Board Paper of Class 10 2019 Science Delhi(Set - 1) | Past Year Papers for Class 10 PDF Download
Ques 1: Name and define the SI unit of current.
Ans: The SI unit of current is ampere. One ampere is defined as the current produced at a point through which, 1 Coulomb of charge passes in 1 second or flow of one coulomb of charge in one second through a point.
Ques 2: Write the name of the main constituent of Biogas. Also, state its percentage.
Ans: The main constituents of biogas are Methane and Carbon dioxide and their percentage is as follows:
1. Methane is 75%
2. Carbon Dioxide is 23%
Other gases are approximately 2%
Ques 3: How is O2 and CO2 transported in human beings?
Ans: Inhaled air is rich in oxygen and is carried to the lungs. The diffusion of oxygen to the blood occurs in the capillaries, in alveoli, where the oxygen combines with the haemoglobin to form oxyhaemoglobin. This oxygen-rich blood is taken to the heart, for distribution, via the pulmonary vein. The carbon dioxide moves from the tissues to the plasma and red blood cells which are carried to capillaries in alveoli via the pulmonary artery. Carbon dioxide diffuses out from the capillaries in alveoli. The carbon dioxide rich air is at last expelled from the body during exhalation while breathing.
Ques 4: Write the structure of eye lens and state the role of ciliary muscles in the human eye.
Ans: The eye lens being convex in nature converges the light rays incident on it. Hence, it focuses the light falling on it on a thin layer of nerve cells called the retina. Two Ciliary muscles hold the lens within the eye-ball and it relaxes and tightens to change the focal length of the eye lens to get the clear image on the retina.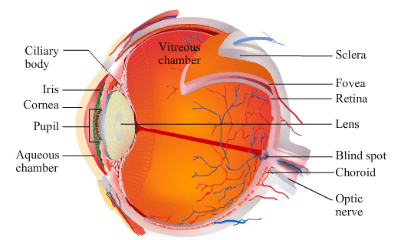
Ques 5: Identify the acid and base which form sodium hydrogen carbonate. Write chemical equation in support of your answer. State whether this compound is acidic, basic or neutral. Also write its pH value.
Ans: Sodium hydroxide(base) and hydrogen carbonate(acid) combine to form sodium hydrogen carbonate.
2NaOH + H2CO3 → Na2CO3 + 2H2O
Sodium hydrogen carbonate is a basic salt because NaOH is a strong base and H2CO3 is a weak acid. pH value of sodium hydrogen carbonate is 8.27
Ques 6: Based on the group valency of elements write the molecular formula of the following compounds giving justification for each:
(i) Oxide of first group elements.
(ii) Halide of the elements of group thirteen, and
(iii) Compound formed when an element, A of group 2 combines with an element, B of group seventeen.
Ans:
(i) Oxides of the first group elements have the common formula of M2O.
Example- Na2O, K2O. This is because, the first group elements have a common valency of 1, and the valency of Oxygen is 2 so, to satisfy the combining capacity of Oxygen two 1st group metals are required.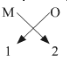 (ii) Halides of group 13 elements have a common formula of MX3 , where M-metal and X- halogen element.
(ii) Halides of group 13 elements have a common formula of MX3 , where M-metal and X- halogen element.
Example- AlCl3, BF3 . This is because the valency of group 13 elements is 3 and that of halogens is 1 so, to satisfy the combining capacity of aluminum or other group 13th elements three of halogens are required in the molecular formula.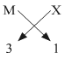 (iii) The general formula for those kinds of compounds would be AB2.
(iii) The general formula for those kinds of compounds would be AB2.
Example- MgCl2, CaCl2. This is because the valency of group 2 elements is 2 and that of group 17th elements if 1 so to satisfy the combining capacity of group 2 elements two of group 17 elements are required in the molecular formula.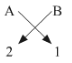
Ques 7: 2 g of silver chloride is taken in a china dish and the china dish is placed in sunlight for sometime. What will be your observation in this case? Write the chemical reaction involved in the form of a balanced chemical equation. Identify the type of chemical reaction.
OR
Identify the type of reactions taking place in each of the following cases and write the balanced chemical equation for the reactions.
(a) Zinc reacts with silver nitrate to produce zinc nitrate and silver.
(b) Potassium iodide reacts with lead nitrate to produce potassium nitrate and lead iodide.
Ans: When 2 g of silver chloride, AgCl, is kept in sunlight then AgCl breaks down into Ag and Cl2. The color of the silver chloride turns to grey.
The following change can be represented by the chemical reactions as: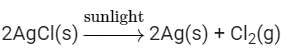 This type of reaction is an example of a photochemical decomposition reaction.
This type of reaction is an example of a photochemical decomposition reaction.
OR
(a) The given reaction is a displacement reaction in which more reactive zinc will displace less reactive silver from silver nitrate solution.
Zn(s) + 2AgNO3(aq) → Zn(NO3)2(aq) + 2Ag(s)
(b) The given reaction is a double displacement reaction.
2KI(aq) + Pb(NO3)2(aq) → 2KNO3(aq) + PbI2(s)
Ques 8: Define the term transpiration. Design an experiment to demonstrate this process.
Ans: Loss of water vapour through the stomatal openings of the leaves of a plant is termed as transpiration.
Following experiment can be performed to demonstrate transpiration in a plant:
1. Place a healthy growing plant on a horizontal and plane slab in the sun.
2. Place a glass bell jar over the potted plant and seal its end to the slab by applying vaseline at its edges.
3. Allow the set-up to remain in the sun for some time.
4. Observe the presence of water droplets on the inner surface of the glass bell jar.
5. This collection of water droplets is indicative of transpiration.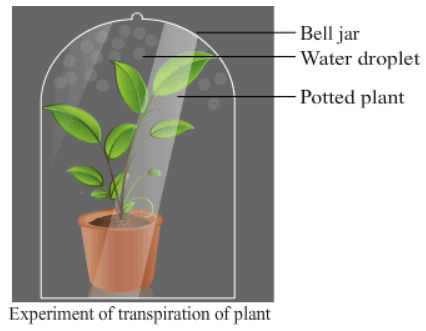
Ques 9: What is feedback mechanism of hormone regulation. Take the example of insulin to explain this phenomenon.
Ans: The endocrine glands secrete hormones depending upon the need of the organism. The level of hormones secreted should be in an accurate amount. The regulation of the quantity of the hormones and the timing of its release are controlled by feedback mechanisms.
There are two types of feedback mechanisms:
(i) Positive feedback: In this mechanism, the response accelerates after the feedback. The effect is further intensified in the same direction. It helps in speeding up the process occurring in various body systems. It is the opposite of negative feedback.
(ii) Negative feedback: In this mechanism, the information given by the feedback causes a reverse response. It occurs when the system needs to slow down or completely stop a process. For example, when we consume a carbohydrate-rich diet, it is digested into glucose.
The glucose is then absorbed by the blood. This results in the increase of blood sugar level and leads to the stimulation of the pancreas to secrete insulin. Insulin stimulates the target cells to take up the extra glucose from the blood. This glucose is either used during respiration or stored as glycogen. Thus, the level of insulin is reduced as pancreas receive negative feedback.
Ques 10: What are plant hormones? Name the plant hormones responsible for the following:
(i) Growth of stem
(ii) Promotion of cell division
(iii) Inhibition of growth
(iv) Elongation of cells
Ans: In plants, growth, development, and response to the environment are controlled and coordinated by a special class of chemical substances known as Phytohormones. They are naturally occurring organic substances which are synthesized in minute quantities. These hormones are produced in one part of the plant body and are translocated to other parts.
Example: A hormone produced in the roots is translocated to other parts where they are required.
So, the respective plant hormones are:
(i) Gibberellins
(ii) Cytokinins
(iii) Abscisic acid
(iv) Auxins
Ques 11: Why should there be equitable distribution of resources? List three forces that would be working against an equitable distribution of our resources.
Ans: Natural resources, like water, forest among others are resources that are needed by all organisms. They have biological as well as ecological importance in any ecosystem. Ecological services like oxygen production, food production are a few to name. Hence, they should be equally distributed for healthy sustenance of organisms and ecosystems.
There are certain forces that disrupt the equal distribution of resources:
- Geographical limitations: While the equatorial regions are rich in natural resources, the regions near the poles are not.
- Human exploitation: Humans have and are consuming natural resources at an unprecedented rate, degrading their availability in certain regions.
- Selfish attitude: Natural resources also suffer at the hand of rich and powerful as they use the resources to their advantage.
Ques 12: How can we help in reducing the problem of waste disposal? Suggest any three methods.
OR
Define an ecosystem. Draw a block diagram to show the flow of energy in an ecosystem.
Ans: The three methods we can utilise for reducing the problem of waste disposal are:
1. Segregation of waste into biodegradable and non-biodegradable.
2. Following the principle of 3R- Reduce, Reuse and Recycle.
3. Converting biodegradable waste into useful commodities like energy from biogas, using the compost as fertiliser.
OR
Ecosystem refers to the living and nonliving components in an area and the interactions between them. Energy flows across the trophic levels as shown in the diagram below, following the ten percent law. Only ten percent of the energy available to a trophic level is passed on to the next trophic level. The remaining is dissipated away.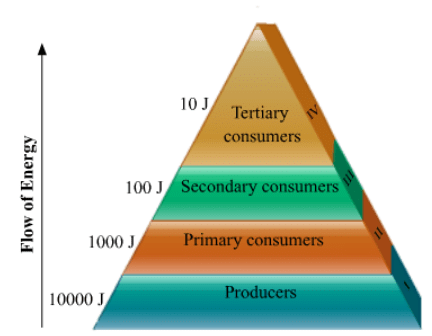 Assuming 10000 J is the energy available to the producers, then
Assuming 10000 J is the energy available to the producers, then
1000 J will be available to the primary consumers,
100 J will be available to secondary consumers and
10 J will be available to tertiary consumers.
Ques 13: What is a rainbow? Draw a labelled diagram to show the formation of a rainbow.
Ans: The rainbow is a natural phenomenon in which white sunlight splits into beautiful colours by water droplets, which remain suspended in air after the rain. Formation of a rainbow: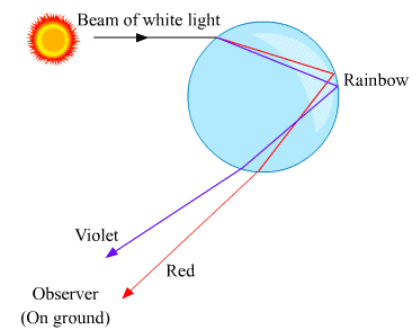
Ques 14: What is a solenoid? Draw the pattern of magnetic field lines of
(i) a current carrying solenoid and
(ii) a bar magnet
List two distinguishing features between the two fields.
Ans: A solenoid is a long cylindrical coil of wire consisting of a large no. of turns bound together very tightly.
(i) 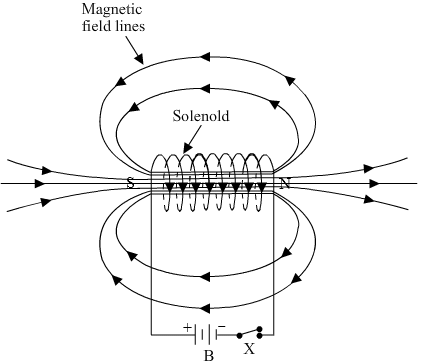
(ii)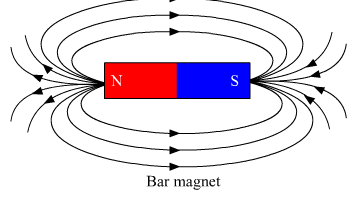 Two distinguishing features between the two fields:
Two distinguishing features between the two fields:
1. Magnetic field of the solenoid can be varied as per our requirements just by changing the current or core of the solenoid whereas the magnetic field of the bar magnet is fixed.
2. Magnetic field outside the solenoid is negligible as compared to the bar magnet.
Ques 15: Define pollination. Explain the different types of pollination. List two agents of pollination? How does suitable pollination lead to fertilization?
OR
(a) Identify the given diagram. Name the parts 1 to 5.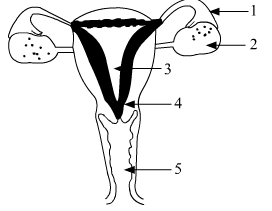 (b) What is contraception? List three advantages of adopting contraceptive measures.
(b) What is contraception? List three advantages of adopting contraceptive measures.
Ans: Transfer of pollen grain from the anther of a flower to stigma is termed as pollination. Based on the transfer of pollen grains between plants, pollination can be of two types:
1. Self Pollination: When pollen of a plant is transferred to the stigma of a flower on the same parent plant then it is termed as self-pollination.
2. Cross Pollination: When pollen of a plant is transferred to the stigma of a flower of a plant different from the one from which pollen is obtained then it is termed as cross-pollination.
Some of the most common agents of pollination that helps in carrying the pollen from the anther to the stigma of a flower are insects and wind.
As the pollen of the right type is deposited on to the stigma of the flower of the same species, it quite often leads to germination of pollen grain as a result of a chemical cross-talk between the pollen and the carpel. Germination leads to the growth and extension of the pollen tube through the style of the flower to its ovary. The pollen tube carries the male gametes all the way to the ovule inside the ovary, leading to fertilisation of male gamete with the female gamete inside the ovule.
OR
(a) The labelled parts of the female reproductive system are as follows:
1. Oviduct or Fallopian Tube
2. Ovary
3. Uterus
4. Cervix
5. Vagina
(b) Contraception includes methods or ways to prevent fertilisation and pregnancy in a fertile female as a result of successful copulation between a fertile male and female.
Some of the major advantages of adopting various contraceptive methods include:
(i) Prevention of unwanted pregnancies
(ii) Help in family planning and population control
(iii) Some contraceptive devices like condoms and female diaphragm prevent spread of STDs like AIDS and Hepatitis B.
Ques 16: In the experimental set up to show that "CO2 is given out during respiration", name the substance taken in the small test tube kept in the conical flask. State its function and the consequence of its use.
Ans: In the above mentioned experimental setup, lime water is taken in a small test tube which is kept in the conical flask. Lime water is used to detect the presence of carbon dioxide. When carbon dioxide passes through lime water, it turns milky due to the formation of calcium carbonate. Hence, it is used in the above experiment to check whether CO2 is released during respiration.
Ques 17: A student is observing the temporary mount of a leaf peel under a microscope. Draw labelled diagram of the structure of stomata as seen under the microscope
OR
Draw a labelled diagram in proper sequence to show budding in hydra.
Ans: Structure of stomata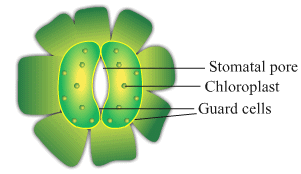
OR
Budding in Hydra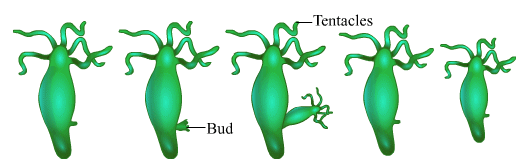
Ques 18: List four precautions which a student should observe while determining the focal length of a given convex lens by obtaining image of a distant object on a screen.
Ans: Following are the precautions while making the image by the help of convex lens:
1. Fix the convex lens vertically in the lens holder.
2. The base of the lens and white screen should be in a line with the measuring scale.
3. Record the position of the lens and screen only when a well defined sharp image is formed.
4. There should not be any obstacle in the path of the convex lens.
Ques 19: In three test tubes A, B, and C, three different liquids namely, distilled water, underground water and distilled water in which a pinch of calcium sulphate is dissolved, respectively are taken. Equal amount of soap solution is added to each test tube and the contents are shaken. In which test tube will the length of the foam (lather) be longest? Justify your answer.
Ans: 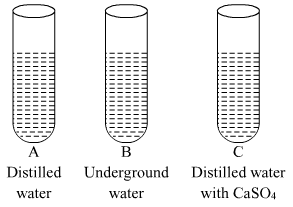 Test tube A contains distilled water which is considered as soft water, free from ions like Mg2+, Ca2+, etc. So, in this case, the length of foam will be the longest(maximum).
Test tube A contains distilled water which is considered as soft water, free from ions like Mg2+, Ca2+, etc. So, in this case, the length of foam will be the longest(maximum).
Test tube B contains underground water which contains ions like Mg2+, Ca2+, etc. which react with soaps to form salts of fatty acids called scum, which are insoluble in water. So, in this case, the length of foam will be the less in comparison to test tube A.
Test tube C contains distilled water with CaSO4, which contains Ca2+ ions which react with soaps to form salts of fatty acids called scum, which are insoluble in water. So, in this case also, the length of foam will be the less in comparison to test tube A.
Ques 20: Blue litmus solution is added to two test tubes A and B containing dilute HCl and NaOH solution respectively. In which test tube a colour change will be observed? State the colour change and give its reason.
OR
What is observed when 2 mL of dilute hydrochloric acid is added to 1 g of sodium carbonate taken in a clean and dry test tube? Write chemical equation for the reaction involved.
Ans: Test tube A contains dil. HCl and test tube B contains dil. NaOH. On adding blue litmus solution to both the test tubes, the colour of the test tube A will change from blue to red. This is because HCl is an acid and acids turn blue litmus to red.
OR
On adding dilute hydrochloric acid to sodium carbonate taken in a clean and dry test tube, a brisk effervescence will be observed due to the evolution of carbon dioxide gas.
2HCl + Na2CO3 → 2NaCl + H2O + CO2
FAQs on Board Paper of Class 10 2019 Science Delhi(Set - 1) - Past Year Papers for Class 10
| 1. What is the exam pattern for the Class 10 Science Delhi Board Paper? |  |
| 2. How many marks are allotted to each question in the Class 10 Science Delhi Board Paper? |  |
| 3. Can I use a calculator during the Class 10 Science Delhi Board Exam? |  |
| 4. What are the important topics to focus on for the Class 10 Science Delhi Board Exam? |  |
| 5. Is there any negative marking in the Class 10 Science Delhi Board Paper? |  |

















