Algae and Its Classification | Biology Class 11 - NEET PDF Download
What are Algae?
Algae are simple plants that contain chlorophyll and can make their own food. They're mostly found in water, but can also be present on damp surfaces like rocks and wood. Some even live with fungi (like lichen) or animals (like on sloths). They come in different shapes and sizes, from small groups like Volvox to long, thread-like ones like Ulothrix and Spirogyra. Some algae in the ocean, like kelp, can grow really big.
 Algae
Algae
Characteristics of Algae
- Chlorophyll-Bearing: Algae contain chlorophyll, allowing them to perform photosynthesis.
- Simple: They are relatively simple in structure.
- Thalloid: Algae lack complex structures and are typically flat and undifferentiated.
- Autotrophic: Algae produce their own food through photosynthesis.
- Aquatic Habitat: They are mainly found in water, including both freshwater and marine environments. They can also thrive on moist stones, soils, and wood, and sometimes even in association with fungi (lichen) or animals (e.g., on sloth bears).
Note: Mnemonics are like memory tricks that can make it much easier to understand and remember what you're learning in the chapter. To make things easier for you, EduRev offers a document packed with these helpful memory aids
If you click on the provided link, you'll be taken to the mnemonics document.
Modes of Reproduction
 Modes of Reproduction of Algae
Modes of Reproduction of Algae
(a) Vegetative Reproduction
- Algae reproduce vegetatively through fragmentation. Each fragment can develop into a new thallus.
Reproduction in algae through fragmentation is a method of asexual reproduction where a parent algal organism breaks or fragments into smaller pieces, and each of these fragments has the potential to develop into a new, independent thallus (body of the algae). - This process can occur in various types of algae, including both multicellular and unicellular species.
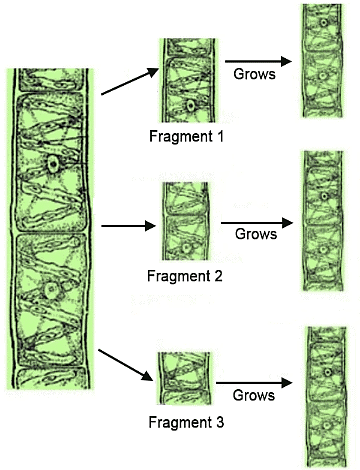
(b) Asexual Reproduction
- Asexual reproduction in many types of algae often involves the production of specialized reproductive cells known as spores, with zoospores being one of the most common types of spores.
- Zoospores are unique because they are motile, meaning they are capable of movement, and they play a crucial role in the reproductive life cycle of certain algae.
- Asexual reproduction involves the production of various spore types, with zoospores being the most common. Zoospores are motile and develop into new plants upon germination.
 Asexual Reproduction
Asexual Reproduction
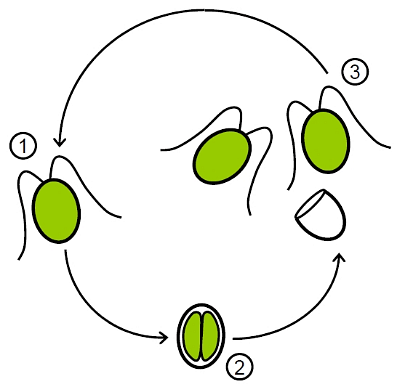
(c) Sexual Reproduction
Sexual reproduction in algae occurs through the fusion of two gametes.
- Isogamous: In some cases, gametes are flagellated and similar in size, as seen in Ulothrix.
- Anisogamous: In species like Eudorina, two gametes of different sizes fuse.
- Oogamous: In organisms like Volvox and Fucus, a large, non-motile female gamete fuses with a smaller, motile male gamete.
 Sexual Reproduction
Sexual Reproduction
Types of Algae
Algae are a diverse group of photosynthetic organisms, and they come in various forms, each with its unique characteristics. Here are some common types:

(a) Chlorophyceae: Green Algae
Green algae, members of Chlorophyceae, are often called so because of their green color, which comes from chlorophyll a and b pigments. They can exist as single cells, colonies, or thread-like structures.
 Algae: Chlorophyceae
Algae: Chlorophyceae
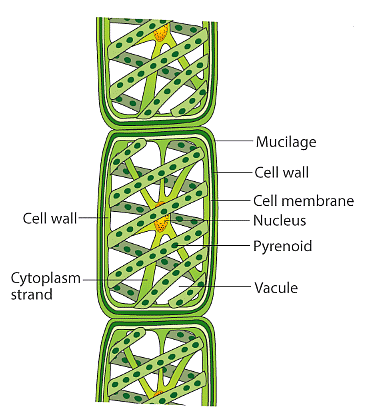
Cell Structure and Pigments:
- Green algae typically have chloroplasts containing chlorophyll pigments, which vary in shape from disc-shaped to spiral or ribbon-like.
- These chloroplasts may contain pyrenoids, which store protein and starch, contributing to the algae's energy reserves.
 Pyrenoid
Pyrenoid
- Some species store food as oil droplets.
- Their cell walls are rigid, composed of cellulose and pectose layers.
Reproduction:
- Vegetative reproduction occurs through fragmentation or the formation of various types of spores.
- Asexual reproduction involves the production of flagellated zoospores from specialized structures called zoosporangia.
- Sexual reproduction varies in the types and formation of sex cells, which can be isogamous (similar), anisogamous (differently sized), or oogamous (large non-motile egg and small motile sperm).

Common Green Algae Species:
- Some commonly encountered green algae include Chlamydomonas, Volvox, Ulothrix, Spirogyra, and Chara.
Learn more about Green Algae through this video:
Algae: Chlorophyceae (Green Algae)
(b) Phaeophyceae: Brown Algae
Brown algae, members of Phaeophyceae, are primarily found in marine environments and exhibit diverse sizes and shapes. They range from simple filamentous forms like Ectocarpus to towering kelps, some reaching heights of 100 meters.
 Brown AlgaeCell Composition and Pigments:
Brown AlgaeCell Composition and Pigments:
- Brown algae contain chlorophyll a, chlorophyll c, carotenoids, and xanthophylls, giving them a range of colors from olive green to various shades of brown, depending on the amount of fucoxanthin pigment present.
- They store food as complex carbohydrates, such as laminarin or mannitol.
- Vegetative cells have a cellulosic wall, often covered by a gelatinous coating of algin. The protoplast contains plastids, a central vacuole, and a nucleus.
Plant Structure:
- Brown algae usually stick to something using an anchor-like structure called a holdfast. They also have a stem called a stipe and a leaf-like part that does photosynthesis called a frond.
Reproduction:
- Vegetative reproduction occurs through fragmentation.
- Asexual reproduction involves the production of biflagellate zoospores, which are pear-shaped and have two unequal flagella.
- Sexual reproduction can be isogamous, anisogamous, or oogamous. Gamete union may occur in water or within specialized structures like the oogonium.
- Gametes are pear-shaped and possess two lateral flagella.
Common Brown Algae Species:
- Some commonly encountered brown algae include Ectocarpus, Dictyota, Laminaria, Sargassum, and Fucus.
(c) Rhodophyceae: Red Algae
Red algae, members of Rhodophyceae, are named for their predominant red pigment, r-phycoerythrin. They are mostly found in the ocean, particularly in warmer regions, and can thrive in well-lit surface waters as well as in deep ocean areas with minimal light penetration.
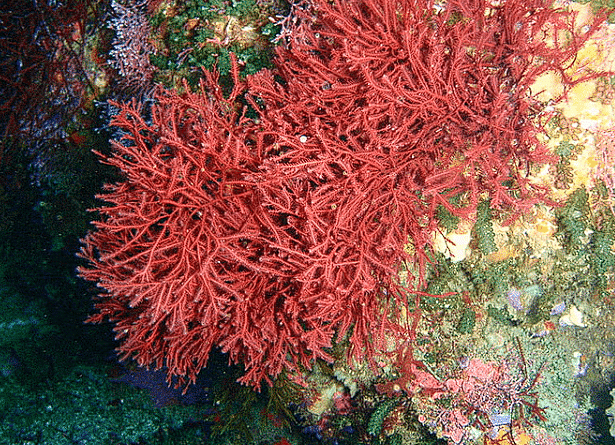 Red AlgaeCell Structure and Pigments:
Red AlgaeCell Structure and Pigments:
- Most red algae have multicellular thalli, with some displaying complex body structures.
- They store food as floridean starch, which is similar in structure to amylopectin and glycogen.
Reproduction:
- Vegetative reproduction typically occurs through fragmentation.
- Asexual reproduction involves the production of non-motile spores.
- Sexual reproduction is oogamous, with non-motile gametes. It involves complex post-fertilization developments.
Common Red Algae Species:
Some commonly found red algae include Polysiphonia, Porphyra, Gracilaria, and Gelidium.
Uses of Algae
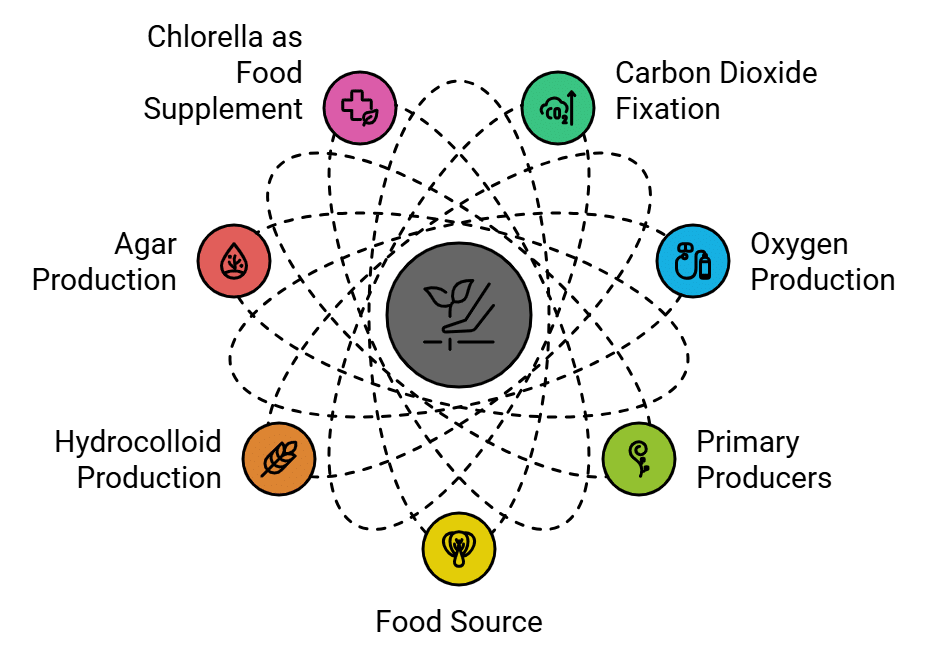 Uses of Algae
Uses of Algae
1. Carbon Dioxide Fixation: Algae play a significant role in reducing carbon dioxide levels on Earth by using photosynthesis to convert it into organic compounds.
2. Oxygen Production: Through photosynthesis, algae also increase the amount of dissolved oxygen in their surroundings, benefiting the ecosystem.
3. Primary Producers: Algae are essential as primary producers, providing energy-rich compounds that form the basis of the aquatic food chain, sustaining various aquatic animals.
4. Food Source: Many species of marine algae, such as Porphyra, Laminaria, and Sargassum, are consumed as food by humans. They are among the 70 species of marine algae utilized for this purpose.
5. Hydrocolloid Production: Certain types of marine brown and red algae produce large quantities of hydrocolloids, such as algin (from brown algae) and carrageen (from red algae), which have commercial applications.
6. Agar Production: Commercial products like agar, derived from Gelidium and Gracilaria algae, are used in various applications, including microbiology for growing microbes, as well as in food products like ice creams and jellies.
7. Chlorella as Food Supplement: Chlorella, a unicellular algae rich in proteins, is utilized as a dietary supplement, even by astronauts during space travel.
Check How much you have learned about Algae by attempting this test:
Test: Algae - 1
NEET Previous Year Questions - Algae
Q.1. An example of colonial alga is:
(a) Spirogyra
(b) Chlorella
(c) Volvox
(d) Ulothrix
Correct Answer is Option (c)
Volvox is a unicellular green alga found in freshwater bodies. It is photosynthetic in nature. It forms colonies of around 50,000 cells which are spherical in shape.
Q.2. Which of the following pairs include unicellular algae?
(a) Gelidium & Gracilaria
(b) Anabaena & Volvox
(c) Chlorella & Spirulina
(d) Laminaria & Sargassum
Correct Answer is Option (c)
- Chlorella and Spirulina are unicellular green algae, which are commercially very important.
- Anabaena is Cyanobacteria, Laminaria, Sargassum, Gelidium, Gracilaria are multicellular algae.
- Volvox is unicellular colonial algae.
So, the correct answer is 'Chlorella and Spirulina'
Additional Information
Different forms of Green algae (Structure)
1. Unicellular
A unicellular organism, also known as a single-celled organism, is an organism that consists of only one cell, unlike a multicellular organism that consists of more than one cell. Types of Unicellular Algae:
- Chlamydomonas: Motile unicellular algae. This alga moves with the help of flagella.
 Unicellular Organism
Unicellular Organism - Chlorella: Non-motile unicellular algae. Calvin discovered the "Calvin Cycle" by experimenting with Chlorella.
 Chlorella Unicellular Alga
Chlorella Unicellular Alga - Acetabularia: Umbrella plant - It is the largest unicellular plant. The diameter of its cell is 10 cm. Hammerling experimented on Acetabularia.
 Acetabularia Umbrella Plant
Acetabularia Umbrella Plant
2. Coenocytic
Some green algae are coenocytic, i.e. multi-nucleated.
Example: Caulerpa
Note: According to the five-kingdom system the algae described above should be placed in Protista but exceptionally due to their life cycle, it is similar to green algae. They are placed in Plantae. But now modern scientist place above algae in Protista.
3. Colonial
Some green algae are found in colonies. They form a colony of cells. The number of cells in a colony is fixed. A colony with a fixed number of cells is called coenobium.
Example: Volvox- Motile colony Hydrodictyon- Non-motile colony (called a water net).
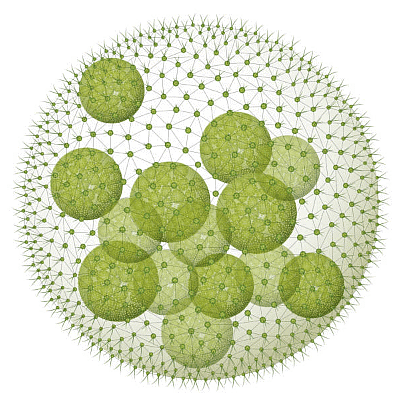 Volvox
Volvox
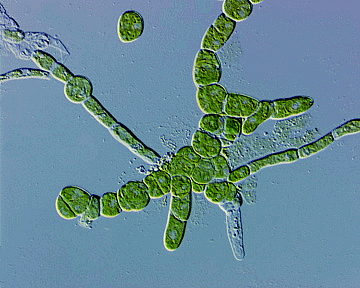
4. Multicellular Filamentous
Most algae are multicellular filamentous.
Example: Ulothrix- Known as pond wool, Spirogyra- Known as pond silk.
 Spirogyra
Spirogyra
Note: Some green algae are heterotrichous i.e. prostrate branches and erect branches. Erect system of filaments in the plant body develops from the prostate system of filaments. Branches in prostrate branches are just above the ground, but branches in erect branches are held upright. Green algae such as Fritschiella, Draparnaldia, and others have a heterotrichous habit. (Fritschiella tuberosa has an approach to the early land plants).
 Fritschiella
Fritschiella
5. Multicellular Thalloid or Parenchymatous
- Some algae are multi-cellular in length & width
To practice questions on the topic of "Green Algae", you just read, attempt the tests given below:
|
181 videos|361 docs|148 tests
|
FAQs on Algae and Its Classification - Biology Class 11 - NEET
| 1. What are algae and how are they classified? |  |
| 2. What are the modes of reproduction in algae? |  |
| 3. What are the key characteristics of Chlorophyceae (Green Algae)? |  |
| 4. What are the economic uses of algae? |  |
| 5. How do Phaeophyceae (Brown Algae) differ from Rhodophyceae (Red Algae)? |  |

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|