CML: Pathology | Medical Science Optional Notes for UPSC PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Pathogenesis of CML |

|
| CML Clinicopathology |

|
| Cirrhosis of Liver - Etiology |

|
| Cirrhosis of Liver - Pathogenesis |

|
| Cirrhosis of Liver - Histopathology |

|
Pathogenesis of CML


CML Clinicopathology


- Asymptomatic
- CML burden
- Thrombotic/Hyperviscocity related features
- Platelet dysfunction
Cirrhosis of Liver - Etiology
Cirrhosis is described as a widespread condition marked by fibrosis and the transformation of the typical liver structure into structurally irregular nodules. The extent of cirrhosis varies depending on the size of these nodules-

Cirrhosis of Liver - Pathogenesis
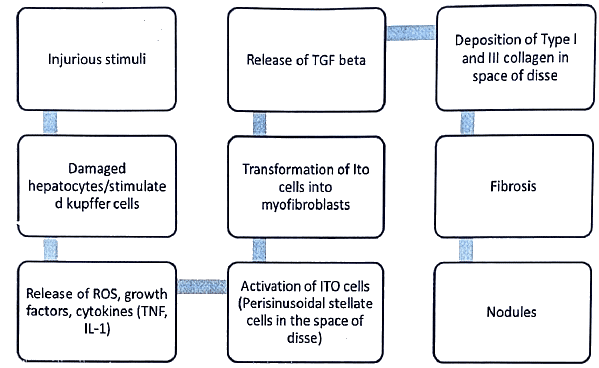
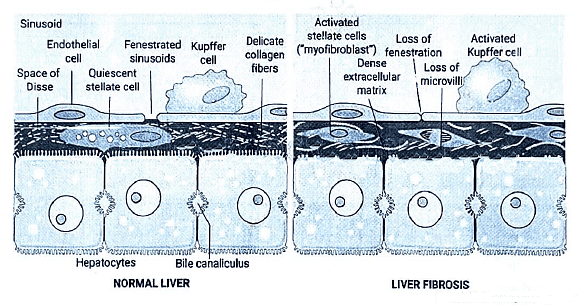
Cirrhosis of Liver - Histopathology

Delicate bands or broad scars, known as fibrous septa, surround multiple adjacent lobules. Parenchymal nodules are encompassed by these fibrous bands. The regeneration process involves preexisting long-lived hepatocytes and newly formed hepatocytes derived from stem cells, particularly the canals of Hering.
|
7 videos|219 docs
|
FAQs on CML: Pathology - Medical Science Optional Notes for UPSC
| 1. What is the pathogenesis of chronic myeloid leukemia (CML)? |  |
| 2. What are the clinicopathological features of chronic myeloid leukemia (CML)? |  |
| 3. What is the etiology of cirrhosis of the liver? |  |
| 4. What is the pathogenesis of cirrhosis of the liver? |  |
| 5. What are the histopathological features of cirrhosis of the liver? |  |

|
Explore Courses for UPSC exam
|

|
















