Atoms & Molecules Summary Class 9 Science
Introduction
- Around 500 B.C., Indian philosopher Maharishi Kanad, postulated the theory if we go on dividing matter (padarth), we will obtain smallest particle beyond which further division can't be possible which is known as 'parmanu'.

- Ancient Greek philosophers – Democritus and Leucippus called these particles atoms.
- Antoine L. Lavoisier laid the foundation of chemical sciences by establishing two important laws of chemical combination.
Laws of Chemical Combination
- This law established after the experiments by Lavoisier and Joseph L. Proust.
- The chemical reaction between two or more substances give rise to products which is governed by certain laws called Laws of Chemical Combination.
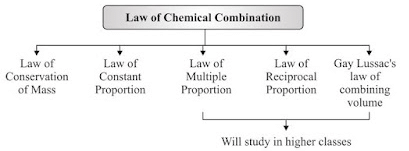
- Law of Conservation of Mass
- During a chemical reaction, the total mass of reactants will be equal to the total mass of the products.
- Mass can neither be created nor destroyed in a chemical reaction.
- Example: A (reactant) + B (reactant) → AB (product)
mass of A + mass of B = mass of AB
- Law of Constant Proportions
- In a chemical reaction, compounds always contain the same elements present in definite proportions by mass irrespective of their source.
- It was given by Lavoisier.
- For example:
(i) 18 gm of H2O = 2 gm of hydrogen + 16 gm of oxygen
⇒ mass of hydrogen/mass of oxygen = 2/16 = 1/8
(ii) 36 gm of H2O = 4 gm of hydrogen + 32 gm of oxygen
⇒ mass of hydrogen/mass of oxygen = 4/32 = 1/8
(iii) 9 gm of H2O = 1 gm of hydrogen + 8 gm of oxygen
⇒ mass of hydrogen/mass of oxygen = 1/8
This verifies law of constant proportions as the ratio of mass of hydrogen to oxygen is always same.
Dalton's Atomic Theory
- According to Dalton’s atomic theory, all matter, whether an element, a compound or a mixture is composed of small particles called atoms.
- Six Postulates of Dalton's atomic theory:
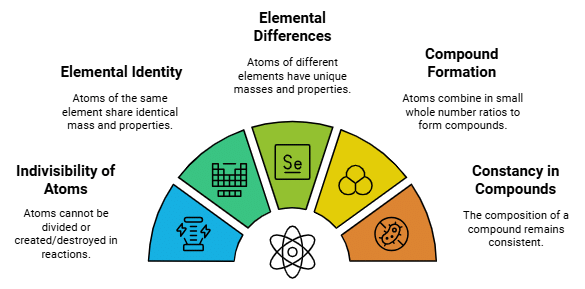
- All matter is made of very tiny particles called atoms.
- Atoms are indivisible particles, which cannot be created or destroyed in a chemical reaction.
- Atoms of a given element are identical in mass and chemical properties. (Law of conservation of mass)
- Atoms of different elements have different masses and chemical properties.
- Atoms combine in the ratio of small whole numbers to form compounds. (Law of constant proportion)
- The relative number and kinds of atoms are constant in a given compound.
Atoms
- Atoms are building blocks of all matter.
- According to modern atomic theory, an atom is the smallest particle of an element which takes part in chemical reaction.
- Atoms are very small and which can’t be seen even through very powerful microscope.
- Atomic radius is measured in nanometres.
Nanometres = 10-9 m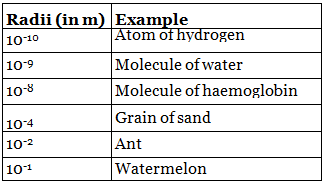
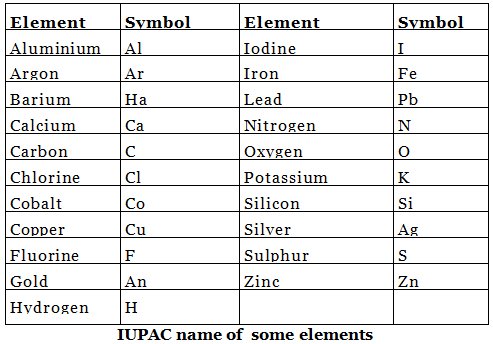
- Modern day symbols of Elements
- Dalton was the first scientist to use the symbols for elements.
- Berzilius suggested that the symbols of elements should be made from one or two letters of the name of the element.
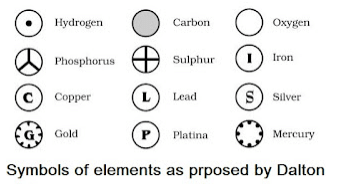
- The name copper was taken from Cyprus, a place from where it was found for first time.
- Now, IUPAC (International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry) approves names of elements.
- The first letter of a symbol is always written as a capital letter (uppercase) and the second letter as a small letter (lowercase). For example: hydrogen (H), aluminium (Al), cobalt (Co).
- Some other symbols have been taken from the names of elements in Latin, German or Greek. For example: Fe from its Latin name ferrum, sodium is Na from natrium, potassium is K from kalium.
- Atomic Mass
- Dalton’s atomic theory proposed the idea of atomic mass which explained the law of constant proportions so well.
- The mass of an atom of an element is called its atomic mass.
- In 1961, IUPAC have accepted ‘atomic mass unit’ (u) to express atomic and molecular mass of elements and compounds.
- The atomic mass unit is defined as the quantity of mass equal to 1/12 of mass of an atom of carbon-12.
1 amu or u = 1/12 × Mass of an atom of C12
1 u = 1.66 × 10-27 kg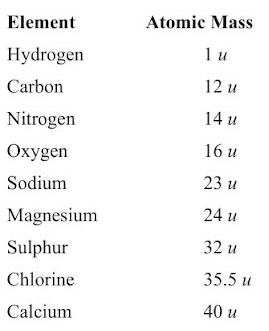
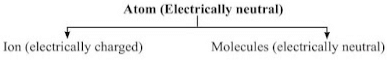
- Atom existence
- Atoms of most of the elements are very reactive and does not exist in free state.
- Only the atoms of noble gases (such as He, Ne, Ar, Kr, Xe and Rn) are chemically unreactive and can exist in the free state as single atom.
- Atoms of all other elements combine together to form molecules or ions.
Molecules
- A molecule is in general a group of two or more atoms that are chemically bonded together
- A molecule is the smallest particle of matter (except element) which is capable of an independent existence and show all properties of that substance.
- Examples: ‘H2O’ is the smallest particle of water which shows all the properties of water.
- A molecule may have atom of same or different elements, depending upon this, molecule can be categorized into two categories:
(i) Homoatomic molecules (containing atom of same element)
Examples: H2, O2, O3, S8, P4 etc.
(ii) Heteroatomic molecules or compounds (containing atoms of different elements)
Examples: H2O, CO2, NaCl, CaCO3 etc.
Atomicity
→ The number of atoms present in one molecule of an element is called its atomicity.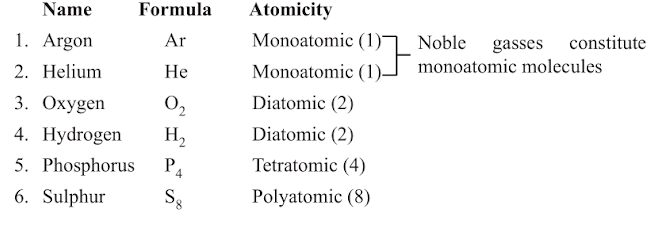
Chemical Formulae
- It is the symbolic representation of the composition of a compound.
- Characteristics of chemical formulae
- The valencies or charges on ion must balance.
- When a compound is formed of metal and non-metal, symbol of metal comes first. E.g., CaO, NaCl, CuO.
- When polyatomic ions are used, the ions are enclosed in brackets before writing the number to show the ratio. E.g., Ca(OH)2 , (NH4)2SO4
- Rules for writing chemical formulae
- We first write symbols of elements which form compound.
- Below the symbol of each element, we should write their valency.
- Now cross over the valencies of combining atoms.
- With first atom, we write the valency of second atom (as a subscript).
- With second atom, we write the valency of first atom (subscript).
Examples: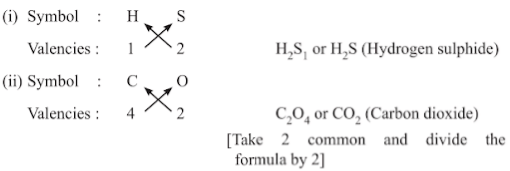 (iii) For Hydrochloric acid (Hydrogen chloride)
(iii) For Hydrochloric acid (Hydrogen chloride)
(iv) For Carbon tetrachloride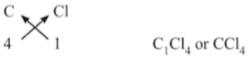
(v) For Magnesium chloride
(vi) For aluminium oxide
(vii) For Calcium oxide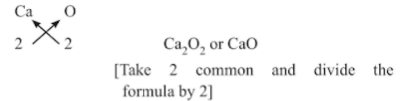
Molecular Mass
- It is the sum of atomic masses of all the atoms in a molecule of that substance.
Example: Molecular mass of H2O = 2 × Atomic mass of Hydrogen + 1 × Atomic mass of Oxygen
So, Molecular mass of H2O = 2 × 1 + 1 × 16 = 18 u
Formula Unit Mass
- It is the sum of atomic mass of ions and atoms present in formula for a compound.
Example: In NaCl,
Na = 23 a.m.u.
Cl = 35.5 a.m.u.
So, Formula unit mass = 1×23 + 1×35.5 = 58.5 u
Ions
- An ion may be defined as an atom or group of atoms having positive or negative charge.
- Some positively charged ions : Na+ , K+, Ca2+ , Al3+
- Some negatively charged ions : Cl- (chloride ion), S2- (sulphide ion), OH- (hydroxide ion), SO42- (sulphate ion)
- We can classify ions in two types:
(i) Simple ions
Mg2+ (Magnesium ion)
Na+ (Sodium ion)
Cl- (Chloride ion)
Al3+ (Aluminium ion)
(ii) Compound ions
NH4+ (Ammonium ion)
CO32- (Carbonate ion)
SO42- (Sulphate ion)
OH- (Hydroxide ion)
- We can classify ions in two types:
- Chemical Formulae of Ionic Compounds (Polyatomic)
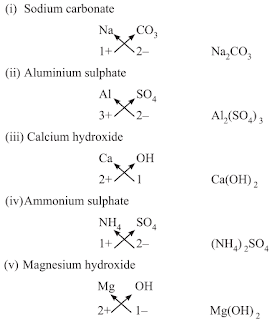
Mole Concept
- A group of 6.022×1023 particles (atoms, molecules or ions) of a substance is called a mole of that substance.
- 1 mole of atoms = 6.022×1023 atoms
- 1 mole of molecules = 6.022 × 1023 molecules
Example, 1 mole of oxygen = 6.022×1023 oxygen atoms
Note: 6.022×1023 is Avogadro Number (L).
- 1 mole of atoms of an element has a mass equal to gram atomic mass of the element.
Molar Mass
- The molar mass of a substance is the mass of 1 mole of that substance.
- It is equal to the 6.022×1023 atoms of that element/substance.
Examples:
(a) Atomic mass of hydrogen (H) is 1 u. Its molar mass is 1 g/mol.
(b) Atomic mass of nitrogen is 14 u. So, molar mass of nitrogen (N) is 14 g/mol.
(c) Molar mass of S8 = Mass of S×8 = 32×8 = 256 g/mol
(d) Molar mass of HCl = Mass of H + Mass of Cl = 1 = 35.5 = 36.5 g/mol
Important Formulae
(i) Number of moles (n) = Given mass / Molar mass = m/M
(ii) Number of moles (n) = Given number of Particles / Avogadro's number
n = N/N0
(iii) m/M = N/N0
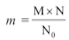
(iv) Percentage of any atom in given compound 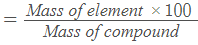
|
31 videos|126 docs|52 tests
|
FAQs on Atoms & Molecules Summary Class 9 Science
| 1. What are atoms and how do they differ from molecules? |  |
| 2. What is the law of conservation of mass in relation to chemical reactions? |  |
| 3. How do you calculate the molar mass of a compound? |  |
| 4. What is the difference between an ionic bond and a covalent bond? |  |
| 5. What is Avogadro's number and why is it important in chemistry? |  |

















