Awareness in Field of IT & Computers- 1 | Science & Technology for UPSC CSE PDF Download
This article talks about, Awareness in the field of IT and Computers and web-based terminologies and concepts in news. Information and Communication Technology & Computers are important areas in science and technology syllabus for the UPSC exam.
This is the second article of the IT and Computers series so first of all, read our first article – Information and Communication Technology.
Awareness in the field of IT and Computers
VOIP (Voice Over Internet Protocol)
VOIP is IP-enabled voice calling technology over the internet. Example: Skype, Yahoo messenger, MSN messenger.
It requires broadband connectivity to make a call along with IP enables devices like Computers, smartphones, etc.
The voice is converted into digital packets and transmitted to destination over packet switched network.
Some of the advantages of VOIP are:
- The cost of calling is cheaper than a normal phone.
- No need to carry a dedicated device for calling if you just have a computer with you.
- Its uses existing LANs so need for dedicated wiring features and hence reduces the complexity of calling.
- Call anywhere anytime; do not worry about Roaming Features and Cost.
- One payment, two services: voice calling and broadband data usage
Disadvantages of VOIP are:
- It is dependent on broadband network connectivity, no internet no calling.
- The quality of voice depends on broadband bandwidth and speed.
- Power shortage can hamper VOIP calling as it’s totally dependent on power enabled devices.
- No emergency calling features like normal and Smartphone.
- The highest disadvantage of VOIP is security. It’s really tough to trace the source and identity if an imposter is at work.
- Threats like phishing, spoofing and sniffing, call tampering, etc. is very common.
3G vs 4G
- 3G was completely a new innovation that transformed mobile telephony.
- For the first time, it provided voice and data connectivity on a single network.
- The true sense of smartphones came into existence by enabling data connectivity.
- The development accelerated new ideas like e-learning, e-governance, etc.
- It was also an improvement in bandwidth and speed of communication.
- 4G is a new technology highly concentrated on bandwidth enhancement and improved speed further. It will take 3G to next level.
- There are 2 existing technologies in 4G: 4G LTE and 4G WiMAX.
- In a nutshell, the difference between 3G and 4G is its difference in SPEED.
4G LTE vs 4G WIMAX
- LTE stands for Long Term Evolution. It’s a first-generation 4G technology termed as “true 4G”.
- WiMAX stands for Worldwide Interoperability for Microwave Access.
- They differ in their bandwidth; LTE has higher bandwidth than WiMAX.
- LTE is compatible with the existing network but for WiMAX, we need an altogether new network.
- The cost of installation of LTE is more than WiMAX.
- Overall LTE is gaining popularity and hopes to exist 4G technology in coming years.
WIMAX
It is a wireless industry coalition dedicated to the advancement of IEEE 802.16 standards for broadband wireless access (BWA) networks.
- WiMAX can provide at-home or mobile Internet access across whole cities or countries. In many cases, this has resulted in competition in markets that typically only had access through an existing incumbent DSL (or similar) operator.
- Additionally, given the relatively low costs associated with the deployment of a WiMAX network (in comparison with 3G, HSDPA, xDSL, HFC, or FTTx), it is now economically viable to provide last-mile broadband Internet access in remote locations.
- WiMAX is competing with the 3rd Generation Partnership Project (3GPP)’s Long-Term Evolution (LTE) in the 4G market.
IEEE
IEEE 802.16 is a series of wireless broadband standards written by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE).
The IEEE Standards Board established a working group in 1999 to develop standards for broadband for wireless metropolitan area networks.
The Workgroup is a unit of the IEEE 802 local area network and metropolitan area network standards committee.
4G vs 5G
The next (5th) generation wireless network will address the evolution beyond mobile internet to massive IoT (Internet of Things) for the horizon 2019/2020. The main evolution compared with today’s 4G and 4.5G (LTE advanced) is that beyond data speed improvements, new IoT and critical communication use cases will require new types of improved performance. For example, “low latency” is what provides real-time interactivity for services using the cloud: this is key to the success of self-driving cars for example. Also, low power consumption is what will allow connected objects to operate for months or years without the need for human assistance.
Unlike current IoT services that make performance trade-offs to get the best from current wireless technologies (3G, 4G, WiFi, Bluetooth, Zigbee, etc…), 5G networks will be designed to bring the level of performance needed for massive IoT. It will enable a perceived fully ubiquitous connected world.
5G Technology
5G networks are the next generation of mobile internet connectivity, offering faster speeds and more reliable connections on smartphones and other devices than ever before. Combining cutting-edge network technology and the very latest research, 5G should offer connections that are multitudes faster than current connections, with average download speeds of around 1GBps expected to soon be the norm.
- The next-generation telecom networks (5G) will hit the market by 2020. Beyond just speed improvements, 5G is expected to unleash a massive IoT ecosystem where networks can serve communication needs for billions of connected devices, with the right trade-offs between speed, latency, and cost.
NGMN Alliance or Next Generation Mobile Networks Alliance define 5G network requirements as:
- Data rates of several tens of Mb/s should be supported for tens of thousands of users.
- 1 Gbit/s to be offered, simultaneously to tens of workers on the same office floor.
- Several hundreds of thousands of simultaneous connections to be supported for massive sensor deployments.
- Spectral efficiency should be significantly enhanced compared to 4G.
- Coverage should be improved.
- Signaling efficiency enhanced.
- Latency should be significantly reduced compared to LTE.
Next Generation Mobile Networks Alliance feels that 5G should be rolled out by 2020 to meet business and consumer demands. In addition to simply providing faster speeds, they predict that 5G networks will also need to meet the needs of new use-cases such as the Internet of Things as well as broadcast-like services and lifeline communications in times of disaster.
3GPP has set an early revision, Non-Standalone release of 5G called New Radio (NR). It will be deployed in two ways, Mobile and Fixed Wireless. The specification is subdivided into two frequency bands, FR1 (<6 GHz) and FR2 (mmWave) respectively.
LI FI Technology: Light Fidelity
As we all know that light reaches everywhere. Imagine if certain information is to be passed using light as a medium. Not only will the communication get fast but also the possibilities coming with it. Such a technique of using light as a medium is dubbed as the Li-Fi.
What is Wi-Fi?
- Wi-Fi stands for Wireless Fidelity.
- It uses a 2.4 to 5 GHz radiofrequency to deliver wireless Internet access around our homes, schools, offices, and in public places.
Main problem with the Wi-Fi
- Bandwidth is typically limited to 50-100 megabits per second (Mbps) today using the IEEE802.11n standard.
- It works fine with many of the internet connections. But it is unable to deliver High Definition Movies, music libraries, or video games.
- With the recent increase in the use of cloud computing (where you store your information on a certain web server & not on your local disk), Wi-Fi is not going to be useful in the future as it will not be able to cater to the need of the increasing bandwidth & speed.
Other Problems with the Radio Spectrum
- Capacity (Costly & Expensive. Less bandwidth compared to other spectrums. Insufficient spectrum for increasing data)
- Efficiency (millions of base stations consume a huge amount of energy)
- Availability (Available within the range of Base Stations. Limited Availability. Unavailable in aircraft)
- Security (Less secure. It passes through walls)
Components of Electromagnetic Spectrum–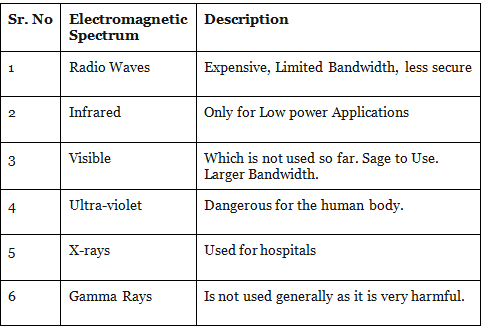
What is Li-Fi?
- Li-Fi is the latest communication technology that can transmit data using the spectrum of visible light.
- Other names for Li-Fi: Optical Wireless technologies / Visible Light Communication (VLC) but mostly called Li-Fi (Light Fidelity)
- Speed possible to Achieve: 10 Gbit/S (Giga bit per second). It is around 250 times faster than “superfast” broadband.
- The name “Li-Fi” was first coined by Edinburgh University’s Prof. Harald Hass in 2001.
How Li-Fi Technology works?
- It works by sending data over the light.
- For this purpose, a LED (Light Emitting Diode) light bulb, anyone at all, can be flicked on and off in order to be able to generate signals. A proper Light Receiver is made for receiving the LED signals.
- The LED bulb will hold a microchip that will do the job of processing the data.
- The light intensity can be manipulated to send data by tiny changes in amplitude.
- Properties of LED: (Fundamental property of Li-Fi):
- Intensity can be modulated into very high speeds and varying amplitudes.
- LED can be switched on and off with a very high speed.
- The question that comes to mind is that why would someone sit below a flickering light bulb? But this is not the thing. The technology is focusing on making sure that the light bulb is flickered up to billions of times a second! At that rate, the human eye simply cannot notice the light bulb being flicked on and off.
- The LIFI product consists of 4 primary sub-assemblies: Bulb, RF power amplifier circuit (PA), Printed circuit board (PCB) & Enclosure
- The PCB controls the electrical inputs and outputs of the lamp and houses the microcontroller used to manage different lamp functions.
- An RF (radio-frequency) signal is generated by the solid-state PA and is guided into an electric field about the bulb. The high concentration of energy in the electric field vaporizes the contents of the bulb to a plasma state at the bulb’s center; this controlled plasma generates an intense source of light. All of these sub-assemblies are contained in an aluminum enclosure.
Infrared Rays in remote control of TV
- Single data stream
- 10,000 or 20,000 bits per second
- Not usable for video streaming
Why Li-Fi
- For increasing Communication speed
- For increasing Flexibility
- For increasing Usability
- Reduced cost
- Greater efficiency
- It uses LED instead of bulbs & hence is indirectly helping the environment.
Drawback of Li-Fi
- The data receiver would have to be in sight of the transmitter-bulb as visible light does not penetrate solid materials. (Note: Some experts are considering it as an advantage as the hackers won’t be able to hack the Li-Fi network without being in sight.
- The presence of Light is required.
Difference between Wi-Fi & Li-Fi
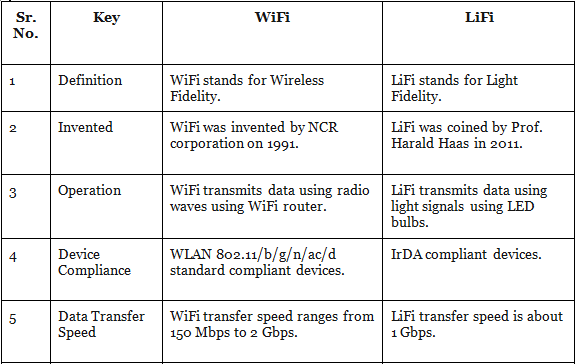
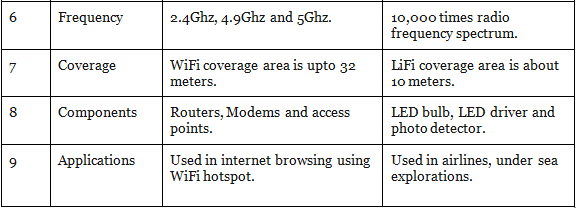
Li-Fi and Wi-Fi
- The appearance of the Li-Fi cannot wipe off the need for Wi-Fi.
- Li-Fi is complementary.
Advantages of use of Visible Light over Radio Waves
- Visible light is more plentiful than radio waves. (more bandwidth)
- Visible light can achieve far greater data density.
- Can be used underwater without radio interference because salt conducts electricity
- Transmission can be blocked by walls so there is less risk for data leaking
- Can be safely used on planes because it does not interfere with radio equipment.
Uses of Li Fi
- It can be used in Hospitals where Radio Frequency signals are a threat to the medical equipment present in the hospital.
- It can be used in Mobiles to transfer data speedily.
- In Radio Frequency Restricted Environments
- In vehicles and traffic lights, reducing accidents and traffic congestion
- Street lamps (as free access points)
- In Aircraft cabins.
Spectrum Auction
What is Spectrum?
- The word spectrum refers to a collection of various types of electromagnetic radiations of different wavelengths.
- Spectrum or airwaves are the radio frequencies on which all communication signals travel.
- In India, the radio frequencies are being used for different types of services like space communication, mobile communication, broadcasting, radio navigation, mobile satellite service, aeronautical satellite services, defense communication, etc.
- Radiofrequency is a natural resource but unlike other resources, it will deplete when used. But it will be wasted if not used efficiently.
- The spectrum allocated to Indian telecom operators is most crowded and inadequate to accommodate the usage by 650 million mobile subscribers as on date. This has affected the quality of customer service and resulted in poor voice quality, call drop, and undelivered messages of mobile services in India.
What is mobile spectrum?
- Mobile or cellular spectrum is that part of the whole electromagnetic spectrum which is used by the Indian government to offer mobile services. Hence the name “Mobile Spectrum”.
- Generally, the following frequencies are used for this purpose – 800 Mhz (for CDMA), 900 Mhz (for 2G) & 1800 Mhz (for 3G/4G).
- But technically any frequency band can be used for any purpose. Like 900 Mhz frequency can be used to deliver 3g Services also.
Agencies allocating Spectrum
- For international purposes, the spectrum is allocated by the world body called the International Telecommunication Union (ITU).
- For domestic purposes, it is done by Wireless Planning and Coordination (WPC) Wing of the Ministry of Communications, created in 1952, is the National Radio Regulatory Authority responsible for Frequency Spectrum Management, including licensing and caters for the needs of all wireless users in the country. It issues licenses to operate wireless stations.
What is Reserve Price?
- It is the minimum amount set by the government from which the auction starts i.e. it is the starting amount or base price from which the auction starts.
Why auction of spectrum is done?
- Spectrum is a scarce resource. It needs to be managed efficiently.
- Also, the spectrum can’t be used by many people. It has to be allocated to some persons who can manage the services under it. Hence it is auctioned.
- Government auctions it because the spectrum is a resource & the ownership rights for it are vested in the Government of India. It is not private property. So, government auctions it.
- Also, a lot of revenue is generated by selling the spectrum. That money can be used for developmental programs in India.
Reasons for superiority of 900 Mhz and 1800 Mhz band
- According to the laws of Physics, for any wave, the higher the frequency of the wave, the lesser will be the distance travelled by it. So naturally, frequencies of 900 Mhz will cover more distance than the frequencies of 1800 Mhz & hence mobile operators are more interested in the 900 Mhz frequency.
- More investment needed by the companies who buy the 1800 Mhz frequency spectrum: the 1800 Mhz frequency has poor coverage than the 900 Mhz frequency. So, for matching the existing coverage mobile operators have to install additional base stations (i.e. mobile towers) to give the same effect as the frequencies under 900 Mhz.
- Also, hardware equipment required for carrying out the operation of 1800 Mhz frequency is costly. The main reason behind it is that the 900 Mhz frequency band has been in use for mobile communications globally for over 20 years and as a result technology standards have been better developed compared with the 1800 Mhz band, which has been in use only recently.
LTE (Long Term Evolution)
LTE (Long Term Evolution) is a wireless broadband technology designed to support roaming Internet access via cell phones and handheld devices. Because LTE offers significant improvements over older cellular communication standards, some refer to it as a 4G (fourth generation) technology along with WiMAX.
LTE, an acronym for Long Term Evolution, commonly marketed as 4G LTE, is a standard for wireless communication of high-speed data for mobile phones and data terminals.
Long Term Evolution or LTE is the first step towards true 4G technologies. To be a truly 4G technology, download speeds of 100 Mb/s and 1Gb/s should be available from moving (i.e. in a car) or pedestrian points respectively. It was however widely decided across the world that companies could market LTE as “4G LTE” due to some having already taken that step and to avoid further consumer confusion with the terms 3.5G or 3.9G that were starting to surface.
LTE offers maximum download speeds of 299.6 Mb/s although there has been controversy over the speeds some operators running LTE networks are providing, sometimes being lower than the supposedly ‘inferior’ HSPA (plus) technology. Commercially available speeds vary wildly and using the (at the time of writing) recently launched UK LTE network, tests have shown anywhere in between 8-50 Mb/s in available areas. LTE requires brand new network technology and masts/radios. This also means that the devices that support LTE will also need to have a compatible receiver.
What is Multiplexing? What are its types?
- Any information i.e. voice/date in this case can be sent to another party only by the use of communication channel.
- In this case, the communication channel is the Radio Waves.
- But the spectrum under these radio waves is limited i.e. limited users can use these communication channels. Hence communication channels have to be used efficiently.
- For efficient use, the communication channel is allotted to the users in number of ways which is called Multiplexing.
- Types of Multiplexing: a) Code Division Multiple Access (CDMA) b) Frequency Division Multiple Access (FDMA) c) Time-Division Multiple Access (TDMA)
- FDMA: In FDMA, the goal is to divide the frequency spectrum into slots and then to separate the signals of different users by placing them in separate frequency slots.
- TDMA: In TDMA, the goal is to divide time into slots and separate the signals of different users by placing the signals in separate time slots.
- CDMA: In CDMA, signals are sent at the same time in the same frequency band. Signals are either selected or rejected at the receiver by recognition of a user-specific signature waveform, which is constructed from an assigned spreading code.
Advantages of CDMA techniques:
- Efficient practical utilization of fixed frequency spectrum.
- Flexible allocation of resources.
- Many users of CDMA use the same frequency, TDD or FDD may be used
- Multipath fading may be substantially reduced because of large-signal bandwidth
- No absolute limit on the number of users, Easy addition of more users.
- Impossible for hackers to decipher the code sent
- Better signal quality
- No sense of handoff when changing cells
- The CDMA channel is nominally 1.23 MHz wide.
- CDMA networks use a scheme called soft handoff, which minimizes signal breakup as a handset passes from one cell to another.
- CDMA is compatible with other cellular technologies; this allows for nationwide roaming.
- The combination of digital and spread-spectrum modes supports several times as many signals per unit bandwidth as analog modes.
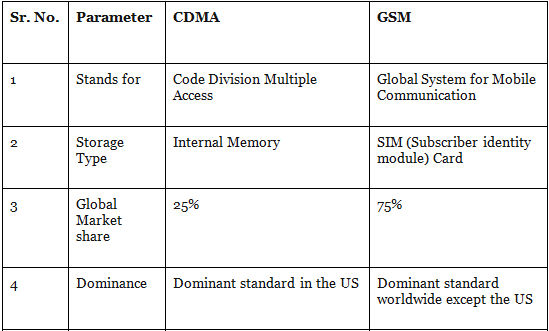
Difference between GSM & CDMA
You may have heard that mobile phones are available in GSM or CDMA. Even when you go to a mobile recharge shop, you are asked by the shopkeeper, “Do you want to recharge for GSM or CDMA?” What exactly is he asking to you is the type of technology being used by your mobile. A recharge voucher meant for GSM mobiles can’t work for CDMA mobiles & vice versa.
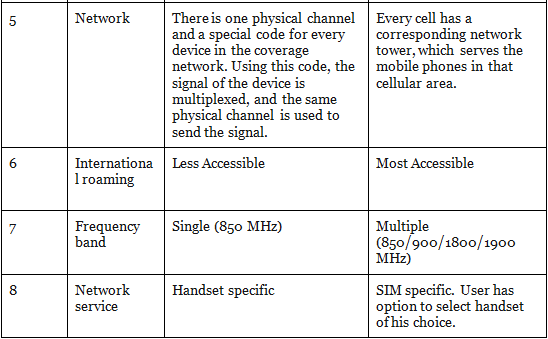
What is GPRS?
GPRS is a system used to transmit data at speeds of up to 60 Kbits per second and is a battery-friendly way to send and receive emails and to browse the internet but in these days of broadband connectivity, it will be seen as slow by some.
What is EDGE?
EDGE (Exchanged Data rates for GSM Evolution) is a recent development based on the GPRS system and has been classified as a ‘3G’ standard due to the fact that it can run at up to 473.6 Kbits per second. If a smartphone is EDGE compliant it can be used for heavy mobile data transmission such as receiving large email attachments and browsing complex web pages at great speed.
What is HSDPA?
HSDPA (High-Speed Downlink Packet Access) is a technology-based on the 3G network which can support speeds of up to 7.2 Mbits per second. In reality, you will most likely get a top speed of around 3 Mbits but this is useful for mobile TV streaming and other high-end data transmissions. To use HSDPA your phone must be able to support the technology and of course, you will need to be located within range of a cell site that has been upgraded to offer the service.
What is HSPA (Plus)?
- This is an evolution of the HSPA (HSDPA & HSUPA) standard and allows for faster speeds. The maximum download speed allowed by the standard is 168 Mbit/s although in reality networks that support HSPA (plus) will offer 21 Mbit/s downloads. This is because the existing 3G network architecture operators would have deployed and made compatible was never designed to handle such massive bandwidth.
- The operators need additional spectrum to improve the quality of services. The Government should formulate a spectrum policy that will promote efficient use of spectrum by developing market incentives and differential pricing of spectrum in congested areas. An open and transparent auction format will ensure that the government realizes the best price for spectrum as per the market forces and at the same time the telecom operators minimize and efficiently use the spectrum.
Optical Fibre Technology
- Fibre-optic communication is a method of transmitting information from one place to another by sending pulses of light through an optical fiber. The light forms an electromagnetic carrier wave that is modulated to carry information.
- Fibre is preferred over electrical cabling when high bandwidth, long-distance, or immunity to electromagnetic interference is required.
- Optical fibre is made up of semiconducting materials and usually has a cylindrical structure. In inner core, there is the material of higher refractive index than in the outer core resulting in Total Internal Reflection (TIR).
Free-Space optical communication (FSO)
Free-space optical communication (FSO) is an optical communication technology that uses light propagating in free space to wirelessly transmit data for telecommunications or computer networking. “Free-space” means air, outer space, vacuum, or something similar. This contrasts with using solids such as optical fiber cable.
It is a Line of Sight (LOS) technology. It consists of an optical transceiver at both ends to provide full duplex (bidirectional) capability.
It is capable of sending up to 1.25 Gbps of data, voice, and video communications simultaneously through the air.
Advantages: low initial investment, flexible network that delivers better speed than broadband, security due to line of sight operation, etc.
Challenges: misalignment errors, geometric losses, background noise, weather attenuation losses and atmospheric turbulence.
Radio-frequency identification (RFID)
Radio-frequency identification (RFID) uses electromagnetic fields to automatically identify and track tags attached to objects. The tags contain electronically-stored information.
Passive tags collect energy from a nearby RFID reader’s interrogating radio waves. Active tags have a local power source (such as a battery) and may operate hundreds of meters from the RFID reader.
Unlike a barcode, the tag need not be within the line of sight of the reader, so it may be embedded in the tracked object. RFID is one method for Automatic Identification and Data Capture (AIDC).
RFID can be used in a variety of applications, such as:
- The electronic key for RFID based lock system
- Access management
- Tracking of goods
- Tracking of persons and animals
- Toll collection and contactless payment
- Machine-readable travel documents
- Smartdust (for massively distributed sensor networks)
- Airport baggage tracking logistics
- Timing sporting events
- Tracking and billing processes
RFID provides a way for organizations to identify and manage stock, tools, and equipment (asset tracking), etc. without manual data entry.
RFID is used for item-level tagging in retail stores. In addition to inventory control, this provides both protection against theft by customers (shoplifting) and employees (“shrinkage”) by using electronic article surveillance (EAS), and a self-checkout process for customers.
Yard management, shipping and freight, and distribution centers use RFID tracking. In the railroad industry, RFID tags mounted on locomotives and rolling stock identify the owner, identification number, and type of equipment and its characteristics. This can be used with a database to identify the lading, origin, destination, etc. of the commodities being carried.
|
146 videos|358 docs|249 tests
|
FAQs on Awareness in Field of IT & Computers- 1 - Science & Technology for UPSC CSE
| 1. What is the importance of awareness in the field of IT and computers? |  |
| 2. How can one enhance their awareness in the field of IT and computers? |  |
| 3. What are the benefits of staying aware of IT and computer-related issues? |  |
| 4. How can awareness in the field of IT and computers contribute to personal and professional growth? |  |
| 5. Are there any potential risks associated with a lack of awareness in the field of IT and computers? |  |
|
146 videos|358 docs|249 tests
|

|
Explore Courses for UPSC exam
|

|

















