UPSC Exam > UPSC Notes > Medical Science Optional Notes for UPSC > Assessment of Immune Function, Monoclonal Antibodies
Assessment of Immune Function, Monoclonal Antibodies | Medical Science Optional Notes for UPSC PDF Download
Assessment of Immune Function
- Historical background and clinical examination
- Standard diagnostic procedures
- Complete Blood Picture (CBP)
- Quantitative levels of Immunoglobulins (Ig)
- Assessment of B-cell function
- Evaluation of naturally occurring antibodies for diseases such as rubella, influenza, tetanus, and diphtheria
- Analysis of response to immunization for conditions like typhoid, polio, CDT, and HBV
- Evaluation of T-cell function i. Skin tests for PPD, Candida, trichophyton, and tetanus toxoid ii. Assessment of contact sensitivity to dinitrochlorobenzene iii. Chest X-ray in children to observe the thymus shadow
- Complement assay
- Individual component assays are challenging, hence the use of total haemolytic complement CH50
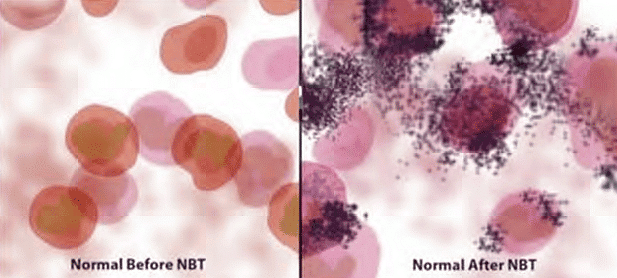
- Assessment of phagocytic function using the Nitroblue tetrazolium test
- Stimulation tests and induced lymphokine assays through lymphocyte cell cultures
- Mixed lymphocyte cultures
- Utilized for compatibility testing in transplant procedures
- Involves incubating one set of irradiated white blood cells with a second set
- A blastogenic transformation occurs if there is sufficient antigenic discrepancy between the two cell sets
- This can clinically manifest as either graft rejection or graft versus host disease
Question for Assessment of Immune Function, Monoclonal AntibodiesTry yourself: What is the purpose of evaluating the levels of Immunoglobulins (Ig) in the assessment of immune function?View Solution
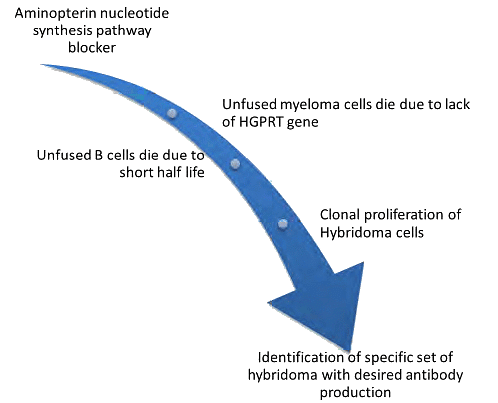
Monoclonal Antibody Production by Hybridoma Technology
Definition of Monoclonal Antibodies
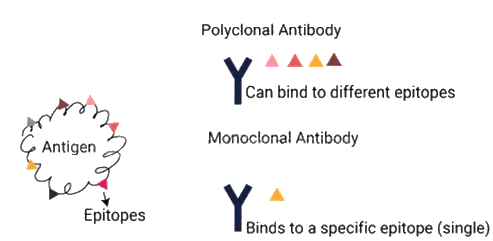
- Infections lead to the production of antibodies with multiple epitopes or antigenic determinants, generating distinct clones of lymphocytes.
- As a consequence, antisera comprises immunoglobulins of various classes, each with specificities against different epitopes of the antigen.
- Antibodies originating from a single clone and targeting a solitary antigenic determinant are termed monoclonal antibodies.
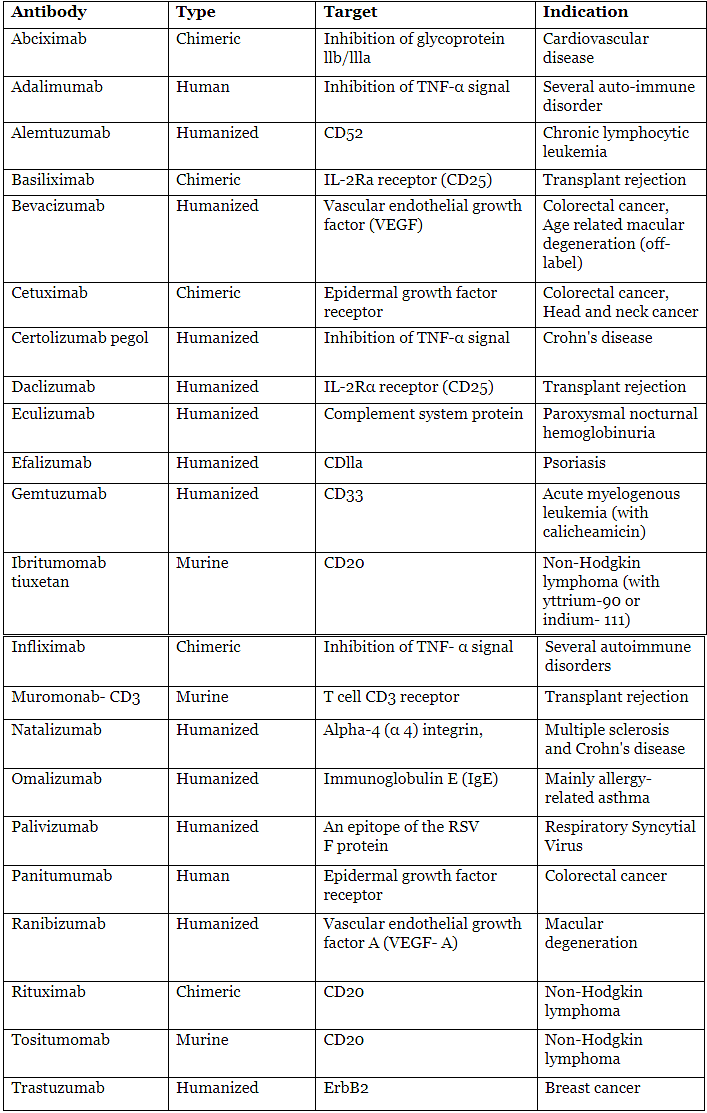
- Monoclonal antibodies find utility in diagnostic and research methodologies.
Note: In 1975, Kohler and Milstein devised a brilliant technique for the extensive production of monoclonal antibodies, earning them the Nobel Prize in Medicine in 1984.

- Monoclonal antibodies (mAb or moAb) are uniform immunoglobulins produced from a solitary B-cell clone.
- These antibodies specifically identify distinct epitopes or binding sites on a singular antigen.
- The key distinction between monoclonal and polyclonal antibodies lies in their origin: monoclonal antibodies derive from a single B-cell clone, targeting a single epitope.
- When an animal is immunized with an antigen, the B cell response is typically polyclonal. However, by selecting a specific B-cell clone and amplifying it, a stock of monoclonal antibodies can be created.

Question for Assessment of Immune Function, Monoclonal AntibodiesTry yourself: What is the key distinction between monoclonal and polyclonal antibodies?View Solution
The document Assessment of Immune Function, Monoclonal Antibodies | Medical Science Optional Notes for UPSC is a part of the UPSC Course Medical Science Optional Notes for UPSC.
All you need of UPSC at this link: UPSC
|
7 videos|219 docs
|
FAQs on Assessment of Immune Function, Monoclonal Antibodies - Medical Science Optional Notes for UPSC
| 1. What is immune function and why is it important for our overall health? |  |
Ans. Immune function refers to the ability of the immune system to defend the body against pathogens and other harmful substances. It plays a crucial role in maintaining overall health by identifying and neutralizing potential threats. Without proper immune function, the body becomes more susceptible to infections and diseases.
| 2. What is monoclonal antibody production and how does it contribute to the field of immune function assessment? |  |
Ans. Monoclonal antibody production refers to the process of creating identical antibodies that specifically target a particular antigen. These antibodies are produced using hybridoma technology, where hybrid cells, called hybridomas, are created by fusing a specific antibody-producing B-cell with a cancerous myeloma cell. This technique allows for the production of large quantities of highly specific and uniform antibodies, which are essential in various diagnostic and therapeutic applications for assessing immune function.
| 3. How does hybridoma technology work in the production of monoclonal antibodies? |  |
Ans. Hybridoma technology involves the fusion of a specific antibody-producing B-cell with a cancerous myeloma cell. The resulting hybrid cell, known as a hybridoma, possesses the ability to produce large amounts of a specific antibody. This technology utilizes the immortal nature of myeloma cells, which can divide indefinitely, and the specificity of B-cells, which produce antibodies against specific antigens. The hybridoma cells can be cultured in the laboratory to produce monoclonal antibodies with consistent characteristics.
| 4. What are the potential applications of monoclonal antibodies in immune function assessment? |  |
Ans. Monoclonal antibodies have various applications in immune function assessment. They can be used in diagnostic tests to detect specific antigens or antibodies, aiding in the identification of infections or autoimmune diseases. Monoclonal antibodies can also be used in immunotherapy, where they are designed to target and neutralize specific cells or molecules involved in immune dysfunction. Additionally, they play a crucial role in research, allowing scientists to study immune responses and develop new treatments for immune-related disorders.
| 5. Are there any limitations or challenges in the production and use of monoclonal antibodies for immune function assessment? |  |
Ans. While monoclonal antibodies have revolutionized immune function assessment, there are some limitations and challenges associated with their production and use. One challenge is the potential for the immune system to recognize and mount an immune response against the administered monoclonal antibodies, leading to reduced efficacy or adverse reactions. There can also be difficulties in producing monoclonal antibodies that accurately represent the diverse immune responses seen in different individuals. Additionally, the cost of production and the need for specialized facilities and expertise can limit their widespread use in certain settings.

|
Explore Courses for UPSC exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
Related Searches
















