UPSC Exam > UPSC Notes > Zoology Optional Notes for UPSC > Biosphere: Biomes
Biosphere: Biomes | Zoology Optional Notes for UPSC PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Defining Biomes |

|
| The Evergreen Rainforest Biome |

|
| Temperate Grassland Biome |

|
| Arctic Tundra Biomes |

|
Defining Biomes
Biomes, often referred to as "biological homes," are natural ecosystems where the entire collection of visible plant and animal components of the landscape is studied. These areas are characterized by shared environmental conditions and house a variety of life forms. Biome classification is influenced by several key factors, such as the length of daylight and darkness, mean temperature, and moisture availability. The relationship between climate and vegetation forms the basis for categorizing biomes, leading to different biome types, which can be further subdivided based on the dominant plant life.
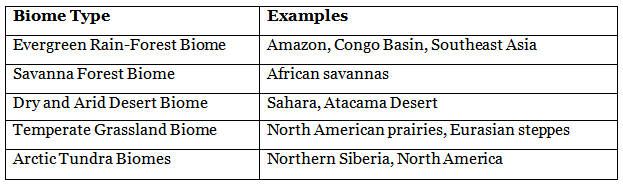
Classification of Biomes
Biomes are classified based on a combination of climate and vegetation, resulting in a rich tapestry of diverse ecosystems. The following table summarizes these classifications:
The Evergreen Rainforest Biome
- Geographical Background: This biome extends around the equator and covers areas in South America, equatorial Africa, and Southeast Asian Islands. It experiences consistent high temperatures and heavy rainfall throughout the year.
- Natural Vegetation and Animal Life: The combination of heat and moisture fosters a remarkable diversity of plant species, including ebony, mahogany, and rosewood. Orchids, ferns, mosses, and herbs thrive at the ground level. This biome is home to numerous bird and mammal species, making it one of the most biologically rich environments globally.
- Human Response: Unfortunately, human activities, such as deforestation and mining, have begun to disrupt this fragile ecosystem, resulting in the decline and extinction of some species. The rainforest biome plays a crucial role in regulating global weather patterns, soil erosion, and river flooding, highlighting the importance of preserving it.
Temperate Grassland Biome
- Geographical Background: Temperate grasslands are found in both the northern and southern hemispheres, characterized by continental climates with distinct seasons. In the northern hemisphere, they stretch across Eurasia and North America, while in the southern hemisphere, they are located in the rain shadow areas of coastal mountains.

- Natural Vegetation and Animal Life: These grasslands are treeless, characterized by an abundance of grasses, mosses, lichens, and low shrubs. Animal species, such as antelopes, wild asses, and kangaroos, thrive in this biome.
- Human Response: The temperate grasslands have witnessed substantial changes due to human activities, including habitat destruction and the introduction of new species. The European settlement in Australia, for example, introduced sheep, altering the composition of native vegetation.
Arctic Tundra Biomes
- Geographical Background: Arctic tundra biomes are found in high-latitude regions of the northern hemisphere, particularly in areas like Northern Russia and Siberia. They endure extremely cold temperatures and minimal precipitation.

- Natural Vegetation and Animal Life: Tundras are dominated by dwarf plant species, including grasses, mosses, and lichens. Animal life is limited but includes reindeer, wolves, musk-ox, and arctic hares.
- Human Response: Indigenous tribes in these areas have transitioned from nomadic to more settled lifestyles. The discovery of valuable minerals has led to mining activities, causing pollution and environmental challenges in this delicate ecosystem.
The document Biosphere: Biomes | Zoology Optional Notes for UPSC is a part of the UPSC Course Zoology Optional Notes for UPSC.
All you need of UPSC at this link: UPSC
|
181 videos|338 docs
|
FAQs on Biosphere: Biomes - Zoology Optional Notes for UPSC
| 1. What is the definition of a biome? |  |
A biome is a large-scale community of plants and animals that are adapted to specific environmental conditions, including climate, soil, and vegetation. It is characterized by distinct types of ecosystems and is often classified based on its predominant vegetation.
| 2. What are the characteristics of the Evergreen Rainforest biome? |  |
The Evergreen Rainforest biome is typically found in tropical regions near the equator. It receives high amounts of rainfall throughout the year, which supports the growth of lush and dense vegetation. The trees in this biome are mostly evergreen, meaning they do not shed their leaves all at once. It is known for its high biodiversity, with a wide variety of plant and animal species.
| 3. How does the Temperate Grassland biome differ from other biomes? |  |
The Temperate Grassland biome, also known as prairies or steppes, is characterized by its vast expanses of grasses with few or no trees. It experiences a moderate climate with distinct seasons, including hot summers and cold winters. Unlike the Evergreen Rainforest biome, which receives abundant rainfall, the Temperate Grassland biome has lower precipitation levels. This biome is often found in the interior regions of continents.
| 4. What are the main features of the Arctic Tundra biome? |  |
The Arctic Tundra biome is a cold and treeless environment found in the northernmost regions of the world, such as Alaska, Canada, and Siberia. It experiences extremely cold temperatures, with long winters and short summers. The soil in this biome is permanently frozen, known as permafrost, which restricts the growth of trees. It is characterized by low-growing vegetation, including mosses, lichens, and small shrubs, and is home to animals such as polar bears, reindeer, and arctic foxes.
| 5. How do biomes contribute to the overall biosphere? |  |
Biomes play a crucial role in the biosphere, which is the sum of all ecosystems on Earth. They provide habitats for a wide range of plant and animal species, contributing to biodiversity and ecological balance. Biomes also influence climate patterns, nutrient cycling, and the overall functioning of the Earth's systems. Understanding and conserving biomes is important for maintaining the health and sustainability of the biosphere.

|
Explore Courses for UPSC exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
Related Searches


















