Blood Pressure-Definitions | Medical Science Optional Notes for UPSC PDF Download
Arterial blood pressure
Arterial blood pressure is defined as the lateral pressure exerted by the column of blood on wall of arteries.
The pressure is exerted when blood flows through the arteries.
Generally, the term 'blood pressure'refers to arterial blood pressure.
Arterial blood pressure is expressed in four different terms:
- Systolic blood pressure-Maximum pressure exerted during systole
- Diastolic blood pressure-Minimum pressure exerted during diastole
- Pulse pressure-Difference between systolic and diastolic pressure
- Mean arterial blood pressure-Average pressure existing in the arteries. It is the diastolic pressure plus one third of pulse pressure.
Factors effecting Blood pressure
Blood pressure = Cardiac Output x Total Peripheral Resistance


Baroieflex
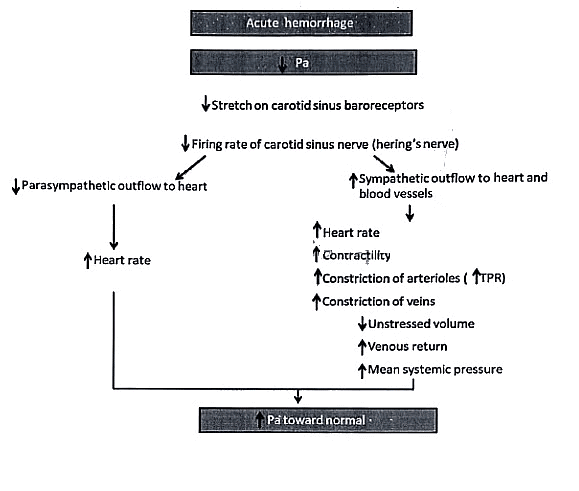
Role of the baroreceptor reflex in the cardiovascular response to hemorrhage. Pa = mean arterial pressure; TPR= total peripheral resistance.
RAAS

Role of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system in the cardiovascular response to hemorrhage. Pa = mean arterial pressure; TPR = total peripheral resistance.
Measurement of cardiac output
The various methods of measuring cardiac output are as follows:
- Doppler combined with echocardiography
- Direct Fick's method
- The indicator dilution method
- Thermodilution method
- Pulse contour devices
- Thoracic bio impedance
The Fick's principle states that the amount of a substance taken up by an organ (or by the whole body) per unit of time is equal to the arterial level of the substance minus the venous level (A-V difference) times the blood flow.
It is the most accurate method to measure cardiac output but is invasive.
Equation-Cardiac output = O2 consumption / [O2]pulmonary vein - [O2]pulmonary artery The equation is solved as follows: O2 consumption for the whole body is measured.
Pulmonary vein [O2 ] is measured in systemic arterial blood.
Pulmonary artery [O2 ] is measured in systemic mixed venous blood.
For example, a 70-kg man has a resting O2 consumption of 250 mL/min, a systemic arterial O2 content of 0.20 mL 02/mL of blood, a systemic mixed venous 02 content of 0.15 mL 02/mL of blood, and a heart rate of 72 beats/min. What is his cardiac output? What is his stroke volume?
Cardiac output = 250 mL/min / 0.20 mL 02/mL - 0.15 mL 02/mL =5000 mL/min, or 5.0 L/min
In the indicator dilution technique, a known amount of a substance such as a dye or, more commonly, a radioactive isotope is injected into an arm vein and the concentration of the indicator in serial samples of arterial blood is determined.
The output of the heart is equal to the amount of indicator injected divided by its average concentration in arterial blood after a single circulation through the heart.
A popular indicator dilution technique is thermodilution, in which the indicator used is cold saline.
This technique has two important advantages:
- the saline is completely innocuous;
- the cold is dissipated in the tissues so recirculation is not a problem, and it is easy to make repeated determinations.
|
7 videos|219 docs
|

















