Amendment of the Constitution - 2 | Law Optional Notes for UPSC PDF Download
Amendment of the Constitution
- Amending the Constitution of India is the process of making changes to the nation’s fundamental law or supreme law. The procedure of amendment in the constitution is laid down in Part XX (Article 368)
- The procedure for amending the Constitution is neither flexible (Britain) nor rigid (USA). It is synthesis of both. It states that Parliament may amend the Constitution but can’t amend those provisions which form basic structure of the Constitution (Kesavananda Bharti case, 1973)
- Feature borrowed from South Africa.
- Article 368 has been amended by the 24th and 42nd Amendments in 1971 and 1976 respectively.
Important Judgement: Kesavananda Bharati Case 1973, Supreme Court ruled that Parliament cannot alter the ‘basic structure’ of the Constitution
Procedure For The Amendment (Art. 368)

Types of Majority

Various Provisions & Type of Majority Required

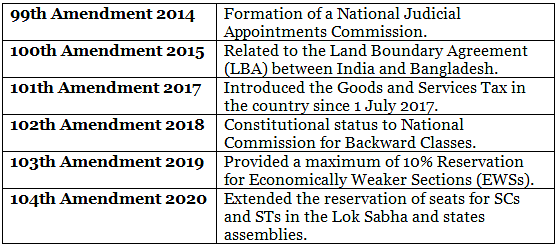
Recent Constitutional Amendments
Criticism of Amendment Procedure
States cannot initiate the amendment (Only parliament can) + States have only one way to propose the amendment i.e. create the legislative council in the state + Constitution does not mention the time within which state legislatures ratify or reject the amendment + Constitution is also silent on whether the states can withdraw their approval once given + no provision for a special body + Only in few cases, the consent of the state legislatures is required + No provision for holding a joint sitting + wide scope for taking the matters to the judiciary due to vague provisions.
What are Constitutional Amendments?
Article 368 of Part XX of the Constitution of India outlines two ways to make changes to the Constitution:
- By a special majority of Parliament.
- By a special majority of Parliament, along with approval from at least half of the total states.
However, there are some other articles that allow certain provisions of the Constitution to be amended by a simple majority of Parliament. This means that a majority of the members present and voting in each House can make these amendments, just like regular laws. It's important to note that these amendments are not considered as changes to the Constitution under Article 368.
Constitutional Provisions
- Special Majority
In the Indian constitution, there are provisions related to special majority that can be grouped into the following categories:
Article 249: This provision requires a two-thirds majority of the members present and voting in order to empower the Parliament to make laws on subjects included in the state list.
Article 368: This article deals with amending the constitution and requires a majority of two-thirds of the members present and voting, supported by over 50% of the total strength of the House.
Article 368 + fifty percent: In addition to the two-thirds majority mentioned in Article 368, this provision requires that the bill be passed by a simple majority in at least half of the state legislatures in India.
Article 361: This provision mandates a two-thirds majority of the total membership of the house for certain matters, but it would be beneficial to rephrase the content in simpler language.
- Absolute Majority
A bill is considered passed when it receives the support of more than half of the total number of members in the house.
- Effective Majority
This means that a majority of more than half of the actual number of members present and eligible to vote in the House.
Types of Amendments in India
There are three ways in which the Constitution can be changed:
- Amendment with a simple majority of the Parliament.
- Amendment with a special majority of the Parliament.
- Amendment with a special majority of the Parliament and the approval of at least half of the state legislatures.
There are three types of amendments in the Indian Constitution. Let me explain each type in simple terms:
Amendments by Simple Majority of Parliament
- Changes to certain parts of the Constitution can be made with just over half of the members of Parliament agreeing.
- These changes involve things like allowing new states to join, changing the names or borders of existing states, setting up or getting rid of special councils in states, deciding how much money public officials should be paid, and making rules about how Parliament works.
Amendments by Special Majority of Parliament
- To change most parts of the Constitution, we need a special kind of agreement from Parliament. This means more than half of all the members in both houses need to agree, and at least two-thirds of the members who are present and voting need to agree.
- This special agreement is required for important things like Fundamental Rights, Directive Principles of State Policy, and other parts not mentioned in the first and third categories.
Amendments by Special Majority of Parliament and Consent of States
- Provisions related to the federal structure of the country can be amended by a special majority of Parliament and the consent of at least half of the state legislatures.
- Even if some states do not take any action on the amendment, as long as half of the states give their consent, it is considered valid. This applies to matters such as the election of the President, the powers of the Union and the states, the Supreme Court and high courts, the distribution of legislative powers, and the lists in the Seventh Schedule.
- These different types of amendments ensure that the Constitution can be modified while maintaining a balance between the central government and the states, and protecting fundamental rights and principles of governance.
The following provisions can be amended in this way:
- How the President is elected and the process for it can be changed.
- The powers of the Union and the states can be adjusted.
- The Supreme Court and high courts can undergo modifications.
- The allocation of legislative powers between the Union and the states can be revised.
- Any of the categories listed in the Seventh Schedule can be modified.
- The representation of states in Parliament can be altered.
Procedure for Amendment of the Constitution
- An amendment can only be started by introducing a bill in either house of the Parliament. The bill can be brought forward by a minister or a private member, and it doesn't need the President's permission. To pass the bill, a special majority is required in each house. This means it needs support from more than half of the total members of the house and two-thirds of the members present and voting.
- Both houses must pass the bill separately. If there is any disagreement, they cannot hold a joint meeting.
- When the bill aims to change the Constitution, it must be approved by the legislatures of at least half of the states, with a simple majority.
- After the bill is passed by both houses, it is presented to the President for his approval. The President must give his approval to the bill. He cannot refuse to approve the bill or send it back to the Parliament for reconsideration.
- Once the President approves the bill, it becomes an act.
Conclusion
The article discusses changes to the Indian constitution, including the different types of majorities required in parliament for amendments. It is divided into separate articles such as "Article 249," "Article 368," and "Article 368 with 50% state agreement." These amendments aim to combine all the provisions and articles, making the constitution the highest law of the state. The constitution's framework is essential for governing institutions and legal and political systems. Amendments can modify or add government agreements.
|
43 videos|394 docs
|

|
Explore Courses for UPSC exam
|

|

















