Biological Anthopology | Anthropology Optional for UPSC PDF Download
Physical anthropology is considered to be the oldest branch of anthropology. Its scope considers man first as a biological organism and secondarily as a social animal. The development of physical anthropology is closely linked with the theoretical developments in the fields of medicine and genetics. Among the developments in biological sciences that have made enormous contributions to the development of the scope of this discipline, the theory of organic evolution and the principles of genetics are significant. Many biologists are responsible for ' the development of this subject. Comte De Buffon, Paul Broca, John Frederick Bluemenbach, Samuel George Morton, Charles Darwin and Alfred; Russell Wallace are considered as the founders of this discipline.
For a systematic study of this kind, there are many fields of specialization within biological anthropology as the following:
- Paleoanthropology
- Primatology
- Human Genetics
- Forensic Anthropology
- Serology
- Dermatoglyphics
- Anthropometry and Craniometry
- Paleopathology
- Bio-archaeology
- Neuro- Anthropology
- Biomedical Anthropology
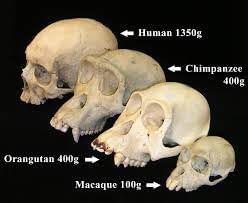
- Paleoanthropology earlier known as human paleontology is the study of human origin and evolution, particularly as inscribed in the fossil record. Palaeo anthropologists are interested in reconstructing the evolutionary stages of humans, based on fossil evidences. They work with archaeologists, and geologists, in unearthing fossil remains from many parts of the world. The knowledge of osteology helps them to examine, measure, and reconstruct these remains to understand the course of human evolution, and identify the possible lines of descent from our ancestors to the present form, Homo sapiens.
- Human Paleontology or Paleoanthropology: Human Paleontology studies the fossil evidences of human skeletons of different stages and thereby reconstructs the evolutionary history of humans. This helps in the classification and comparison of the fossils of different stages to determine the link between the modern humans and their ancestors.
- Primatology is the study of living and extinct primates. Primates include human, apes, monkeys and prosimians. Different stages of human evolution can be understood by analyzing the fossil evidence of the primates. Human paleontology helps us in this regard. Any study of human evolution requires an understanding of the members of primates.
- Primatology is the study of primates, the group to which prosimians, apes, monkeys and humans belong. It focuses on how the behaviour of non-human primates is similar to that of the humans. The anatomy of non-human primates especially monkeys and apes have been studied to ascertain the similarities and differences between these primates and humans.
- Human genetics is the branch of biological anthropology that deals with inheritance and variation. It is the study of gene structure and action and the patterns of inheritance of traits from parents to off-spring. To understand how evolution works, it is important to know the mechanisms of heredity.
- Morphological and genetic variations among humans help biological anthropologists to identify individuals, criminals, victims of misshapes and natural calamities etc. The branch of anthropology specialised in such area is called Forensic Anthropology. It deals with legal matters from an anthropological perspective. It is the application of osteology, paleopathology, archaeology, and other anthropological techniques for the identification of modern human remains or the reconstruction of events surrounding a person’s death and for legal purposes.
- Serology: It is a scientific study of blood groups. It studies plasma serum and other redcell enzymes. In practice, the term usually denotes the diagnostic identification of antibodies in the serum. Serological tests are also used forensically, particularly concerning a piece of evidence.
- Dermatoglyphics is the study of skin ridges on finger palms, toes and soles. Finger print patterns are not only used in Forensic investigation but also genetics to know the variation between two populations.
- Anthropometry is the systematic art/study of taking measurements on skeletons and living human beings.
- Craniometry is the sub branch of anthropometry deals with the measurement of craniums.
New Areas of Biological Anthropology
- Paleopathology is a study of disease in antiquity. It studies the traces of disease and injury in human skeletal remains. More over it focuses on pathogenic conditions observable in bones or mummified soft tissue. It also concentrates on nutritional disorders, variation in stature or the morphology of bones over time, evidence of physical trauma, or evidence of occupationally derived biomechanic stress etc.
- Bio-archaeology is the combination of human osteology or the study of human bones with archaeology to study the human bones associating them with the location of its recovery in order to understand the past human populations
- Neuro-Anthropology is the study of human brain, evolution and culture as neurological adaptation and environment.
- Bio-medical Anthropology incorporates perspectives from the biological and medical anthropology subfields. It mainly seeks to improve medical practice and biomedical science through the holistic integration of cross-cultural or bicultural, behavioral, and epidemiological perspectives on health. As an academic discipline, it is closely related to human biology.
Each of these specialised areas within biological anthropology contributes to the understanding of the biological aspects of humans. The important biological aspects of human beings would include those that are related to the theories of human evolution, human genetics and human variation.
|
209 videos|299 docs
|
FAQs on Biological Anthopology - Anthropology Optional for UPSC
| 1. What is biological anthropology? |  |
| 2. How is biological anthropology different from other branches of anthropology? |  |
| 3. What are the key areas of study in biological anthropology? |  |
| 4. How does biological anthropology contribute to our understanding of human evolution? |  |
| 5. What is the relevance of biological anthropology in modern society? |  |

















