Class 10 Science Chapter 4 Case Based Questions - Carbon and its compounds
| Table of contents |

|
| Case Study - 1 |

|
| Case Study - 2 |

|
| Case Study - 3 |

|
| Case Study - 4 |

|
| Case Study - 5 |

|
Case Study - 1
Ethanoic acid is commonly called acetic acid and belongs to a group of acids called carboxylic acids. 5-8% solution of acetic acid in water is called vinegar and is used widely as a preservative in pickles.
Q1: What is glacial acetic acid?
Ans: The melting point of ethanoic acid is 290K, so its often freezes during winter. Hence, gave rise to new name called as glacial acetic acid.
Q2: Complete the reaction: NaOH + CH3CH2COOH ?
Ans: NaOH + CH3CH2COOH ⇒ CH3CH2COONa + H2O
Q3: What is esterification reaction?
Ans: The reaction of carboxylic acid with an alcohol give rise to fruity smell called as esters. This process of the formation of esters is called esterification reaction.
Example: CH3COOH + CH3CH2OH + Conc. H2SO4 ⇒ CH3COOCH2CH3 + H2O
Q4: What happens when ethanoic acid is reacted with carbonates and bicarbonates?
Ans: They give rise to salt, Carbon dioxide, and water.
Q5: Write the reaction of ethanoic acid with sodium hydrogen carbonate?
Ans: CH3COOH + NaHCO3 ⇒ CH3COONa + H2O + CO2
Case Study - 2
Most dirt is oily in nature and as you know, oil does not dissolve in water. The molecules of soap are sodium or potassium salts of long-chain carboxylic acids. The ionic-end of soap interacts with water while the carbon chain interacts with oil. The soap molecules, thus form structures called micelles, where one end of the molecules is towards the oil droplet while the ionic-end faces outside. This forms an emulsion in water. The soap micelle thus helps in pulling out the dirt in water and we can wash our clothes clean
Q1: What is hydrophobic end?
Ans: Soap molecules have two ends in which one is hydrophobic end which interacts with hydrocarbons and do not dissolve in water.
Q2: Draw the structure of micelle.
Ans:
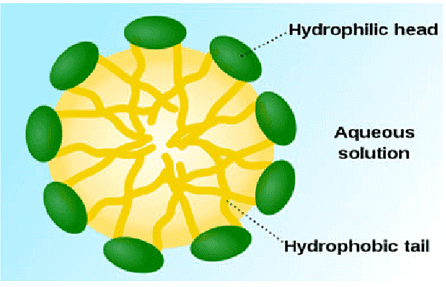
Q3: What are scums?
Ans: An insoluble substance(white precipitate) remains after washing with water. It is formed by the reaction of soaps with the calcium and magnesium salts.
Q4: What is hard water?
Ans: The water which contains Calcium and magnesium salts in it and form insoluble precipitates when treated with soap are called hard water.
Q5: To remove hardness of water, the water is treated with soap or detergent?
Ans: Detergent are effective in hard water as they contain sodium salts of sulphonic acid or ammonium salts with chlorides or bromides ions etc.
Case Study - 3
Carbon compounds can be easily oxidised on combustion. In addition to this complete oxidation, we have reactions in which alcohols are converted to carboxylic acids. We see that some substances are capable of adding oxygen to others. These substances are known as oxidisingagents.
Q1: Give two example of good oxidising agent.
Ans: Alkaline potassium permanganate or acidified potassium dichromate.
Q2: Complete the reaction: CH3CH2CH2OH + Alk. KMnO4?
Ans: CH3CH2CH2OH + Alk. KMnO4 ⇒ CH3CH2COOH.
Q3: What are the uses of alcohol?
Ans: Good solvent, used to make syrups & drinks.
Q4: Why Acidified potassium dichromate is called an oxidising agent?
Ans: It is because they can add oxygen to the reactant molecule very easily and convert them to acid.
Q5: What is the use of ethanoic acid?
Ans: Used as preservatives in pickle and also to make esters.
Case Study - 4
Carbon, in all its allotropic forms, burns in oxygen to give carbon dioxide along with the release of heat and light. Most carbon compounds also release a large amount of heat and light on burning. Saturated hydrocarbons will generally give a clean flame while unsaturated carbon compounds will give a yellow flame with lots of black smoke.
Q1: Complete the reaction: CH3CH2OH +O2 gives
Ans: CH3CH2OH + O2 ⇒ CO2 + H2O + heat & light.
Q2: What is the reason for incomplete combustion?
Ans: When the supply of air is limited for combustion, then the fuel goes partial combustion which results in sooty flame.
Q3: Combustion is an oxidation or reduction type of reaction?
Ans: It is an oxidation type of reaction as oxygen get added to reactant.
Eg: C + O2 ⇒ CO2 + heat aand light.
Q4: What is homologous series?
Ans: A series of compound in which the same functional group substitutes for hydrogen in a carbon chain.
Example: C2H6 & C3H6. – these differ by CH2 unit.
Case Study - 5
Carbon has the unique ability to form bonds with other atoms of carbon, giving rise to large molecules. This property is called catenation. These compounds may have long chains of carbon, branched chains of carbon or even carbon atoms arranged in rings. In addition, carbon atoms may be linked by single, double or triple bonds.
Q1: What are saturated compounds?
Ans: Compounds of carbon that are linked by only single bond between the carbon atoms are called as saturated compounds.
Example: C2H6, CH4
Q2: What is the another versatile property of carbon?
Ans: The tetravalent nature of carbon i.e it has four valency and it is capable of bonding with other four atoms of carbon or any other atom of monovalency.
Q3: Give two example of unsaturated compounds.
Ans: Ethene- C2H4 & Ethyne- C2H2
Q4: Name any one element other than carbon which show catenation property?
Ans: Sulphur i.e S8 molecule.














