UPSC Exam > UPSC Notes > Indian Polity for UPSC CSE > Central Bureau of Investigation - (Part - 2)
Central Bureau of Investigation - (Part - 2) | Indian Polity for UPSC CSE PDF Download
Steps Taken
CVC ACT, 2003
- In Vineet Narayan vs. Union of India (1998), the apex court laid down that the director, CBI shall be appointed on the recommendation of a committee comprising the Central Vigilance Commissioner, vigilance commissioners, secretary (home) and secretary (personnel), and that he shall have a minimum tenure of two years. In pursuant with SC order, the CBI Director has been provided security of tenure in office by CVC Act 2003
- The Central Vigilance Commission (CVC) was given statutory status free of control from any executive authority as per the provisions of Central Vigilance Commission (CVC) Act, 2003. It was authorised to exercise superintendence over the CBI in the investigation of offences committed under the Prevention of Corruption Act.

The Lokpal and Lokayuktas Act (2013)
It amended the Delhi Special Police Establishment Act (1946) and made the following changes with respect to the composition of the CBI:
- The Central Government shall appoint the director of CBI on the recommendation of a three-member committee consisting of the Prime Minister as Chairperson, the Leader of Opposition in the Lok Sabha and the chief justice of India or judge of the Supreme Court nominated by him.
- There shall be a Directorate of prosecution headed by a Director for conducting the prosecution of cases under the Lokpal and Lokayuktas Act, 2013. He shall function under the overall supervision and control of the Director of the CBI. He shall be appointed by the Central Government on the recommendation of the Central Vigilance Commission and hold office for a period of two years.
- The Central Government shall appoint officers of the rank of SP and above in the CBI on the recommendation of a Committee consisting of the Central Vigilance Commissioner as Chairperson, the Vigilance Commissioners, the secretary of the Home Ministry and the Secretary of the Department of Personnel.
Delhi Special Police Establishment (Amendment) Act, 2014
It made a change in the composition of the Committee related to the appointment of the Director of C.B.I. It states that where there is no recognized leader of the Lok Sabha, then the leader of the single largest opposition party in the Lok Sabha would be a member of that committee.
Major Committees and recommendations
- P. Singh Committee, 1978 recommended the enactment of a comprehensive central legislation to remove the deficiency of not having a central investigative agency with a self-sufficient statutory charter of duties and functions.
- Estimates Committee of the Parliament (1991-92) under Jaswant Singh had recommended that the CBI be given statutory status and have legal powers to investigate cases with inter-state ramifications.
- The 19th report of the parliamentary standing committee (2007) recommended that a separate Act should be promulgated for the CBI in tune with the requirements of the time to ensure credibility and impartiality.
- The 24th report of the parliamentary standing committee (2008) was of the unanimous opinion that “the need of the hour is to strengthen the CBI in terms of legal mandate, infrastructure and resources”.
- Parliamentary Committee (2015) recommended integrating Central Vigilance Commission and anti-corruption wing of the CBI to work directly under the command and control of Lokpal to deal with corruption cases.
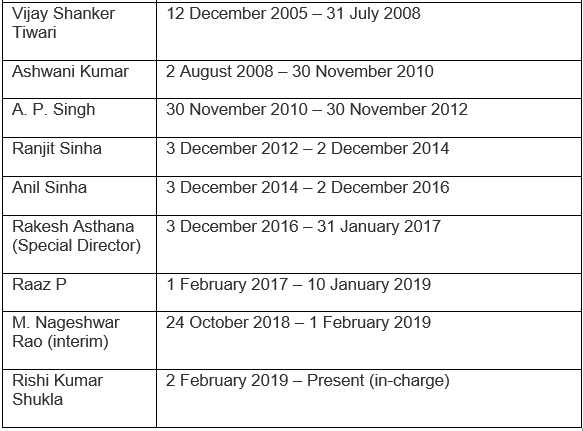
List of CBI Directors of India
The following tables give information about the CBI Directors through the years: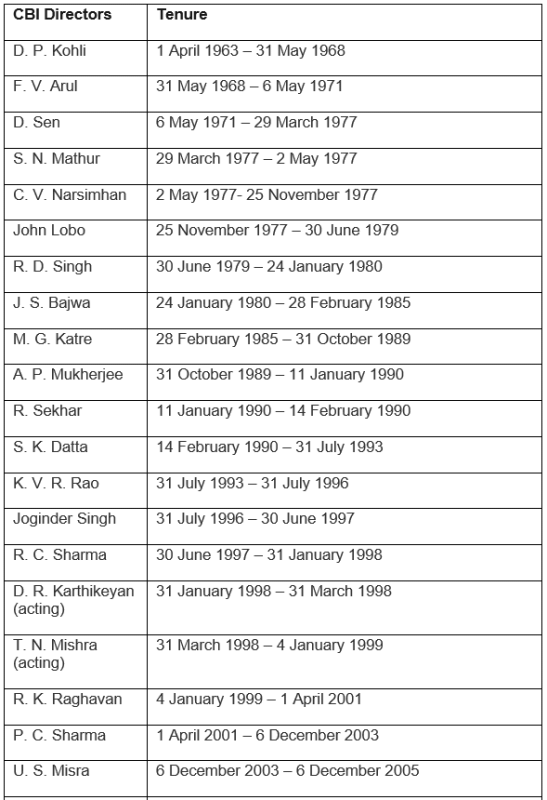
Way Ahead
- A comprehensive new central law should be formulated for the governance of the CBI and ensure autonomy to the agency. Further, the charter of duties should be clearly defined and stated.
- Measures should be taken to restore the institutional integrity of the CBI and boost public confidence in the institution.
- CBI should develop its own dedicated cadre of officers who are not bothered about deputation and abrupt transfers.
- The infrastructure and human resources should be strengthened for effective investigation and to avoid delays in concluding investigations.
- Measures should be taken to ensure transparency in the process of investigations by CBI. Further, there should be public discourse on whether CBI should be brought under the RTI Act.
The document Central Bureau of Investigation - (Part - 2) | Indian Polity for UPSC CSE is a part of the UPSC Course Indian Polity for UPSC CSE.
All you need of UPSC at this link: UPSC
|
142 videos|777 docs|202 tests
|
FAQs on Central Bureau of Investigation - (Part - 2) - Indian Polity for UPSC CSE
| 1. What is the role of the Central Bureau of Investigation (CBI) in India? |  |
Ans. The Central Bureau of Investigation (CBI) is the premier investigative agency in India. It is responsible for investigating cases of corruption, economic offenses, special crimes, and cases of national importance as directed by the central government. The CBI also acts as the Interpol agency of India and assists in international investigations.
| 2. How does the Central Bureau of Investigation (CBI) handle corruption cases in India? |  |
Ans. The Central Bureau of Investigation (CBI) handles corruption cases in India by conducting thorough investigations into allegations of corruption and collecting evidence. The agency has the authority to conduct searches, make arrests, and file charges against the accused. The CBI also works closely with other law enforcement agencies and the judicial system to ensure fair and impartial trials.
| 3. Can the Central Bureau of Investigation (CBI) investigate cases without the permission of the state government? |  |
Ans. Yes, the Central Bureau of Investigation (CBI) can investigate cases without the permission of the state government under certain circumstances. The agency has the power to take up cases that fall under the jurisdiction of the central government or cases that have been referred to it by the courts. However, for cases that fall under the jurisdiction of the state government, the CBI requires the consent of the state government to initiate an investigation.
| 4. How does the Central Bureau of Investigation (CBI) maintain its independence in India? |  |
Ans. The Central Bureau of Investigation (CBI) maintains its independence in India through various measures. The agency functions under the administrative control of the Department of Personnel and Training, which ensures its autonomy. The CBI follows a strict code of conduct and is guided by its own manual of instructions. The agency also has a separate budget and is not subject to financial control by any state government. Moreover, the CBI is accountable to the Central Vigilance Commission, which oversees its functioning and ensures transparency.
| 5. What is the process for filing a complaint with the Central Bureau of Investigation (CBI) in India? |  |
Ans. To file a complaint with the Central Bureau of Investigation (CBI) in India, one can either approach the agency directly or submit a complaint through the CBI website. The complaint should provide detailed information about the alleged offense and the individuals involved. It is advisable to provide supporting documents or evidence to strengthen the complaint. The CBI will then assess the complaint and initiate an investigation if it falls within their jurisdiction and meets the necessary criteria.
Related Searches
















