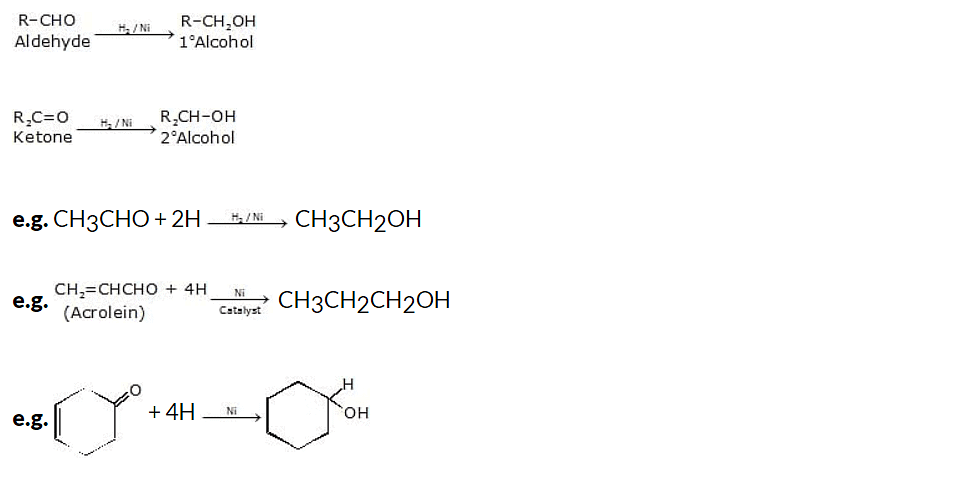
(i) Catalytic hydrogenation of aldehydes and ketones
One method of synthesizing alcohols from carbonyl compounds is through catalytic hydrogenation of aldehydes and ketones. This process involves the use of a catalyst, typically a transition metal catalyst, and hydrogen gas (H2) to reduce the carbonyl group to an alcohol.
 General reaction:
General reaction:
(ii) Lithium Aluminium Hydride reduction of aldehydes and ketones
Another method for synthesizing alcohols from carbonyl compounds is through the reduction of aldehydes and ketones using lithium aluminum hydride (LiAlH4). LiAlH4 is a powerful reducing agent that can selectively convert carbonyl groups into alcohols.
General reaction:
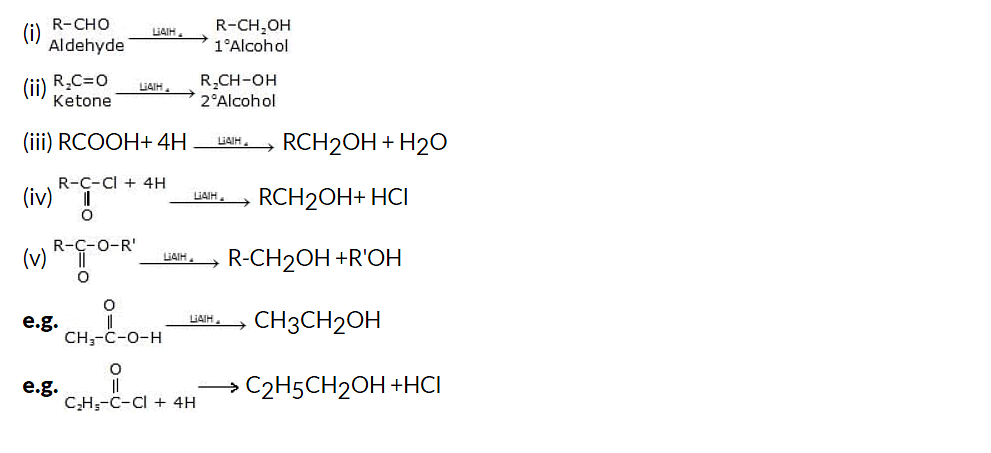
Question. Identify (X) in the following reaction:

Ans. 
(iii) NaBH4 (Sodium Borohydride) reduction of aldehydes and ketones
Another method for the synthesis of alcohols from carbonyl compounds is through the reduction of aldehydes and ketones using sodium borohydride (NaBH4). NaBH4 is a mild and selective reducing agent that is commonly used for this purpose.
It is insoluble in ether and is used in an aqueous ethanolic solution to reduce carbonyl compounds. It does not reduce esters and acids.
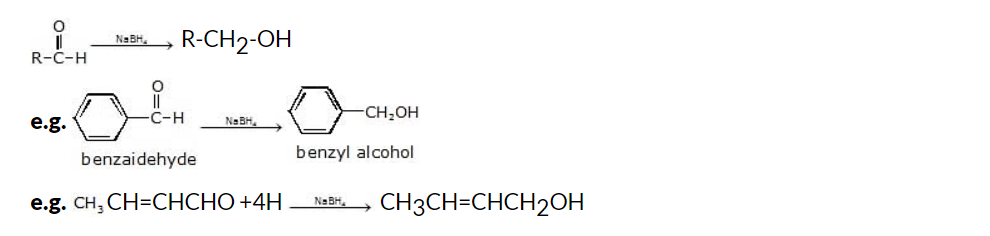
Note: Reduction of a ketone gives secondary alcohol
(iv) Bouveault-Blanc Reduction
The reduction of aldehydes, ketones, or esters using excess of sodium and ethanol or n-butanol as the reducing agent.
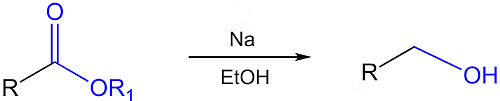
General reaction:
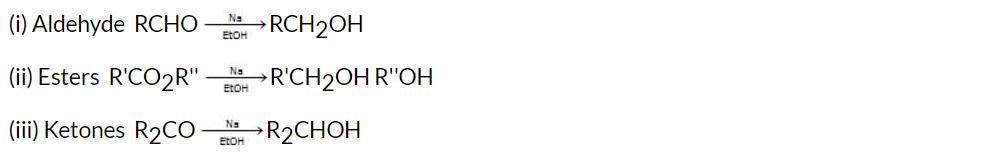
The Bouveault-Blanc reduction is believed to occur in steps involving the transfer of one electron at a time.
Mechanism: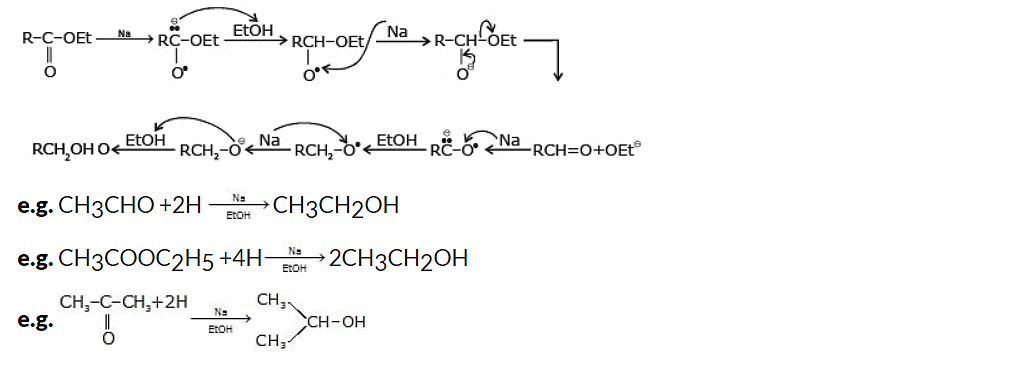
5. By Reaction of Nitrous Acid on Aliphatic Primary Amines
The reaction of nitrous acid (HNO2) with aliphatic primary amines (R-NH2) leads to the formation of alcohols. This process is known as the nitrous acid reaction or nitrosation reaction.General reaction: 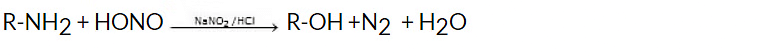
Mechanism:
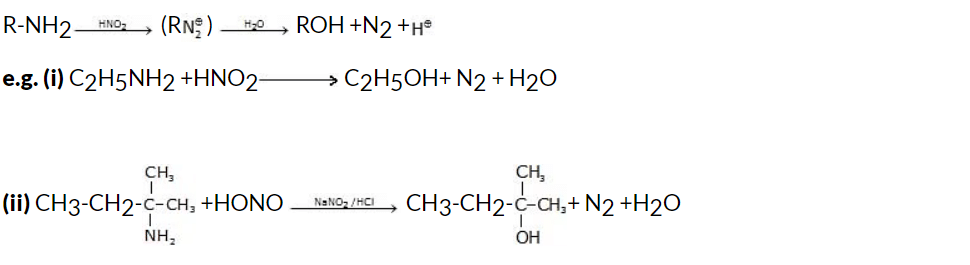
Mechanism:
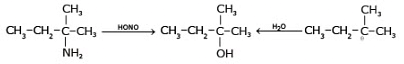
6. Formation of diols by Hydroxylation
Converting an alkene to a glycol requires adding a hydroxy group to each end of the double bond. This addition is called hydroxylation of the double bond.
(a) Syn hydroxylation, using KMnO4 / NaOH or using OsO4/H2O2
Syn hydroxylation is a chemical reaction that introduces hydroxyl (-OH) groups onto an unsaturated compound, typically an alkene. It is commonly achieved using two different reagent systems: potassium permanganate (KMnO4) with sodium hydroxide (NaOH), or osmium tetroxide (OsO4) with hydrogen peroxide (H2O2).
General reaction :
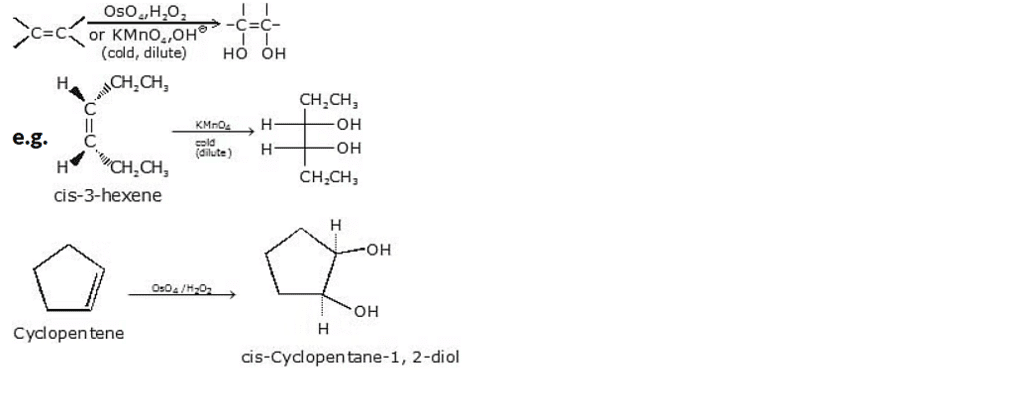
(b) Anti-hydroxylation, using peracids
Anti-hydroxylation is a chemical reaction that introduces hydroxyl (-OH) groups onto an unsaturated compound, specifically an alkene, in an anti-addition manner. One common method for achieving anti-hydroxylation is by using peracids, which are peroxy acids.

Preparation of Phenols
Preparation of phenols can be done from diazonium salts, benzene sulphonic acid, haloarenes, and cumene. They are also known as carbolic acids. They are weak acids and mostly form phenoxide ions by dropping one positive hydrogen ion (H+) from the hydroxyl group.
Phenol was mainly manufactured from coal tar. Nowadays, with developments in technologies, some new methods have come up for the making of phenols in laboratories. In laboratories, phenol is mainly created from benzene derivatives.
Some of the approaches to the preparation of phenols are explained below:
1. Preparation of Phenols From Haloarenes
Chlorobenzene is an example of haloarenes which is made by mono replacement of the benzene ring. When chlorobenzene is reacted with sodium hydroxide at 623K and 320 atm sodium phenoxide is formed. Finally, sodium phenoxide on acidification makes phenols.
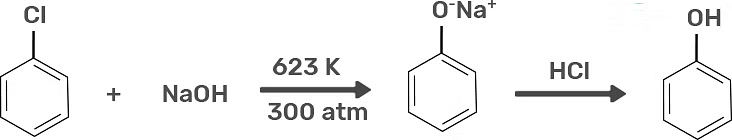 Preparation of Phenols from Haloarenes
Preparation of Phenols from Haloarenes
2. Preparation of Phenols From Benzene Sulphonic Acid
Benzene sulphonic acid can be acquired from benzene by reacting it with oleum. Benzene sulphonic acid hence is fused with molten sodium hydroxide at a very high temperature which leads to the development of sodium phenoxide. Lastly, sodium phenoxide on acidification gives phenols.
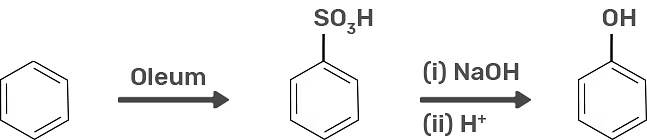 Preparation of Phenols from Benzene Sulphonic Acid
Preparation of Phenols from Benzene Sulphonic Acid
3. Preparation of Phenols From Diazonium Salt
When an aromatic primary amine is fused with nitrous in the presence of HCl(NaNO2 + HCl) acid at 273 – 278 K, diazonium salts are gained. These diazonium salts are extremely reactive in nature. Upon warming with water, these diazonium salts, end and hydrolyze to phenols. Phenols can also be acquired from diazonium salts by treating them with dilute acids. Preparation of Phenols from Diazonium Salts
Preparation of Phenols from Diazonium Salts
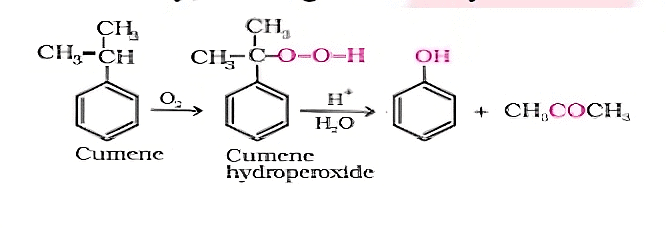
4. Preparation of Phenols From Cumen
Cumene is an organic compound acquired by Friedel-Craft's alkylation of benzene with propylene. On oxidation of cumene (isopropylbenzene) in the presence of air, cumene hydroperoxide is found. Upon further action of cumene hydroperoxide with dilute acid, phenols are produced. Acetone is also made as one of the by-products of this reaction in large quantities. Therefore, phenols prepared by these techniques need purifications.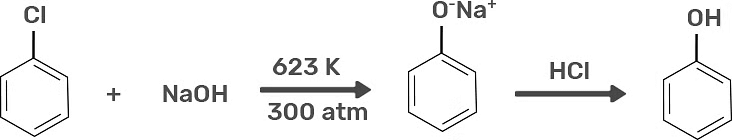 Preparation of Phenols from Cumene
Preparation of Phenols from Cumene
5. Dow Proces
In this process, chlorobenzene is reacted with dilute sodium hydroxide at a temperature of about 300°C and 3000 psi pressure. The following figure exemplifies the Dow process. Dow Process
Dow Process
6. Air Oxidation of Cumene
The oxidation of cumene in the presence of air (isopropylbenzene) will lead to the making of both acetone and phenol, as shown in the following figure. The mechanisms for the development and degradation of cumene hydroperoxide need closer looks, which are delivered following the figure.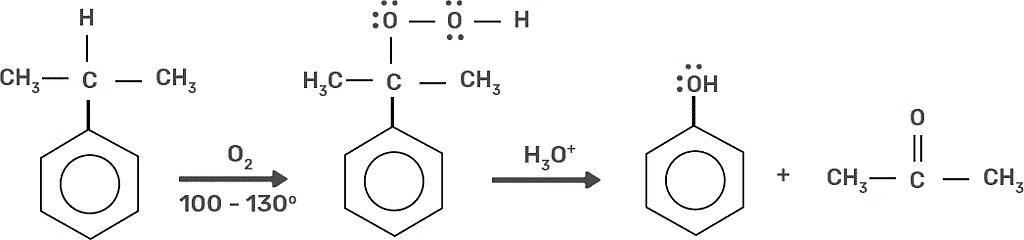 Air Oxidation of Cumene
Air Oxidation of Cumene
Solved Examples
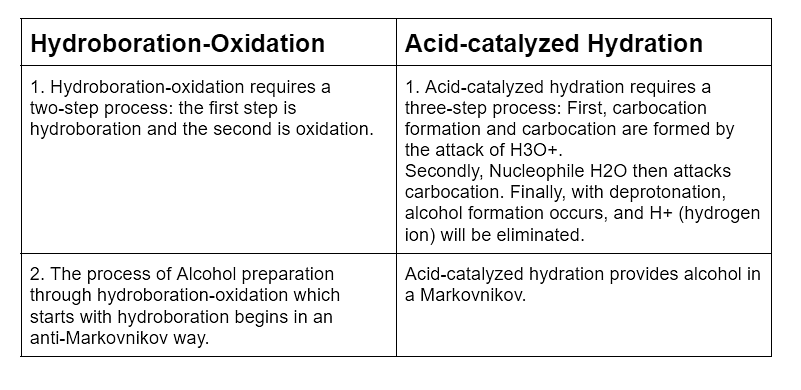
Q1: Differentiate between hydroboration-oxidation and acid- catalysed hydration
Sol:
Q2: Give the equation of reactants for the preparation of phenol from cumene.
Sol: To synthesize phenol, cumene is initially oxidized in the presence of air of cumene hydroperoxide.
Followed by, treating cumene hydroxide with dilute acid to prepare phenol and acetone as by products.
|
75 videos|278 docs|78 tests
|
FAQs on Alcohols and Phenols: Preparation and Synthesis - Chemistry Class 12 - NEET
| 1. How can alcohols be prepared from alkenes? |  |
| 2. What is the method for preparing alcohols from alkyl halides? |  |
| 3. How can alcohols be prepared from Grignard reagents? |  |
| 4. What is the process for preparing alcohols by reduction of carbonyl compounds? |  |
| 5. How are phenols prepared from haloarenes? |  |