Analyzing Competition | Management Optional Notes for UPSC PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| Competitor Analysis Defined |

|
| Components of competitor's analysis (Porter, 1980) |

|
| Porter's five forces |

|
Introduction
In the dynamic landscape of the business world, maintaining a competitive edge is crucial for sustained success. Achieving and sustaining a competitive advantage requires businesses to go beyond easily imitable factors and focus on elements like brand recognition, patented processes, and exclusive rights. Conducting a comprehensive competitor analysis becomes a cornerstone of corporate strategy, aiding in effective decision-making and adaptation.
Competitor Analysis Defined
Competitor analysis involves evaluating the strengths and weaknesses of current and potential rivals. It provides a strategic context to identify opportunities and threats, consolidating relevant information for effective strategy formulation, execution, monitoring, and adjustment. Recognizing competitors, understanding their strategies, and assessing their strengths and weaknesses relative to one's own product or service are essential components.
Competitive Strategy
Competitive strategy revolves around leveraging distinctive capabilities to exploit value, setting the stage for perceptive competitor analysis. The goal is to create a profile of competitors, predicting their potential strategy changes, responses to industry moves, and reactions to broader environmental shifts.
Two Key Characteristics of Competitor Analysis:
- Gathering information about rivals' resources, behavior, and success.
- Using the information to predict and preempt future strategies and behavior of competitors.
Objective of Competitor Analysis:
The primary objective is to understand and think like competitors, allowing the formulation of a competitive strategy that considers expected competitor actions and responses. It involves identifying top competition, assessing strengths/weaknesses, developing strategies for success, and analyzing both successful and unsuccessful competitors.
Techniques for Competitor Analysis:
Creating a competitor array involves defining the industry, identifying competitors, understanding customer expectations, determining industry success factors, ranking success factors, and evaluating competitors based on these factors.
Media Scanning for Analysis:
Media scanning, especially analyzing competitors' advertisements, reveals valuable insights into marketing strategies, target markets, product offerings, pricing, promotion, and distribution strategies. It unveils shifts in positioning, branding, and competitive advantage.
Understanding Competitors' Strategies:
Strategists must comprehend competitors' objectives, assumptions, strategies, and capabilities. Michael Porter's framework emphasizes analyzing these factors to estimate potential strategy changes, predict responses to strategic moves, and understand reactions to industry and environmental shifts.
Components of competitor's analysis (Porter, 1980)
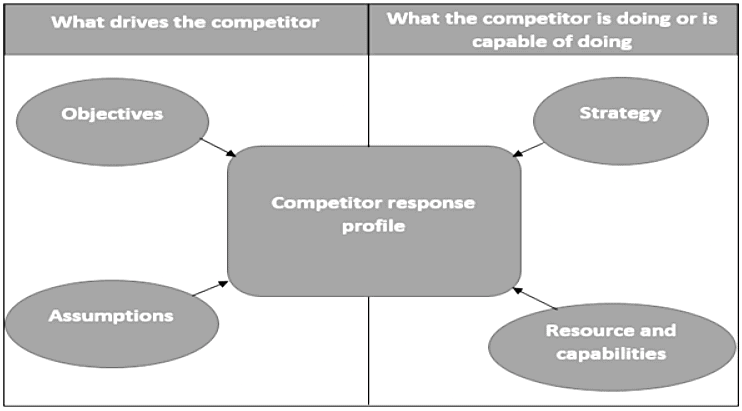
- Competitor's Objectives: To effectively analyze competitors, it's crucial to grasp their primary objectives. This understanding enables a company to anticipate a competitor's business moves and explore ways to influence their behavior. For instance, if a rival prioritizes profit margins, undercutting their products might not prompt a strong response. However, if a competitor aims for market share, they are likely to fiercely defend their position and cut prices to thwart new entrants.
- Competitor's Strategy: Companies must comprehend a competitor's strategy, considering their current performance and any publicly disclosed plans. This insight helps in formulating responses and strategic decisions based on the actions and directions taken by competitors.
- Competitor's Resources: Examining a competitor's resources is essential for predicting their future actions and responses to market dynamics. Identifying a competitor's strengths and weaknesses, akin to a SWOT analysis, assists in understanding their capabilities. It is also crucial to evaluate their ability to respond swiftly to market changes, as this can impact the feasibility of targeting them as competitors.
- Competitor's Assumptions: Understanding a competitor's assumptions about the market and their own business is pivotal. These assumptions influence their market capture strategies. For example, if past products in a market have failed, competitors may assume a similar fate for any new product. Challenging these assumptions can create opportunities for strategic advantage.
- Competitor Response Profile: Gathering comprehensive details about a competitor's objectives, strategy, resources, and assumptions allows the creation of a response profile. This profile outlines potential moves a competitor may make in response to a company's strategy, aiding in predicting and influencing their behavior. It covers both aggressive moves into new markets and defensive responses to protect existing market positions.
- Competitive Analysis Tools: Management experts recommend performing a formal SWOT analysis to assess a company's strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. Additionally, Michael E. Porter's Five Forces model helps evaluate industry competitiveness, guiding businesses to recognize forces that impact effectiveness and formulate strategic responses.
Porter's five forces
- Achieving greater volume through under-pricing the competition can lead to cost reduction via economies of scale. However, maintaining a healthy profit margin is essential, emphasizing the importance of lowering costs rather than just prices.
- In competitor analysis, companies should strive for differentiation in product or service quality. This entails studying various companies that have successfully established such distinctions.
- Companies must also attain supply or distribution leverage in competitor analysis. Targeting a market niche, particularly one overlooked by dominant industry players, can be effective. As companies expand, decisions may arise to discontinue servicing specific segments, not because the needs vanish but due to inefficiencies in providing for them efficiently.
- It is crucial to evaluate competitors by categorizing them into strategic groups based on how directly they compete for a share of the customer's spending. Detailed information on competitors or strategic groups includes their products or services, profitability, growth patterns, marketing objectives, assumptions, current and past strategies, organizational and cost structures, strengths and weaknesses, and the size of their business in sales.
- For global success, companies need to analyze current competitors and anticipate future competitive threats. New competitors may emerge from related product/market segments, those using associated technologies, or companies targeting the same market segment with unrelated products. The entry of new competitors is expected when profit margins are high, industry supply is insufficient, there are no major entry barriers, future growth potential exists, competitive rivalry is weak, and gaining a competitive advantage is feasible.
- Competitive analysis is integral to a company's marketing plan. It allows businesses to establish the uniqueness of their products or services, incorporating special features to attract the target market. In today's highly competitive market, strategic insight is necessary to gain and maintain a competitive advantage.
- While competitive analysis offers valuable insights, it faces criticism from some experts. Concerns include potential flaws and inaccuracies in the analysis leading to faulty business strategies, increased complexity due to diversified products and services, and a potential decline in internal innovation when excessively focused on competitors.
- To summarize, competitive analysis involves collecting and assessing information about a company's competitors, their practices, products, strengths, weaknesses, and business trends. This process allows a company to assess its market position, improve products, and refine marketing strategies. Competitive analysis provides an accurate view of competition, identifies areas for improvement, and helps in comparing products before making marketing and promotional decisions, ultimately saving both time and money.
FAQs on Analyzing Competition - Management Optional Notes for UPSC
| 1. What is competitor analysis? |  |
| 2. What are the components of competitor analysis according to Porter's five forces? |  |
| 3. How can competitor analysis benefit businesses? |  |
| 4. How can businesses gather information for competitor analysis? |  |
| 5. How often should businesses conduct competitor analysis? |  |



















