Cell Cycle and Cell Division Class 11 Notes Biology Chapter 10
1. Introduction: It is the process by which a mature cell divides and forms two nearly equal daughter cells which resemble the parental cell in a number of characters.
2. Discovery: Prevost and Dumas (1824) first to study cell division during the cleavage of zygote of frog.
3. Nagelli (1846) was the first to propose that new cells are formed by the division of pre-existing cells.
4. Rudolf virchow (1859) proposed “omnis cellula e cellula” and “cell lineage theory”.
5. A cell divides when it has grown to a certain maximum size which disturb the karyoplasmic index (KI)/Nucleoplasmic ratio (NP)/Kernplasm connection.
6. Two processes take place during cell reproduction.
- Cell growth: (Period of synthesis and duplication of various components of cell).
- Cell division: (Mature cell divides into two cells).
7. Cell cycle: Howard and Pelc (1953) first time described it. The sequence of events which occur during cell growth and cell division are collectively called cell cycle. Cell cycle completes in two steps:
- Interphase
- M-phase/Dividing phase
(i) Interphase: It is the period between the end of one cell division to the beginning of next cell division. It is also called resting phase or not dividing phase. But, it is actually highly metabolic active phase, in which cell prepares itself for next cell division. In case of human beings it will take approx 25 hours. Interphase is completed in to three successive stages.
(a) G1 phase/Post mitotic/Pre-DNA synthetic phase/Gap Ist
(b) S-phase/Synthetic phase
(c) G2-phase/Pre mitotic/Post synthetic phase/gap-IInd
(ii) M-phase/Dividing phase/Mitotic phase
(a) Nuclear division i.e. karyokinesis occurs in 4 phases – prophase, metaphase, anaphase and telophase. It takes 5-10% (shortest phase) time of whole division.
(b) Cytokinesis: Division of cytoplasm into 2 equal parts. In animal cell, it takes place by cell furrow method and in plant cells by cell plate method.
8. Duration of cell cycle: It depends on the type of cell and external factors such as temperature, food and oxygen. Time period for G1, S, G2 and M-phase is species specific under specific environmental conditions. e.g. 20 minutes for bacterial cell, 8-10 hours for intestional epithelial cell, and onion root tip cells may take 20 hours.
9. Regulation of cell cycle: Stage of regulation of cell cycle is G1 phase during which a cell may follow one of the three options.
- It may start a new cycle, enter the S-phase and finally divide.
- It may be arrested at a specific point of G1 phase.
- It may stop division and enter G0 quiscent stage. But when conditions change, cell in G0 phase can resume the growth and reenter the G1 phase.
10. Cell division is of three types, Amitosis, Mitosis and Meiosis.
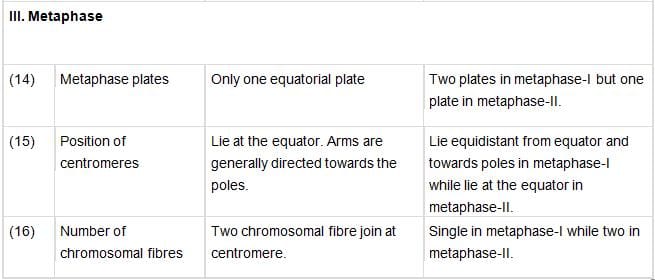
11. Difference between cell Mitosis and Meiosis





12. Types of Mitosis
- Anastral mitosis: It is found in plants in which spindle has no aster.
- Amphiastral mitosis: It is found in animals in which spindle has two asters, one at each pole of the spindle. Spindle is barrel-like.
- Intranuclear or Promitosis: In this nuclear membrane is not lost and spindle is formed inside the nuclear membrane e.g. Protozoans (Amoeba) and yeast. It is so as centriole is present within the nucleus.
- Extranuclear or Eumitosis: In this nuclear membrane is lost and spindle is formed outside nuclear membrane e.g. in plants and animals.
- Endomitosis: Chromosomes and their DNA duplicate but fail to separate which lead to polyploidy e.g. in liver of man, both diploid (2N) and polyploid cells (4N) have been reported. It is also called endoduplication and endopolyploidy.
- Dinomitosis: In which nuclear envelope persists and microtubular spindle is not formed. During movement the chromosomes are attached with nuclear membrane.
Types of meiosis: On the basis of time and place, meiosis is of three types
- Gametic/Terminal meiosis: In many protozoans, all animals and some lower plants; meiosis takes place before fertilization during the formation of gametes. Such meiosis is described as gametic or terminal.
- Zygotic or Initial Meiosis: In fungi, certain protozoan groups, and some algae fertilization is immediately followed by meiosis in the zygote, and the resulting adult organisms are haploid. Such a meiosis is said to be zygotic or initial. This type of life cycle with haploid adult and zygotic meiosis is termed the haplontic cycle.
- Sporogenetic Meiosis
(a) Diploid sporocytes or spore mother cells of sporophytic plant, undergo meiosis to form the haploid spores in the sporangia.
(b) Haploid spore germinates to form haploid gametophyte which produces the haploid gametes by mitosis.
(c) Haploid gametes fuse to form diploid zygote which develops into diploid sporophyte by mitotic divisions. e.g. in higher plants like pteridophytes, gymnosperms and angiosperms.
FAQs on Cell Cycle and Cell Division Class 11 Notes Biology Chapter 10
| 1. What is the cell cycle and why is it important for cell division? |  |
| 2. What are the different phases of the cell cycle? |  |
| 3. How is the cell cycle regulated? |  |
| 4. What happens during mitosis? |  |
| 5. What are the consequences of abnormal cell cycle regulation? |  |

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|


















