Bond Parameters: Bond angle, Bond length, Bond order | Chemistry Optional Notes for UPSC PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| What are bond parameters? |

|
| Classification of bond parameters |

|
| Factors affecting Bond parameters |

|
| Solved Examples |

|
What are bond parameters?
Bond parameters are a set of parameters that are used to characterize the molecular structure. These factors provide information on a chemical compound's stability and the strength of the chemical bonds that hold its atoms together.
Classification of bond parameters
Bond parameters are classified as:

Bond angle: It is defined as the angle between the orbitals that contain bonding electron pairs around the central atom in a molecule. It is expressed in degrees that can be experimentally determined by spectroscopic techniques. It gives some idea regarding the orientation of orbitals around the central atom in a molecule. Hence, it can be used in determining the shape of the molecules.
Example: The bond angle between H-O-H bond in H2O molecules is 104.5°

Bond length: Bond length is defined as the closest internuclear distance between the nuclei of two bonded atoms. In a molecule, bond lengths are measured by spectroscopic techniques like X-ray diffraction and electron diffraction techniques.
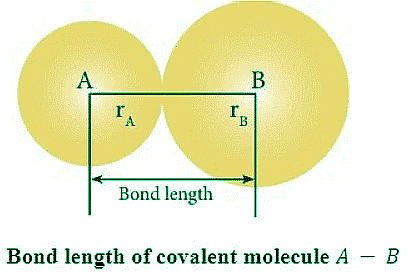
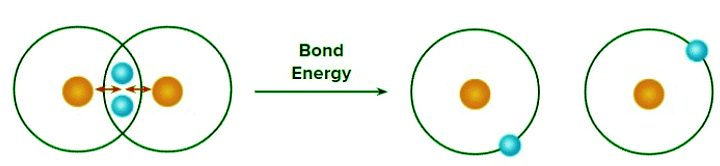
Bond energy: Amount of energy required to break 1 mole of a particular type of bonds between two atoms in gaseous state is called bond energy. The SI unit of bond energy is kJ/mol.
Bond order: The number of bonds between the two atoms in a molecule is called bond order.
Example: Oxygen molecule contain a double bond between two oxygen atoms.

Factors affecting Bond parameters
- Factors affecting Bond angle
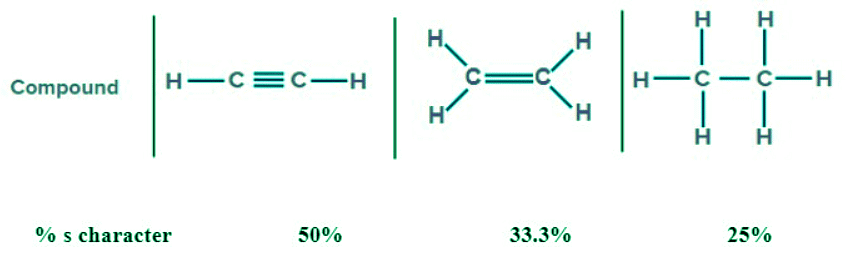
- Hybridization: As the % s character increases, the bond angle increases.
Note: In sp3 hybridization % s character is 25%
- In sp2 hybridization % s character is 33.3%
- In sp hybridization % s character is 50%
Examples:

Steric repulsion: For the same hybridization, the bond angle increases with an increase in steric repulsion of side atoms.
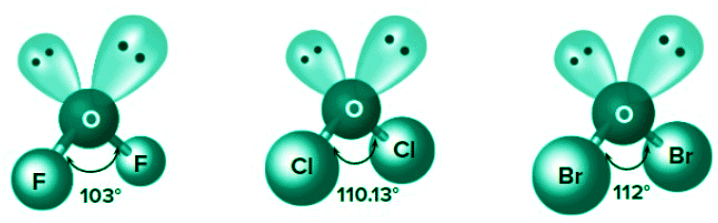
Number of lone pairs on the central atom: For the same hybridization, bond angle decreases with increase in the number of lone pairs on the central atom.
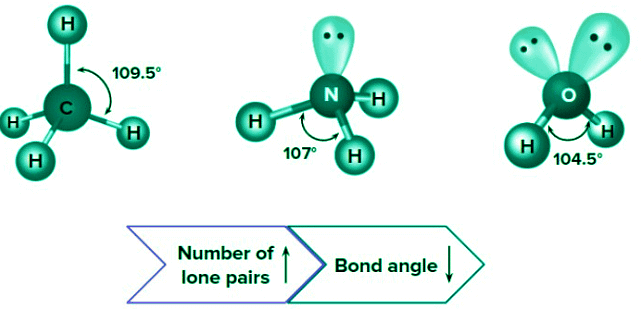
Electronegativity of the central atom: Bond angle increases with increase in the electronegativity of the central atom. Electronegativity order of group 16: O>S>Se

Electronegativity of the side atoms: The bond angle is inversely related to the electronegativity of the side atoms.

Factors affecting bond length:

- Size of the bonded atom: As the size of the atoms increases, the distance between both the nuclei also increases. Hence, the bond length also increases.
- Number of lone pairs on bonded atoms: As the number of lone pairs on the bonded atom increases. The bond length also increases due to repulsion between the lone pairs.
- Multiplicity of bond (Bond order): Bond length is inversely related to the multiplicity of bond (bond order). As the bond order increases, the bond strength also increases. Since the bonded electrons are bound strongly between the two nuclei, the bond length decreases.
Bond length: C–C > C=C > C≡C - Electronegativity difference: Bond length is inversely related to the electronegativity difference between the two bonded atoms.
Example: C-H(0.4)>N-H(0.9)>O-H(1.4)>F-H(1.9) - Percentage s-character: As the percentage of the s-character in the bond increases, the bond length decreases.
Factors affecting bond energy: As the bond order increases, the bond energy increases. This is because when the bond order increases, the electron density increases. So, the force of attraction between the electron and nucleus increases. So, in order to break the bond, more energy is required. Therefore, the bond energy increases. As the bond length decreases, the bond energy increases.
- Factors affecting bond order: Bond order is inversely related to the bond length. As the bond order increases, the bond strength also increases.
- Bond Order : C–C < C=C < C≡C
Solved Examples
Example 1: What are isoelctronic species? Do they have same bond order?
Ans: The species having same number/arrangement of electrons are known as isoelectronic species. They have generally identical bond orders. For example: F2 and O22- have same bond order = 1
Example 2: How would you relate resonance and bond length?
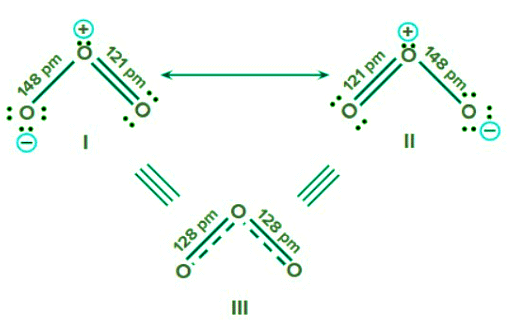
Ans: When a single Lewis structure cannot accurately describe a molecule, a number of structures with similar energy, nuclei locations, bonding and non-bonded pairs of electrons are taken as the canonical structures of the hybrid, which accurately characterises the molecule. This concept is known as resonance. In resonating structure bond length is always described as the average of all the canonical structure. This can be explained in the below example of O3.
Example 3: The SI unit in which bond energy is measured is
(a) kJ
(b) kJ mol-1
(c) kg
(d) kJ cal-1
Ans: (b)
The SI unit of bond energy is measured in kJ mol-1 .
Example 4: Bond angle between H-N-H in NH3 is
(a) 109.5°
(b) 104.5°
(c) 107°
(d) 112.5°
Ans: (c)
Angle between H-N-H in NH3 is 107°. Due to lone pair-bond pair repulsion, the bond angle slightly decreases from normal 109.5° to 107°.
FAQs on Bond Parameters: Bond angle, Bond length, Bond order - Chemistry Optional Notes for UPSC
| 1. What are bond parameters? |  |
| 2. How are bond parameters classified? |  |
| 3. What factors affect bond parameters? |  |
| 4. What is bond angle? |  |
| 5. How is bond order defined? |  |

|
Explore Courses for UPSC exam
|

|
















