Chapter - 3: Salient Features of the Constitution (Gist) | Additional Study Material for UPSC PDF Download
Salient Features of the Constitution
- The framers of the Indian Constitution have borrowed various provisions from different constitutions across the globe. But still, the Indian Constitution has several salient features which distinguish it from others.
- The Constitution has undergone several amendments since its adoption in November 1949. Some of the important amendments to the Constitution include 7th, 42nd, 44th, 73rd, 74th, 97th and 101st amendment acts which changed the Indian Constitution to a great extent.
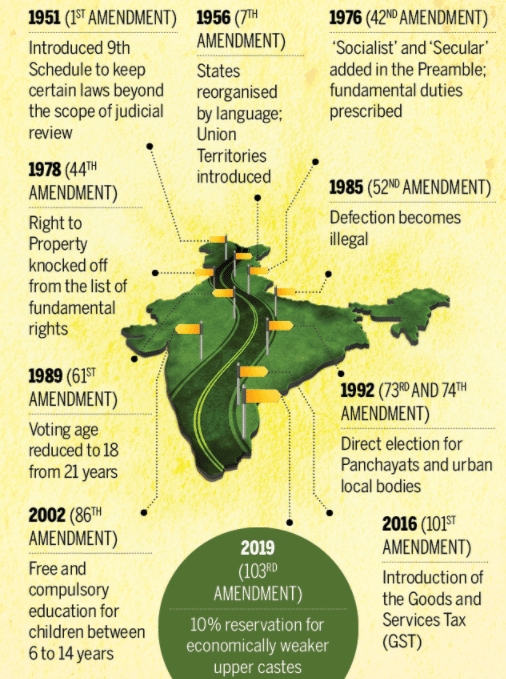 Major Constitutional Amendments that Changed the Course of India
Major Constitutional Amendments that Changed the Course of India
- 42nd amendment act is also known as the ‘Mini Constitution’ due to the important and large number of changes made by it in various parts of the Constitution.
- But, Supreme Court in famous Keshvananda Bharti Case (1973), ruled that the article 368 cannot alter the basic structure of the Constitution.
Salient Features of Indian Constitution
1. Lengthiest Written Constitution
- Indian Constitution is the lengthiest written constitution of the world due to its diverse geography, vast historical background along with the provision of single Constitution for both Center and State and dominance of lawyers in the Constituent Assembly.
- Originally (1949), the Constitution had a Preamble, 395 Articles, 22 Parts and 8 Schedules.
- Presently (January 2020), the Constitution has a Preamble, 448 Articles, 25 Parts and 12 Schedules.
12 Schedules of Indian Constitution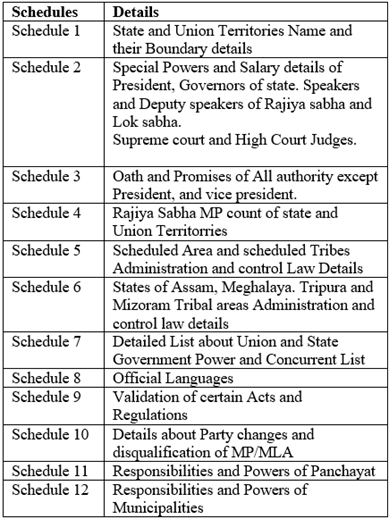
- Till January 2020, a total of 104 amendments have been incorporated in the Indian Constitution.
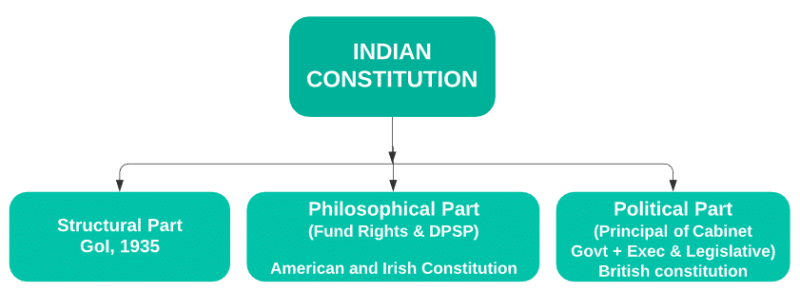
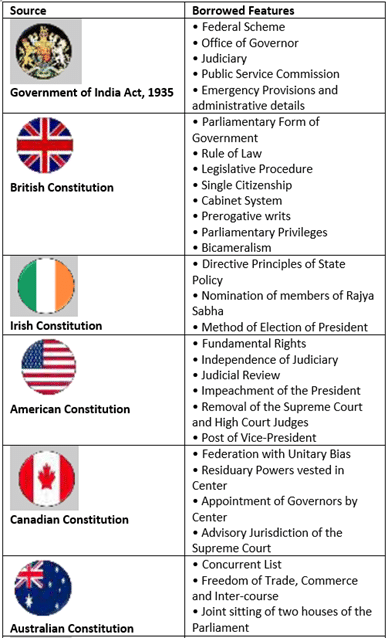
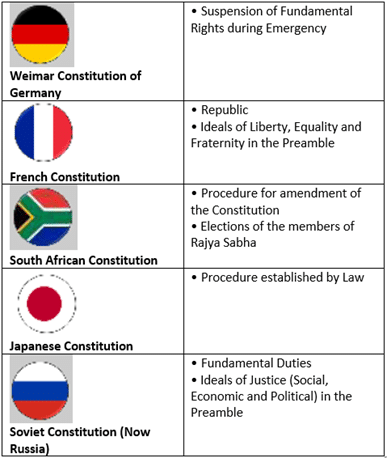
2. Drawn from Various Sources
 3. Blend of Rigidity and Flexibility
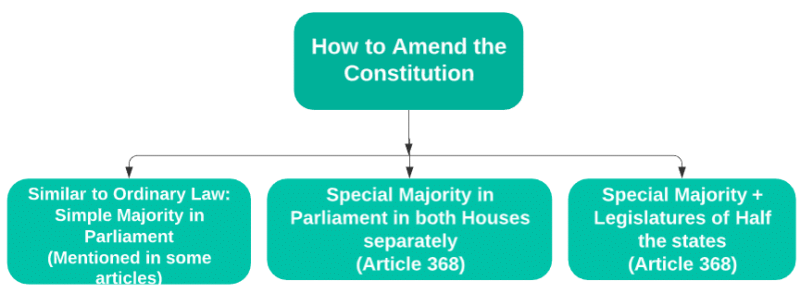
3. Blend of Rigidity and Flexibility
- The Constitution is a blend of both flexibility and rigidity as some features can be amended easily while others cannot be.
- Some provisions can be amended by Simple Majority of the Parliament while Article 368 provides for two types of amendments:
(i) Amendment by a special majority of Parliament
(ii) Amendment by a special majority of Parliament and with the ratification by half of the total states
4. Federal System with Unitary Bias
(i) Federal features include
- Two Government
- Division of Powers
- Written Constitution
- Supremacy of Constitution
- Rigidity of Constitution
- Independent Judiciary
- Bicameralism
(ii) Unitary or non-federal features include
- Strong Center
- Single Constitution
- Single Citizenship
- Flexibility of Constitution
- Integrated Judiciary
- Appointment of state governors by the Center
- All-India Services
- Emergency Provisions
5. Parliamentary form of Government
(i) Also known as the Westminster Model of Government, Responsible Government and Cabinet Government.
(ii) It is based on the principle of co-operation and co-ordination between the legislative and executive organs.
(iii) Features of Parliamentary Government in India are
- Presence of nominal and real executives
- Majority party rule
- Executive is responsible to the legislature
- Membership of the ministers in the legislature
- Leadership of the Prime Minister or the Chief Minister
- Dissolution of the lower house
6. Synthesis of Parliamentary Sovereignty and Judicial Supremacy
- Indian Constitution provides for a unique blend of the principle of Parliamentary sovereignty and Judicial supremacy
- The Supreme Court of India can declare the parliamentary laws as unconstitutional through its power of judicial review while the Parliament can amend the major portion of the Constitution through its constituent power.
7. Integrated and Independent Judiciary
- India has a hierarchy of courts from the Supreme Court being the apex court of appeal and guarantor of the fundamental rights of citizens and guardian of the Constitution, followed by High Courts and other subordinate courts.
- Constitution has various provisions to ensure its independence which include security of tenure of judges, all expenses of the Supreme Court to be charged on the Consolidated Fund of India, prohibition on discussing the conduct of judges in the legislature, etc.
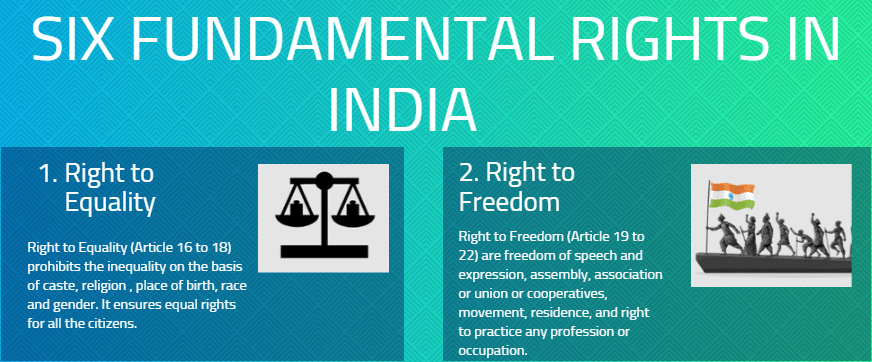
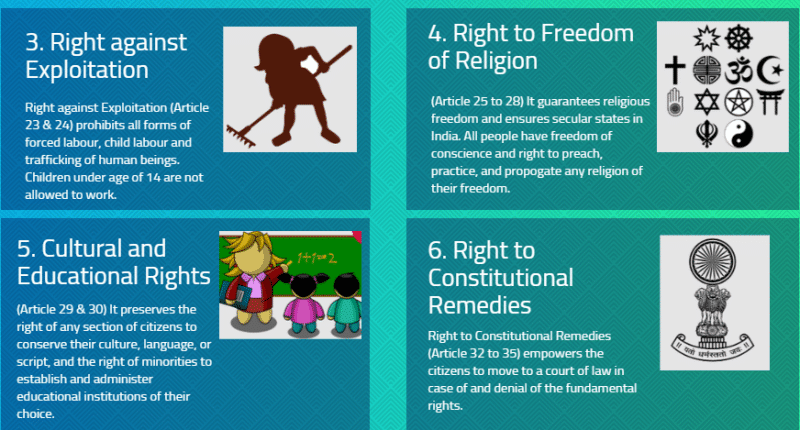
8. Fundamental Rights
- Part III of the Indian Constitution guarantees six fundamental rights to all its citizens.


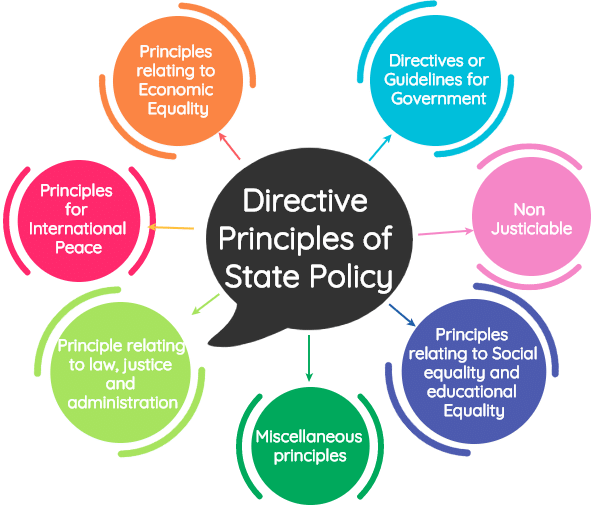
9. Directive Principles of State Policy
- Included in Part IV of the Indian Constitution.
- Classified into three categories: Socialistic, Gandhian and Liberal-intellectual.
- Promote the ideal of social and economic democracy and seek to establish a welfare state in India.
10. Fundamental Duties
- Part IV-A of the Indian Constitution deals with the Fundamental Duties of the citizens.
- It has only one article 51-A which specify 11 fundamental duties.
- It was not the part of original Constitution and added by the 42nd Constitutional Amendment Act of 1976 on the recommendations of the Swaran Singh Committee.
- The 86th Constitutional Amendment Act of 2002 added one more fundamental duty.
11. A Secular State
- The Constitution of India establishes the country as a secular state i.e. it does not uphold any religion as its official religion.
- The term ‘Secular’ was added to the Preamble of the Constitution by the 42nd Constitutional Amendment Act of 1976.
- It embodies the positive concept of secularism i.e. giving equal respect to all religions or protecting all religions equally.
- Abolished the system of Communal representation prevalent during British India but provides for temporary reservation of seats for the scheduled castes and scheduled tribes to ensure adequate representation to them.
12. Universal Adult Franchise
- It adopts Universal Adult Franchise as a basis of elections to the Lok Sabha and the State Legislative Assemblies.
- Every citizen who is not less than 18 years of age (reduced from 21 to 18 by 61 st Constitutional Amendment Act of 1988) has a right to vote without any discrimination of caste, race, religion, sex, literacy, wealth and so on.
13. Single Citizenship
- Constitution though provides for federalism and dual polity in India but provisions for only one citizenship i.e. Indian Citizenship
- Single Citizenship provides the same political and civil rights all over the country
14. Independent Bodies
- Provides for some independent bodies including Election Commission, Comptroller and Auditor General of India, Union Public Service Commission and State Public Service Commission
15. Emergency Provisions
The Constitution envisages three types of emergencies, namely:
- National emergency on the ground of war or external aggression or armed rebellion under article 352.
- State emergency (President’s rule) on the ground of failure of Constitutional machinery in the states under article 365.
- Financial emergency on the ground of threat to financial stability or credit of India under article 360.
16. Three-tier Government
- The 73rd and 74th Constitutional Amendment Acts of 1992 have added a third-tier of Government.
- 73rd Constitutional Amendment Act of 1992 gave constitutional recognition to the Panchayats and added part IX and schedule 11 to the Constitution.
- 74th Constitutional Amendment Act of 1992 gave constitutional recognition to municipalities by adding Part IX-A and Schedule 12 to the Constitution.
17. Co-operative Societies
- The 97th Constitutional Amendment Act of 2011 gave constitutional status and protection to co-operative societies.
- The new Part IX-B contains various provisions related to co-operative societies.
Criticism of the Indian Constitution
- Borrowed Constitution: Indian constitution has been criticized by describing it as a bag of borrowings or hotchpotch Constitution or a patchwork as all the major provisions taken from different Constitutions across the globe.
- A Carbon Copy of the 1935 Act:
(i) N. Srinivasan said that both language and substance of the Constitution reflects a close copy of the 1935 Act.
(ii) British Constitutionalist, Sir Ivor Jennings, also found the Indian Constitution as the textbook copy of the 1935 Act.
(iii) P. R. Deshmukh, a member of the Constituent Assembly, said that the Indian Constitution is essentially the Government of India Act of 1935 with only adult franchise added. - Un-Indian or Anti-Indian: Indian Constitution is Un-Indian or Anti-Indian as it does not reflect the political traditions and the spirit of India.
- Un-Gandhian Constitution: It is Un-Gandhian because it does not contain the philosophy and ideals of Gandhi Ji which envisioned it to be raised and built upon village panchayats and districts panchayats.
- Elephantine Size: Very lengthy and complicated
- Paradise of the Lawyers: Too legalistic and very complicated due to adoption of legal language and phraseology.
|
20 videos|561 docs|160 tests
|
FAQs on Chapter - 3: Salient Features of the Constitution (Gist) - Additional Study Material for UPSC
| 1. What are the salient features of the Constitution? |  |
| 2. How long is the Constitution of India? |  |
| 3. What is the flexibility of the Indian Constitution? |  |
| 4. What is the federal structure of the Indian Constitution? |  |
| 5. What are the fundamental rights and directive principles of state policy in the Constitution? |  |
|
20 videos|561 docs|160 tests
|

|
Explore Courses for UPSC exam
|

|