Anti Defection Law | Indian Polity for UPSC CSE PDF Download
Introduction
Recently, some of the sitting MLAs in the Manipur government defected to the opposition creating instability in the state's polity. This politics of defection in Manipur is not unique, there have been some other recent examples of defection in Karnataka, Madhya Pradesh, Arunachal Pradesh and Uttarakhand.
For a very long time, the Indian political system was impacted by political defections by members of the legislature. This situation brought about greater instability and chaos in the political system.
Thus, in 1985, to curb the evil of political defections, the 52nd constitution amendment act on anti-defection was passed and the 10th Schedule was added in the Indian Constitution.
However, the recent examples of defection in the Indian polity show that the law needs a relook in order to plug the loopholes and achieve a balance between the rights of legislators and interests of legislative stability.
Issues Associated With the Defection
- Subversion of electoral mandates: Defection is the subversion of electoral mandates by legislators who get elected on the ticket of one party but then find it convenient to shift to another, due to the lure of ministerial berths or financial gains.
- Affects the normal functioning of government: The infamous “Aaya Ram, Gaya Ram” slogan was coined against the background of continuous defections by the legislators in the 1960s. The defection leads to instability in the government and affects the administration.
- Promote horse-trading: Defection also promotes horse-trading of legislators which clearly go against the mandate of a democratic setup.
91st Constitution Amendment Act-2003
- It aimed at limiting the size of the Council of Ministers to debar defectors from holding public offices, and to strengthen the anti-defection law.
- Earlier, a defection by one-third of the elected members of a political party was considered a ‘merger’. The amendment changed it to at least two-thirds.
Kihota Hollohon vs. Zachilhu (1992)
- In the judgment, the Supreme Court clarified that the 10th schedule is constitutionally valid. It neither impinges upon the freedom of speech and expression nor subverts the democratic rights of elected members.
- It also upheld the sweeping discretion available to the Speaker in deciding cases of disqualification of MLAs.
(1) However, it also held that Presiding Officer’s decisions of disqualification shall be open to judicial review.
Challenges of Anti-Defection Law
- Against the true spirit of representative democracy: The anti-defection law seeks to provide a stable government by ensuring the legislators do not switch sides.
(1) However, this law also enforces a restriction on legislators from voting in line with their conscience, judgement and interests of his electorate. - Impedes legislative control on government: The anti-defection law impedes the oversight function of the legislature over the government, by ensuring that members vote based on the decisions taken by the party leadership.
(1) In short, if legislators are not able to vote on laws independently, they would not act as an effective check on the government.
(2) The Anti-Defection Law, in effect, dilutes the separation of powers between the Executive and the Legislature – and centralises power in the hands of the executives. - Role of presiding officer of the house: The law lays down that legislators may be disqualified on grounds of defection by the Presiding Officer of a legislature based on a petition by any other member of the House.
(1) However, there are many instances when presiding officers play a part with the vested interests of a political party/government in power.
(2) Also, the law does not specify a time period for the Presiding Officer to decide on a disqualification plea.
(3) The decision thus is sometimes based on the whims and fancies of the presiding officer. - Affects the debate and discussion: The Anti-Defection Law has created a democracy of parties and numbers in India, rather than a democracy of debate and discussion.
(1) In this way, it does not make a differentiation between dissent and defection and weaken the Parliamentary deliberations on any law.
Steps To Be Taken
- Rational use of the anti-defection law: Several experts have suggested that the law should be valid only for those votes that determine the stability of the government. e.g. passage of the annual budget or no-confidence motions.
- Advice of Election Commission: Various commissions including National Commission to review the working of the constitution (NCRWC) have recommended that rather than the Presiding Officer, the decision to disqualify a member should be made by the President (in case of MPs) or the Governor (in case of MLAs) on the advice of the Election Commission.
- Independent authority to deal with disqualification: Justice Verma in Hollohan judgment said that tenure of the Speaker is dependent on the continuous support of the majority in the House and therefore, he does not satisfy the requirement of such independent adjudicatory authority.
(1) Also, his choice as the sole arbiter in the matter violates an essential attribute of the basic feature.
(2) Thus, the need for an independent authority to deal with the cases of defection. - Promoting the principle of intra-party democracy: 170th Law Commission report underscored the importance of intra-party democracy by arguing that a political party cannot be a dictatorship internally and democratic in its functioning outside.
(1) Thus, the parties should listen to the opinions of the members and have discussions on the same. This would give the freedom of speech and expression to its members and promote inner-party democracy.
Conclusion
Though due to anti-defection law, political instability caused by the frequent and unholy change of allegiance on the part of the legislators of our country has been contained to a very great extent, yet there is a need for a more rationalised version of anti-defection laws which will help establish a truly representative democracy.
Direct Democracy V/s Representative Democracy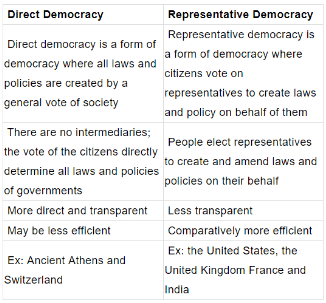
|
142 videos|780 docs|202 tests
|
FAQs on Anti Defection Law - Indian Polity for UPSC CSE
| 1. What is the purpose of the Anti Defection Law in India? |  |
| 2. How does the Anti Defection Law work in India? |  |
| 3. Can a member of parliament be disqualified under the Anti Defection Law? |  |
| 4. Are there any exceptions or safeguards in the Anti Defection Law? |  |
| 5. What are the penalties for violating the provisions of the Anti Defection Law? |  |
















