Humanities/Arts Exam > Humanities/Arts Notes > Political Science Class 12 > Chapter Notes: Contemporary Centres of Power
Alternative Centres of Power Class 12 Political Science
| Table of contents |

|
| What do we understand by Alternative Centres of Power? |

|
| European Union |

|
| Association of South East Asian Nations [ASEAN] |

|
| Rise of the Chinese Economy |

|
| India-China Relations |

|
What do we understand by Alternative Centres of Power?
Alternative centres of power refer to regional or international organizations that wield significant influence in global affairs alongside traditional superpowers like the United States, China, and Russia. These alternative centres often emerge from cooperation among multiple countries seeking to address common challenges or pursue shared interests.
European Union
- Many European leaders struggled with the question of how Europe should be regarded after the Second World War.
- The Second World War shattered the structure on which the European states had based their relations.
- The Cold War aided the integration of Europe after 1945. The European economy was revived by the extensive financial support by USA under the ‘Marshall Plan’.
- To direct help to the West European nations, the Organisation for European Economic Cooperation (OEEC) was founded in 1948. The establishment of the Council of Europe in 1949 was another advancement in political cooperation.
- The disintegration of USSR led to the formation of European Union in 1992 which laid the foundation for a common foreign and security policy, cooperation on justice and creation of a single currency.
 European Union Flag
European Union Flag
- The EU has evolved over time from an economic union to an increasingly political one.
- The EU has economic, political, diplomatic and military influence.
- The European Union has the largest economy in the world. In 2005, its GDP exceeded $12 trillion. Its currency Euro, can pose a threat to the dominance of the US dollar.
- On the political and diplomatic ground, France, the member of EU is a permanent member of the UN Security Council.
- The combined armed forces of the European Union are the second-largest in the world in terms of defence.
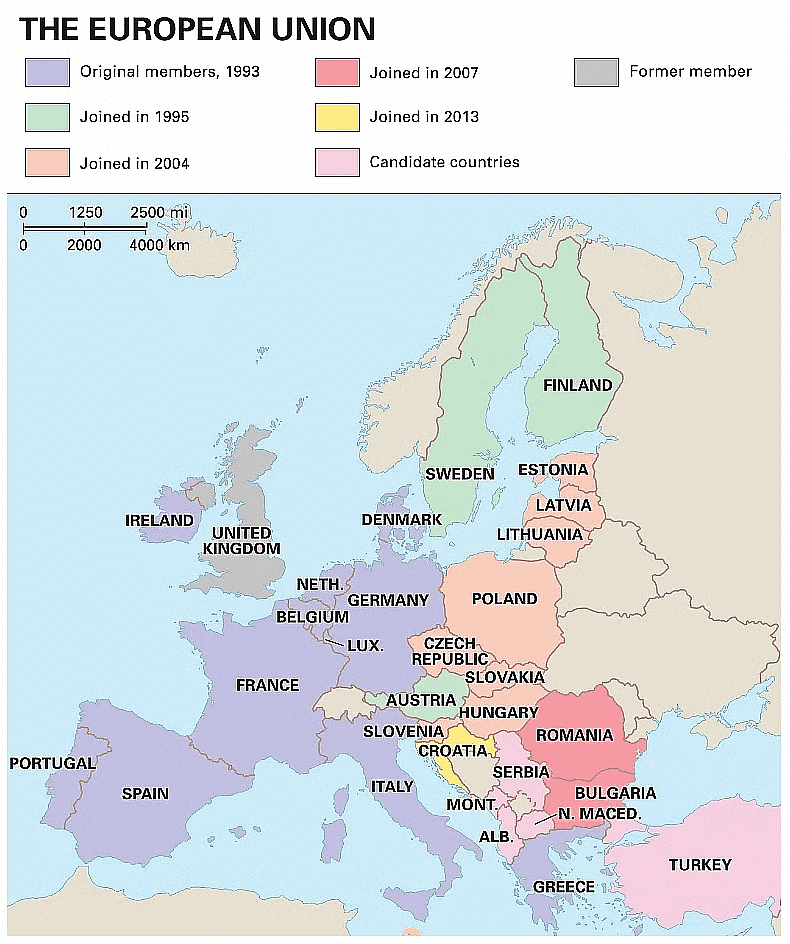 European Union Map
European Union Map
Question for Chapter Notes: Contemporary Centres of PowerTry yourself:Which Organsation has the largest economy in the world?
View Solution
Association of South East Asian Nations [ASEAN]
- South East Asia suffered greatly through repeated colonisation, including that of the European and Japanese empires, both before and during the Second World War.
- There were problems of nation-building, ravages of poverty and economic backwardness and a pressure to align with any of the two super blocs.
- As an alternative to the Bandung Conference and the Non-Aligned Movement, the South East Asian countries founded the Association of South East Asian Nations (ASEAN) in 1967.
- The ten rice stalks that make up the ASEAN emblem stand in for the ten South East Asian nations united in friendship and unity. The circle represents ASEAN's unity.
 ASEAN Emblem with ten nations
ASEAN Emblem with ten nations
- There were five founding countries-Indonesia, Malaysia, Philippines, Singapore and Thailand.
- The objectives of ASEAN was to accelerate economic growth, social progress, promote regional peace, stability and cultural development.
- The members of the association promoted ASEAN way, a form of interaction that is informal, non-confrontationist and cooperative.
- An ASEAN community with three pillars—the ASEAN socio-cultural community, the ASEAN economic community, and the ASEAN security community—was founded in 2003.
- The member states promised to uphold peace, neutrality, cooperation, non-interference and respect for national differences and sovereign rights.
- The ASEAN Economic Community seeks to create a single market and to promote regional, social and economic development.
- According to ASEAN's vision 2020, the region will play an outward-looking role in the global community.
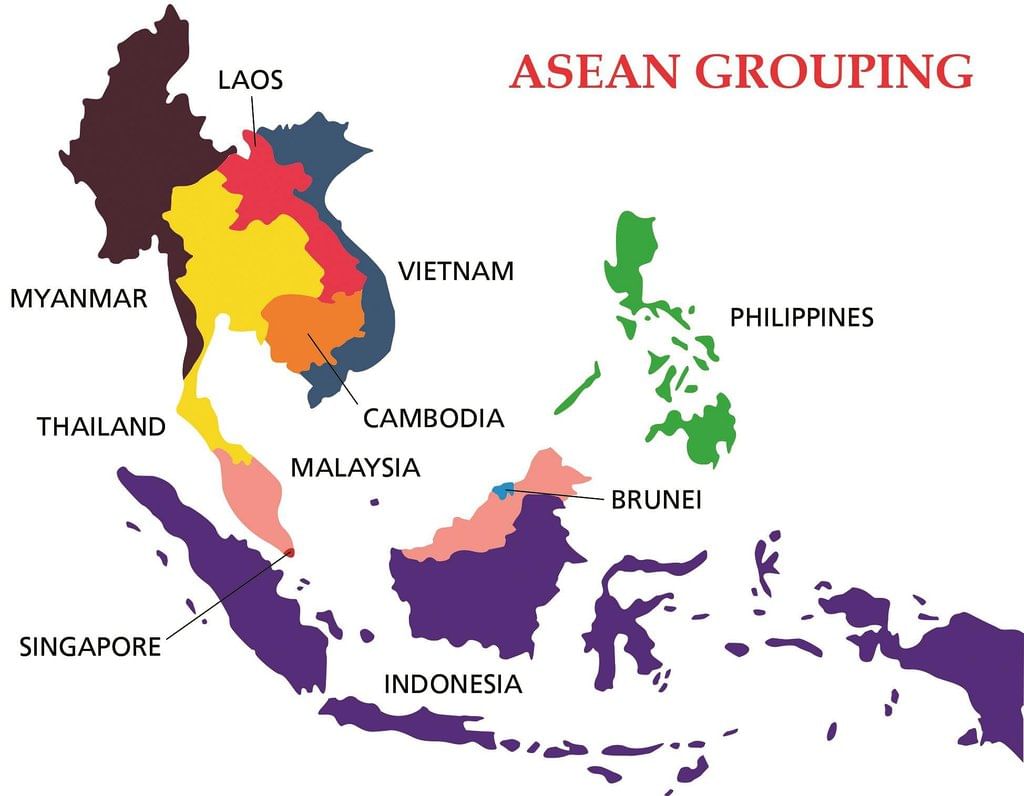 ASEAN Countries Map
ASEAN Countries Map
Rise of the Chinese Economy
- Since 1978, China has been growing as an economic power. By 2040, it is anticipated to surpass the US as the greatest economy in the world. China's economy was modelled on the Soviet model in 1949. It was now dependent on internal resources.
- During 1970’s, China established relations with the USA ending its political and economic isolation.
- Deng Xiaoping announced a "Open Door Policy" in 1978 with the goal of boosting production through foreign investments in capital and technology.
- Special economic zones were set up. State had a centralised role in setting up of China’s economy.
- Still, not everyone in China benefited from the Chinese economy. Working conditions and female employment are poor, and the unemployment rate has increased.
- However, regionally and globally, China has been in limelight economic power.
Question for Chapter Notes: Contemporary Centres of PowerTry yourself: What was the main objective of the Association of South East Asian Nations (ASEAN)?View Solution
India-China Relations
- India and China had a cordial relations since time immemorial. Both have political, economic and cultural relations.
- Following India's independence, both nations enjoyed peaceful relations. The slogan "Hindi-Chini-Bhai Bhai" gained popularity during this time.
- Very soon both the countries involved in border dispute. The difference aroused from the Chinese takeover of Tibet in 1950.
- India experienced military setbacks in the 1962 battle. Up until 1976, the two nations' military relations were deteriorating.
- It was during the visit paid by Indian Prime Minister Rajiv Gandhi to China in 1988 December, the relation between the two countries started improving.
The document Alternative Centres of Power Class 12 Political Science is a part of the Humanities/Arts Course Political Science Class 12.
All you need of Humanities/Arts at this link: Humanities/Arts
|
36 videos|436 docs|77 tests
|
FAQs on Alternative Centres of Power Class 12 Political Science
| 1. What are Alternative Centres of Power in the global context? |  |
Ans. Alternative Centres of Power refer to influential entities or regions that hold significant political, economic, and military power outside of the traditional superpowers like the United States and Russia.
| 2. How does the European Union function as an Alternative Centre of Power? |  |
Ans. The European Union is considered an Alternative Centre of Power due to its collective economic and political influence, as well as its ability to shape global policies and regulations.
| 3. How does the Association of South East Asian Nations (ASEAN) contribute to the global power dynamics? |  |
Ans. ASEAN serves as an Alternative Centre of Power by promoting regional cooperation, economic growth, and political stability among its member countries in Southeast Asia.
| 4. What role does the rise of the Chinese economy play in the emergence of Alternative Centres of Power? |  |
Ans. The rapid growth of the Chinese economy has positioned China as a major player in global affairs, leading to its recognition as an Alternative Centre of Power alongside established superpowers.
| 5. How do India-China relations impact the distribution of power among Alternative Centres of Power? |  |
Ans. The relationship between India and China influences the balance of power in Asia, with both countries vying for influence and control in the region, contributing to the emergence of multiple Alternative Centres of Power.
Related Searches
















