Class 10 Exam > Class 10 Notes > Geography for GCSE/IGCSE > Causes of Earthquakes & Volcanoes
Causes of Earthquakes & Volcanoes | Geography for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Earth's Structure |

|
| Plate tectonics |

|
| Causes of Earthquakes & Volcanic Eruptions |

|
| Causes of Earthquake Hazards |

|
Earth's Structure
The Earth is composed of several layers, each with unique characteristics and compositions.
- Inner Core: The inner core is a solid and dense layer at the center of the Earth, approximately 1400km in diameter. It consists mainly of iron and nickel and reaches temperatures as high as 5500°C.
- Outer Core: Surrounding the inner core, the outer core is a semi-molten metal layer, about 2100km thick. Temperatures in the outer core range between 5000-5500°C.
- Mantle: Beneath the outer core lies the mantle, a semi-molten layer approximately 2900km thick. It is less dense than the outer core and plays a crucial role in the Earth's geological processes.
- Crust: The Earth's crust varies in thickness and is made up of two main types: continental crust and oceanic crust.
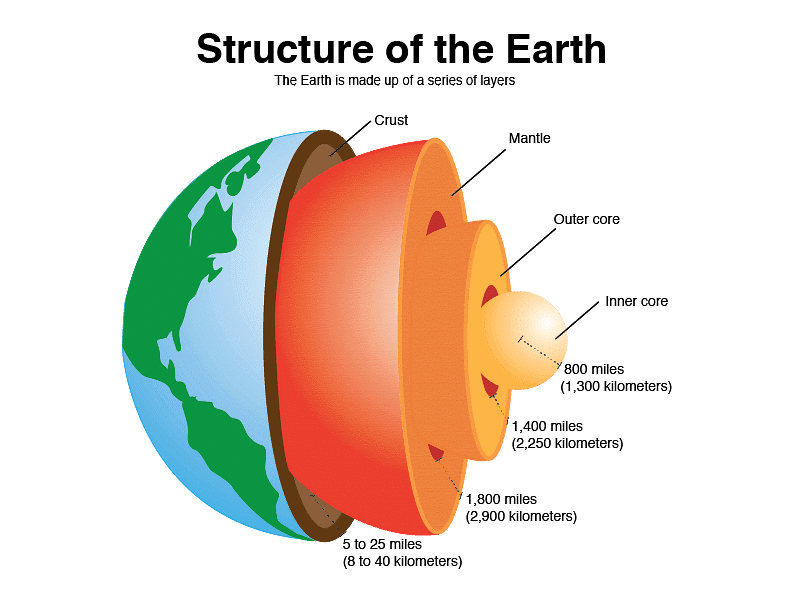
Crust
- There are two types of crust:
- Continental Crust: The continental crust is thicker, ranging from 25-90km. It is older and less dense compared to oceanic crust.
- Oceanic Crust: On the other hand, oceanic crust is thinner, about 5-10km in thickness. It is heavier and denser than continental crust.
- Oceanic crust is continually formed and destroyed due to plate tectonics. It is denser, leading it to subduct beneath the less dense continental crust.
Plate tectonics
- The Earth's crust is divided into several tectonic plates.
- These plates travel atop the partially molten mantle beneath them.
- The motion of the plates is influenced by the convection currents occurring within the mantle.
- A plate boundary or margin refers to the area where two plates come into contact.
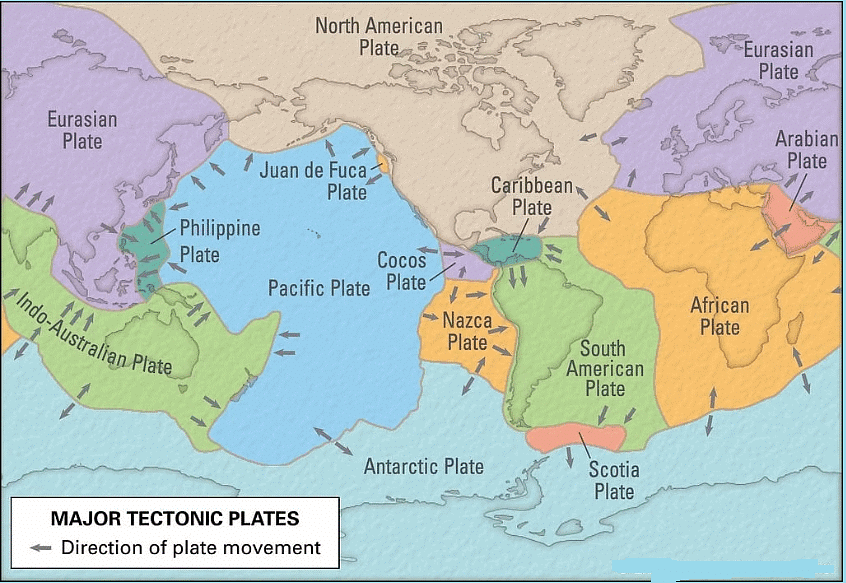
Types of plate boundary
- Volcanic eruptions and earthquakes often occur near plate boundaries.
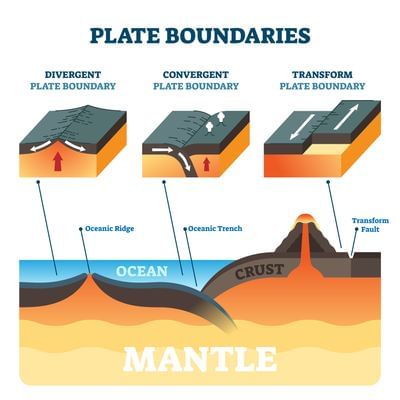
- There are four main types of plate boundaries:
- Divergent Boundaries (Constructive): Plates move apart, creating new crust.
- Convergent Boundaries (Destructive): Plates collide, leading to subduction or mountain formation.
- Transform Boundaries (Conservative): Plates slide past each other horizontally.
- Collision Boundaries: Plates crash into each other, forming extensive mountain ranges.
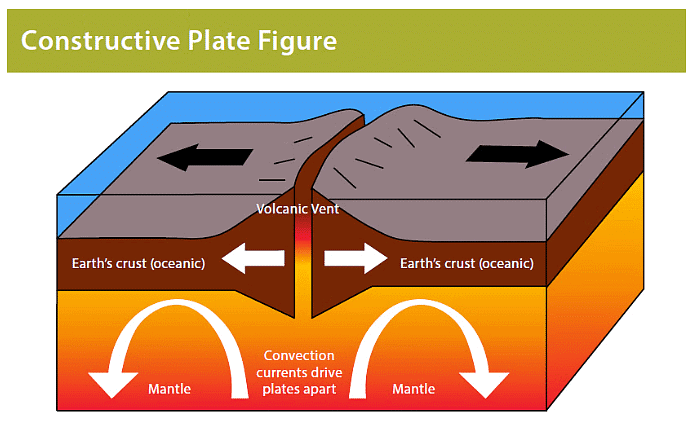
Divergent (constructive) plate boundary
- At a divergent boundary, the plates are separating from each other.
- The Mid-Atlantic Ridge serves as an illustration of a divergent plate boundary.
- This type of plate boundary is associated with both volcanic eruptions and earthquakes.
Convergent Plate Boundary
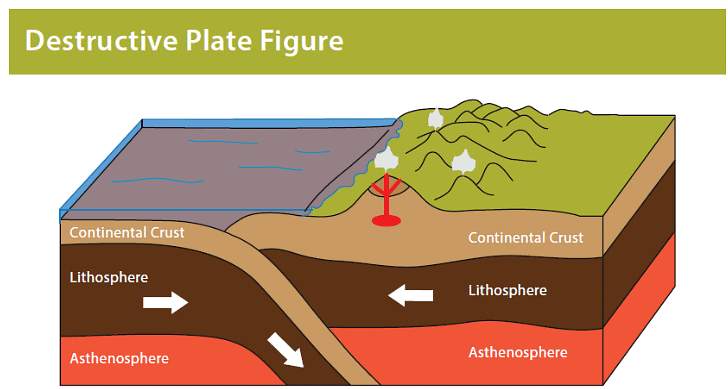
- At a convergent boundary, tectonic plates move towards each other.
- The denser oceanic plate subducts beneath the lighter continental plate.
- An example of a convergent boundary is the interaction between the Nazca plate and the South American plate.
- Both volcanic eruptions and earthquakes are common at convergent boundaries.
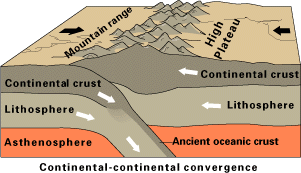
Collision Boundary
- When plates of similar density collide at a boundary, they push against each other without subducting.
- This compression forces the land upwards, creating majestic fold mountains like the Himalayas.
- Earthquakes represent the primary hazard at this type of plate boundary.
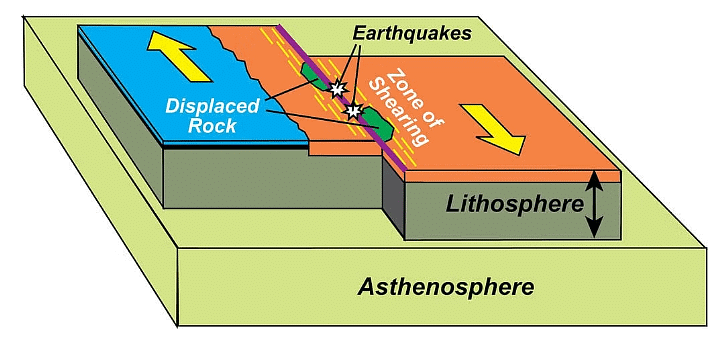
Transform (Conservative) Boundary
- At a transform boundary, plates slide past each other in opposite or different speeds.
- Earthquakes are the primary hazard at this boundary.
Question for Causes of Earthquakes & VolcanoesTry yourself: Which layer of the Earth is mainly composed of iron and nickel?View Solution
Causes of Earthquakes & Volcanic Eruptions
- Volcanoes are found at divergent (constructive), convergent (destructive) plate boundaries, and hot spots due to the movement of tectonic plates.
- Volcanoes do not form at collision boundaries or transform (conservative) boundaries.
Volcanoes at constructive boundaries
- At a divergent (also known as constructive) boundary, the tectonic plates are separating from one another.
- Divergent plate boundaries frequently occur beneath the ocean.
- Lava emerges through the fissure created as the plates diverge.
- The lava cools and solidifies, resulting in the formation of fresh crust.
- At divergent plate boundaries, the lava typically has a low viscosity, and eruptions are less violent.
- These eruptions give rise to shield volcanoes, characterized by gently sloping sides.
Volcanoes at destructive boundaries
- At a destructive (also known as convergent) boundary, the tectonic plates are converging towards one another.
- The denser oceanic plate descends beneath the lighter continental plate through a process called subduction.
- In the subduction zone where the two plates collide, friction occurs.
- The friction generates heat, causing the plate material to melt and form magma.
- This magma ascends to the surface through fissures in the crust.
- Upon reaching the surface, the cooling lava and ash accumulate, leading to the formation of a volcano.
- At destructive plate boundaries, the lava typically has high viscosity, resulting in explosive eruptions.
- These eruptions tend to give rise to composite or stratovolcanoes.
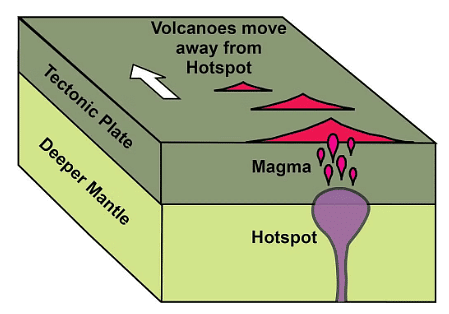
Volcanoes at hot spots
At a hot spot, a tectonic plate traverses a magma plume.
- The magma ascends to the surface via fissures in the crust.
- As the tectonic plate gradually moves over the magma plume, it can result in the formation of a series of islands, such as Hawaii.
Causes of Earthquake Hazards
- Earthquakes may happen in various locations but are most common at or near plate boundaries.
- Earthquakes occur at all types of plate boundaries: divergent (constructive), convergent (destructive), collision, and transform (conservative).
Plate Boundary Types and Earthquake Characteristics
- At divergent (constructive) plate boundaries, earthquakes are typically milder as the plates are moving away from each other.
- Conversely, at convergent (destructive), collision, and conservative (transform) plate boundaries, earthquakes tend to be more intense.
Question for Causes of Earthquakes & VolcanoesTry yourself: What type of volcanoes are formed at divergent plate boundaries?View Solution
The document Causes of Earthquakes & Volcanoes | Geography for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 is a part of the Class 10 Course Geography for GCSE/IGCSE.
All you need of Class 10 at this link: Class 10
|
55 videos|68 docs|78 tests
|
FAQs on Causes of Earthquakes & Volcanoes - Geography for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10
| 1. What are the main causes of earthquakes and volcanic eruptions? |  |
Ans. The main causes of earthquakes are the movement of tectonic plates, volcanic activity, and human activities such as mining and reservoir-induced seismicity. Volcanic eruptions are mainly caused by the movement of magma beneath the Earth's surface, leading to pressure buildup and eventual release.
| 2. How does the Earth's structure contribute to the occurrence of earthquakes and volcanic eruptions? |  |
Ans. The Earth's structure, specifically the presence of tectonic plates and the different types of crust (continental and oceanic), plays a significant role in the occurrence of earthquakes and volcanic eruptions. The movement of these plates and the interactions at plate boundaries create the conditions for seismic activity and volcanic eruptions.
| 3. What is the relationship between plate boundaries and volcanic eruptions? |  |
Ans. Plate boundaries are where tectonic plates interact, and these interactions often result in volcanic eruptions. At convergent boundaries, where plates collide, one plate may be forced beneath the other, leading to the formation of magma and volcanic activity. At divergent boundaries, where plates move apart, magma rises to the surface, creating volcanic eruptions.
| 4. How do convection currents contribute to plate movement and the occurrence of earthquakes and volcanic eruptions? |  |
Ans. Convection currents in the Earth's mantle drive the movement of tectonic plates. As these currents move molten rock within the mantle, they create forces that push and pull on the plates, leading to plate movement. This movement can cause earthquakes and volcanic eruptions at plate boundaries where the stresses are released.
| 5. What role do collision boundaries play in the occurrence of earthquakes and volcanic eruptions? |  |
Ans. Collision boundaries, where two tectonic plates collide, can lead to the formation of mountain ranges and volcanic activity. The intense pressure and friction at these boundaries can cause earthquakes as the plates interact and deform. Additionally, the collision of plates can force magma to the surface, resulting in volcanic eruptions.
Related Searches




















