Article | English Grammar Basic - Class 10 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| What is an Article? |

|
| Types Of Articles |

|
| Use Of ‘A’ |

|
| Use of ‘An’ |

|
| Use of ‘The’ |

|
| Additional Information Regarding the Use of Articles |

|
| Some Assorted Examples |

|
What is an Article?
- An article is a word that precedes a noun/s or noun equivalents. When an article is inserted before any noun, it informs us whether the noun in that sentence or phrase is specific or generic.
- There are three articles in the English language: a, an, and the, each of which is an important part of the phrase.
- Example: After I went to the party, I fell ill.
Here, ‘the’ specifies the party.
Types Of Articles
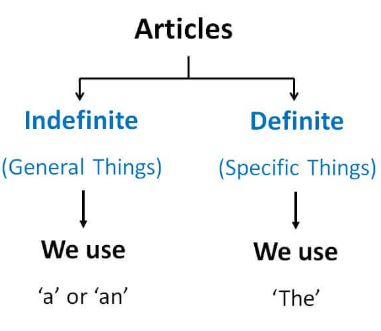
There are two kinds of articles:
- Indefinite article: A/An
- Definite article: The

Indefinite Article
There are two indefinite articles—‘a’ and ‘an’—and their usage is determined by the first letter of the word. The article ‘a’ is used when the following word begins with a consonant. If the following word begins with a vowel, ‘an’ is used. The indefinite article indicates that a word is being considered in general rather than specifically.
As,
- A boy means any boy.
- A teacher means any teacher.
Use Of ‘A’
1. If a consonant is the first letter of a countable singular common noun, we use ‘A’ before it.
Examples :
- Sakshi has book —wrong
Sakshi has a book —correct - I met girl there —wrong
I met a girl there —correct
2. ‘A’ is used before some indefinite numbers.
Examples :
- a lot of
- a large number of
- a quarter of
3. ‘A’ can be used before some indefinite collective numbers.
Example :
- a team of a gang of
- a flock of a herd of
- a swarm of a panel of
4. If an adjective is followed by a singular noun, we use ‘A’ before that adjective.
Examples :
- Madhuri is beautiful girl — wrong
Madhuri is a beautiful girl — correct
↓ ↓
Adjective Noun
But,
Reema has a good health — wrong
Reema has good health — correct
↓
Adjective
So,
Whenever a noun is not used after adjective we do not use article before it.
As,
proper respect
↓ ↓
Adjective Adjective
In a fit
↓
Adjective
In a temper
↓
Adjective
5. ‘A’ is used in place of ‘per’.
Examples :
- Petrol costs twenty-five rupees a litre
6. To show the whole class of common noun, we can use ‘A’ before a common noun.
Examples :
- A bird has two wings.
All birds have two wings.

- A monkey has a tail.
All monkeys have tails.
But, common nouns like Man and Woman do not follow the above rule.
As,
- A man is mortal. — wrong
- Man is mortal. — correct
7. If we put the article ‘A’ before a plural number, the forthcoming noun becomes singular.
Examples :
- A five-day match.
Five days match. - A ten-mile walk.
Ten miles walk. - A fifteen-man committee.
Fifteen men committee.
8. ‘A' is used before these words because they have the sound of a consonant in their first letter.
Examples :
- A university.
- A union.
- A unique film.
- A European.
A one-rupee note. - A one-eyed person.
- A one-act play.
- A one-sided decision.
9. If noun is placed after such, quite, rather, how, etc., we use ‘A’ before that noun.
Examples :
- I have never seen such girl in my life. — wrong
I have never seen such a girl in my life. — correct - Roma is quite dull girl. —wrong
Roma is quite a dull girl. —correct
10. If these words are used in singular, we use ‘A’ before them. Noise, Lie, Hole, Headache etc.
Examples :
- The pupil makes noise in the class. — wrong
The pupil makes a noise in the class. — correct - Joydeb always tells lie. — wrong
Joydeb always tells a lie. — correct
Use of ‘An’
1. Vowel starting nouns or words take use of ‘An’ before them
Examples :
- Siddharth is intelligent boy. —wrong
Siddharth is an intelligent boy. —correct - The President made appeal for the poor. —wrong
The President made an appeal for the poor. —correct
2. An is used before some H starting words in which H is not pronounced
Examples :
- An honest man
- An hour
- An heir
- An honourable person
- An homage to the dead
3. If H, L, M, N, F, R, S, X are the first letters of abbreviations, we use An before them.
Examples :
- An M.A.
- An L.L.B. student
- An F.R.C.S. girl
- An N.C.C. team
- An H.S. school
- An X-ray clinic
Definite Articles
“The” is the article that falls into the category of definite articles. It restricts the meaning of a noun to a single thing. Singular, multiple, and uncountable nouns use the definite article. “The” is used when a noun needs to be associated with something specific.
Use of ‘The’
The following rules are applied for using The before definite noun.
1. Definite article The is used before a noun if it is used for specific nouns that are defined by a relative clause
Examples :
- She is a girl who sings ghazal. —wrong
She is the girl who sings ghazal. —correct - This is a painting that was displayed in the museum. — wrong
This is the painting that was displayed in the museum. — correct
2. The is placed after one of, each of, neither of, either of, none of, everyone of, etc.
Examples :
- One of boys is absent. —wrong
One of the boys is absent. —correct - Neither of girls is intelligent. —wrong
Neither of the girls is intelligent. —correct - Either of men was present. —wrong
Either of the men was present. —correct
3. The is used before the name of the commission.
Examples :
- Verma Commission is still functioning. —wrong
- The Verma Commission is still functioning. —correct
4. If adjective is followed by proper noun use The before that adjective.
Examples :
- We love immortal Gandhi. —wrong
- We love the immortal Gandhi. —correct
↓ ↓
Adjective Proper Noun
5. Whenever common noun is used as adjective it is preceded by definite article The.
Examples :
- When Ritesh found a boy, the father came in him.
↓
the love of father - When Meeta saw a girl, the mother came in her.
↓
the love of mother
Additional Information Regarding the Use of Articles
Using "Some" for Unspecified, Limited Amounts
The word some is used when referring to an unspecified but limited amount of a countable or uncountable noun.
- My cousin was seeking some advice from a counsellor. (Not general advice, but a specific amount.)
- I would love some coffee right now. (Not coffee in general, but a particular quantity.)
- We might get rain tomorrow. Some rain would be good for the crops. (A certain amount of rain, not rain in general.)
- There are some drops of water on the table. (A limited number, but more than one.)
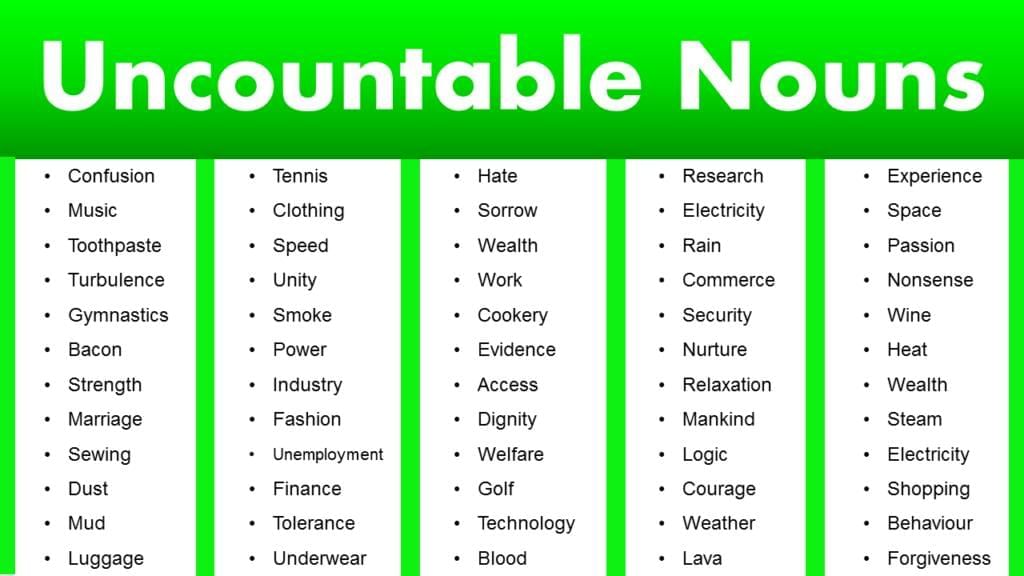
Common Noncount Nouns
Noncount nouns are those that usually cannot be counted individually. Some common examples include:
- Food & Drink Items: bacon, beef, bread, butter, cereal, cheese, chocolate, coffee, corn, cream, fish, flour, fruit, ice cream, lettuce, meat, milk, oil, pasta, rice, salt, spinach, sugar, tea, water, wine, yoghurt.
- Nonfood Substances: air, cement, coal, dirt, gasoline, gold, paper, petroleum, plastic, rain, silver, snow, soap, steel, wood, wool.
- Abstract Nouns: advice, anger, beauty, confidence, courage, employment, fun, happiness, health, honesty, information, intelligence, knowledge, love, poverty, satisfaction, truth, wealth.
- Fields of Study: history, mathematics, biology, etc.
- Sports: soccer, football, baseball, hockey, etc.
- Languages: Chinese, Spanish, Russian, English, etc.
- Other Common Noncount Nouns: clothing, equipment, furniture, homework, jewelry, luggage, lumber, machinery, mail, money, news, poetry, pollution, research, scenery, traffic, transportation, violence, weather, work.
Using "The" with Geographical Names
Geographical names can be tricky because some require the while others do not.
Use "The" With:
- United Countries: the United Arab Emirates
- Large Regions & Deserts: the Thar Desert
- Bodies of Water (Oceans, Seas, Gulfs, Canals, Rivers): the Nile River
- Mountain Ranges & Island Groups: the Aleutians
Do Not Use "The" With:
- Streets & Parks: Nehru Park
- Cities, States, Counties: San Francisco
- Most Countries & Continents: Japan
- Bays, Single Lakes, Single Mountains, Single Islands: San Francisco Bay, Mt. Everest
Some Assorted Examples
Example 1: Kamal has a good health because he takes a nutritious breakfast every morning. —wrong
Kamal has good health because he takes a nutritious breakfast every morning. —correct
Example 2: One of my brothers has given the very accurate answer to the question. —wrong
One of my brothers has given a very accurate answer to the question. —correct
Example 3: It being nice morning, I along with my wife decided to go for a walk. —wrong
It being a nice morning, I along with my wife decided to go for a walk. —correct

Example 4: I do not want to buy a book because, I have to take either a pencil or doll at present. —wrong
I do not want to buy a book because, I have to take either a pencil or a doll at present. —correct
Example 5: Sohon is not only a laborious boy, but also a intelligent student. —wrong
Sohon is not only a laborious boy, but also an intelligent student. —correct
Example 6: The Air India announced that all the flights of that week to Nepal would be stopped because of security lapse which caused the hijack. —wrong
Air India announced that all the flights of that week to Nepal would be stopped because of security lapse which caused the hijack. —correct
Example 7: The gold is a precious metal used in jewellery. — wrong
Gold is a precious metal used in jewellery. — correct
Example 8: The rose is the sweetest of all flowers, so I take it with me whenever I go out. —wrong
Rose is the sweetest of all flowers, so I take it with me whenever I go out. —correct
Example 9: Which is the more precious, silver or gold, as the latter is the more useful than former. —wrong
Which is more precious, silver or gold, as the latter is more useful than the former. —correct
Example 10: The water of well is so dirty that no one is ready to drink it without purification. —wrong
The water of the well is so dirty that no one is ready to drink it without purification. —correct
|
20 videos|143 docs|18 tests
|
FAQs on Article - English Grammar Basic - Class 10
| 1. What is an article in English grammar? |  |
| 2. What are the types of articles? |  |
| 3. Can you provide examples of definite articles? |  |
| 4. Can you provide examples of indefinite articles? |  |
| 5. How are articles used in sentences? |  |





















