Environment & Sustainable Development Class 12 Economics
| Table of contents |

|
| Environment |

|
| Carrying capacity of the environment |

|
| State of India’s Environment |

|
| Sustainable Development |

|
| Strategies for Sustainable Development |

|
| Conclusion |

|
Environment
The environment is everything around us, including all living and non-living things. It’s like our planet’s huge treasure chest containing biotic elements (living things like birds, animals, plants, forests, and fisheries) and abiotic elements (non-living things like air, water, land, rocks, and sunlight). These biotic and abiotic parts work together and affect each other.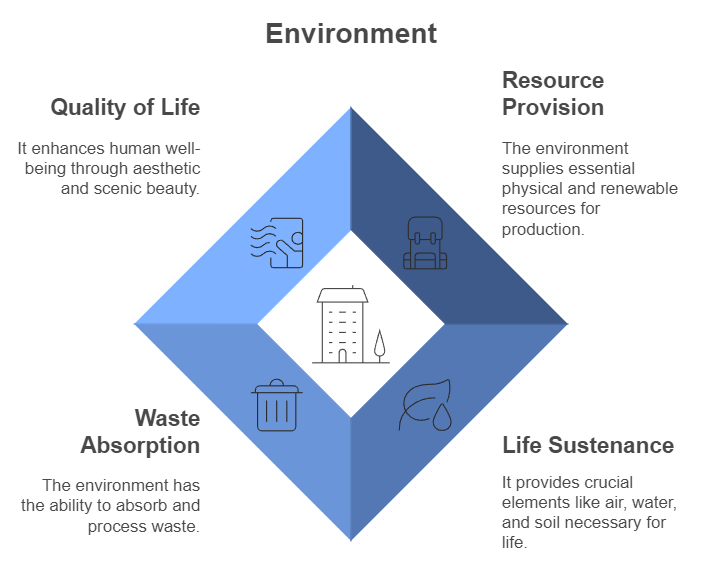
Functions of the Environment
The environment does four main jobs:
1. Providing Resources:
- It gives us the resources we need to live and grow.
- Renewable resources like trees and fish can be replenished naturally, so they don't run out if used wisely.
- Non-renewable resources like fossil fuels (coal, oil, etc.) will eventually run out because they take millions of years to form.
2. Absorbing Waste:
- The environment can handle and process some waste we produce, like how plants clean the air by taking in carbon dioxide.
3. Supporting Life:
- It provides biodiversity (different plants, animals, etc.) that help maintain life on Earth.
4. Providing Beauty and Enjoyment:
- Nature also gives us beautiful landscapes, calming scenery, and enjoyable experiences.
The Problem: Environmental Crisis
The environment can handle all these jobs as long as we don’t overuse or damage it. But now, we’re asking too much from it:
- We’re using resources faster than they can be replaced.
- We’re producing more waste than the environment can handle.
- Pollution and overuse of resources are harming nature’s ability to support life.
For example, polluted rivers and lakes are making clean water harder to find. Bad air and water quality are causing more health problems like breathing issues and water-borne diseases.
Why This Is Happening
- Developing countries have rising populations needing more resources.
- Developed countries are consuming and producing a lot, putting stress on resources.
- The natural environment can’t keep up with all this pressure.
The environment comprises all living and non-living components, including plants, animals, air, water, soil, and minerals, that form the surroundings of an ecosystem and influence our existence and well-being.
The Consequences
- We’re spending more on finding new resources and cleaning up pollution.
- Global issues like global warming and ozone layer depletion are making things worse.
- The cost of healthcare is increasing because of poor environmental quality.
The solution? We need to use resources wisely and make sure the environment’s carrying capacity isn’t pushed beyond its limits.
Carrying capacity of the environment
- The carrying capacity refers to the maximum load that the environment can support without suffering damage.
- Sustainable development occurs when the use of resources is balanced with their natural regeneration.
- Waste production must be within the environment's capacity to absorb to prevent pollution.
- Environmental crises arise when the load exceeds the carrying capacity due to overexploitation of natural resources or excessive waste generation.
State of India’s Environment
- India possesses abundant natural resources and a diverse range of flora and fauna. However, due to development activities, the exploitation of these resources has escalated, resulting in increased strain on the limited natural resources.
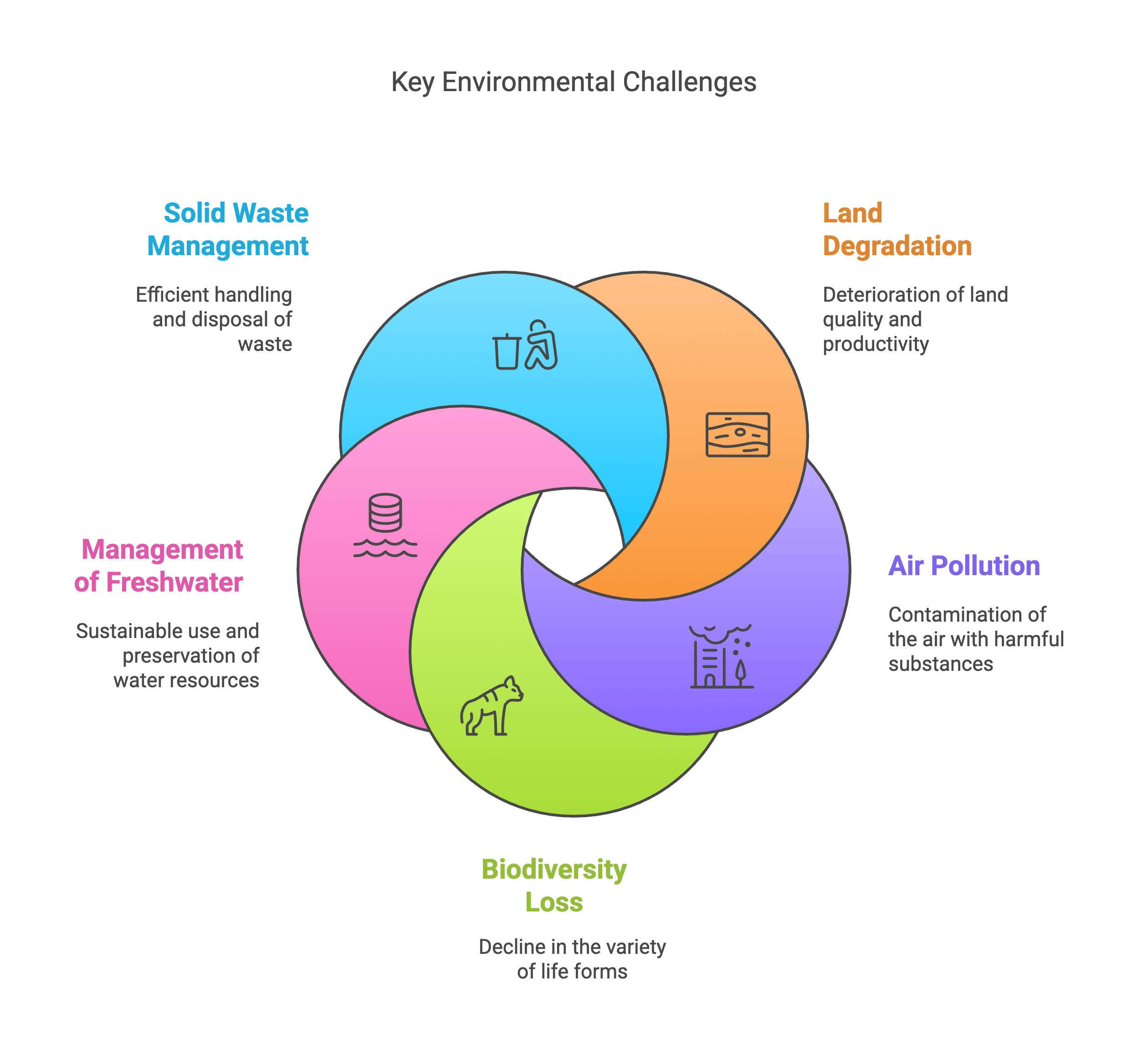
- The major environment-related issues are
1. Land Degradation
2. Air Pollution
3. Biodiversity Loss
4. Management of Freshwater
5. Solid Waste Management.
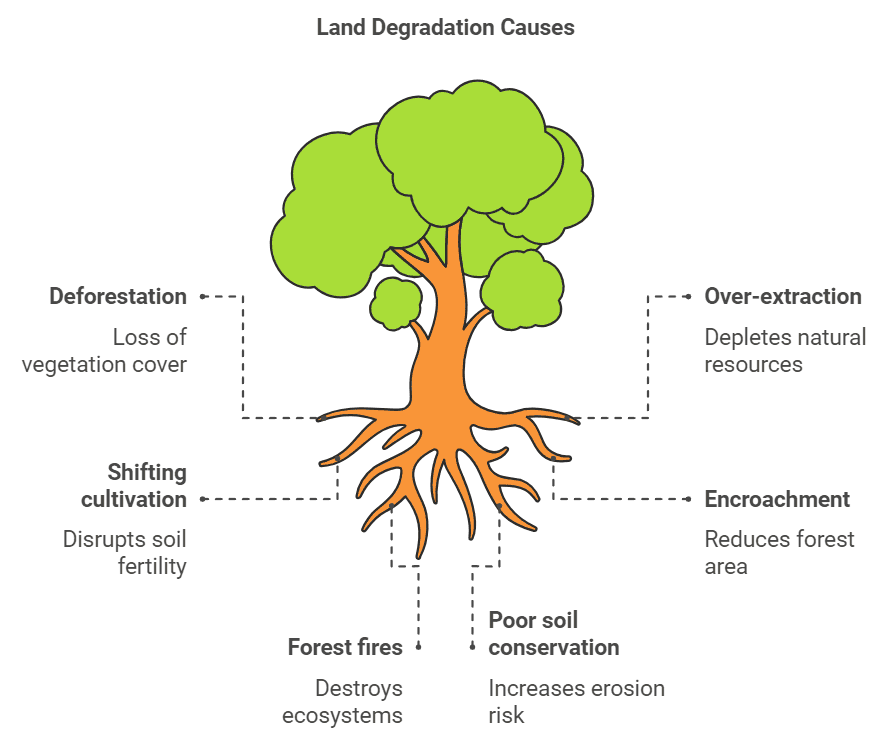
1. Land Degradation
Land degradation is the decline in the fertility of the soil caused by various factors, including but not limited to:
- Deforestation leads to the loss of vegetation.
- Over-extraction of fuelwood and fodder.
- Shifting cultivation practices.
- Encroachment of forest land.
- Forest fires and overgrazing.
- Inadequate implementation of soil conservation measures.
- Improper crop rotation or lack thereof.
- Overuse of agrochemicals such as pesticides and fertilizers.
- Inefficient planning and management of irrigation systems.
- Excessive extraction of groundwater.
2. Air pollution
Air pollution is the presence of harmful substances in the air that can cause health problems. These harmful substances come from various sources such as:
- Industries that use coal as an energy source and emit smoke into the air.
- Chemical treatment of materials that release poisonous gases.
- Motor vehicles that emit gases have increased significantly due to the exponential rise in the number of vehicles.
3. Biodiversity loss
Biodiversity loss refers to the decline or extinction of various living species worldwide. This phenomenon can be attributed to factors such as climate change, pollution, and the over-exploitation of natural resources.
Resource Depletion is a crucial aspect to highlight as it reflects the overall impact of exploitation on natural resources. Sustainable Development is an important concept in the context of managing natural resources effectively. Additionally, Environmental Sustainability is vital in discussions regarding biodiversity loss and resource management.
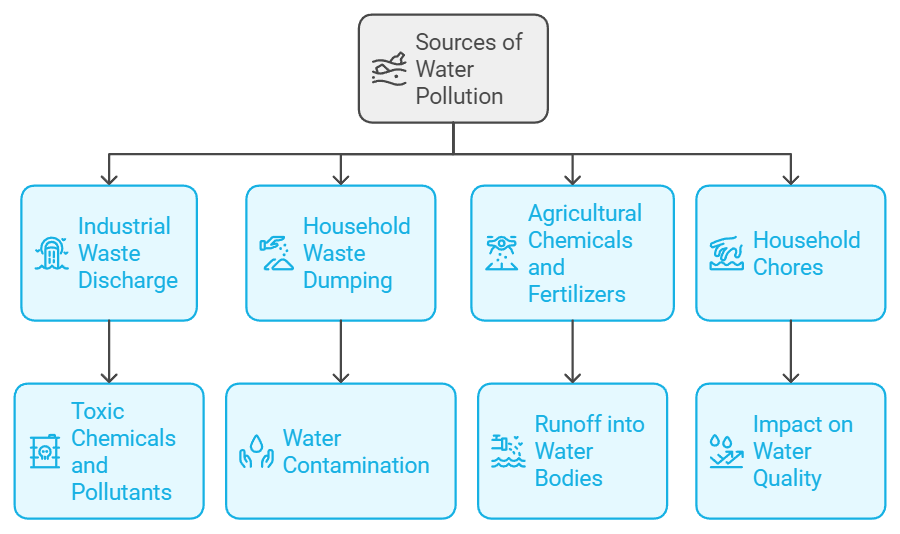
4. Management of Freshwater
The environment is also facing issues related to water resources such as improper management or water pollution. Water pollution is caused by the following factors:
- Discharge of industrial waste in water bodies that contaminates water with toxic chemicals and pollutants.
- Dumping of household waste in water bodies.
- Use of chemicals and fertilizers by farmers, which get mixed up with rainwater and flow into rivers and other water bodies.
- Household chores like washing clothes and bathing also impact water quality.
5. Solid Waste Management
The accumulation of large amounts of waste in both rural and urban areas poses various health risks and diseases. Improper disposal of household waste and littering on the streets are significant environmental threats, emphasizing the urgent need for solid waste management.
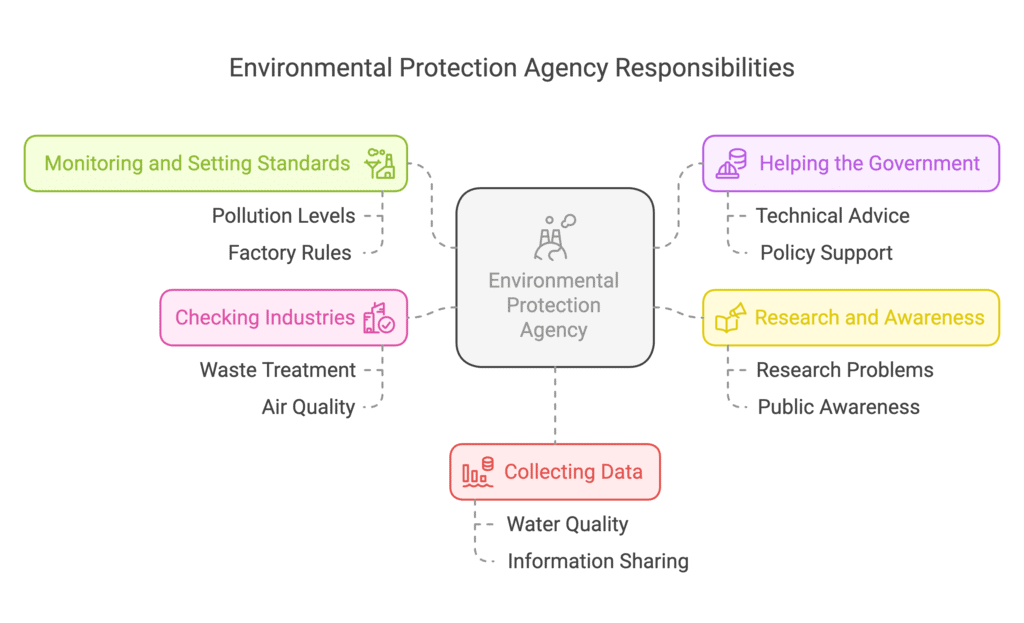
Pollution Control Boards in India
To tackle two big environmental problems in India — Water Pollution and Air Pollution, the government set up the Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB) in 1974. Soon, states also formed their own Pollution Control Boards to handle local environmental issues.
What Do These Boards Do?
Monitoring and Setting Standards:
- They keep track of pollution levels in water, air, and land.
- They set rules for how much pollution factories and industries are allowed to release.
Helping the Government:
- They give technical advice to the government on keeping water bodies clean and air pollution-free.
Research and Awareness:
- They research pollution problems and find ways to control them.
- They spread awareness through newspapers, TV, radio, and billboards to educate people about pollution and how to prevent it.
Checking Industries:
- They regularly inspect industries to ensure they are properly treating their waste before releasing it into the environment.
- They also check air quality to help with planning where industries and towns should be located.
Collecting Data:
- They gather and share information about water pollution.
- They monitor the quality of water in rivers, wells, lakes, ponds, creeks, and canals to see if they are clean or polluted.
Real-Life Activities to Understand Better:
- Visit a Factory: Visit a nearby factory or irrigation department to see how they manage water and air pollution.
- Collect Information: Find ads, news articles, or posters about pollution awareness and discuss them in class.
Sustainable Development
The environment and the economy depend on each other. Development that harms the environment will eventually destroy it, and if the environment is ruined, all life forms, including humans, will suffer. To avoid this, we need something called Sustainable Development.
What is Sustainable Development?
Sustainable development means making progress without harming the environment, so future generations can have a good quality of life too.
The United Nations Conference on Environment and Development (UNCED) defined it as:
“Development that meets the needs of the present generation without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs.”
Important Points to Remember:
1. Needs and Future Generations:
- The word “needs” refers to ensuring resources are shared fairly.
- The phrase “future generations” reminds us of our duty to leave the planet in good condition for those who come after us.
2. What Should We Aim For?
According to Edward Barbier, sustainable development focuses on improving the lives of the poor by providing them with better resources like income, education, healthcare, clean water, sanitation, and housing. It also means creating stable jobs and reducing poverty without harming the environment.
3. The Brundtland Commission’s View:
- We have a moral duty to leave the Earth in good shape for the next generation.
- Future generations should inherit an environment as good or better than what we have now.
What Needs to Be Done? (According to Herman Daly)
To achieve sustainable development, we need to:
- Keep the human population within the environment’s carrying capacity (like a ship’s load limit).
- Use technology that saves resources instead of consuming more.
- Use renewable resources carefully, making sure we don’t use them faster than they can be replaced.
- Limit the use of non-renewable resources and find alternatives that can be renewed.
- Fix pollution problems to avoid damaging the environment.
The 17 Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)
In 2015, the United Nations created 17 SDGs aimed at ending poverty, protecting the planet, and ensuring peace and prosperity for all by 2030.
Strategies for Sustainable Development
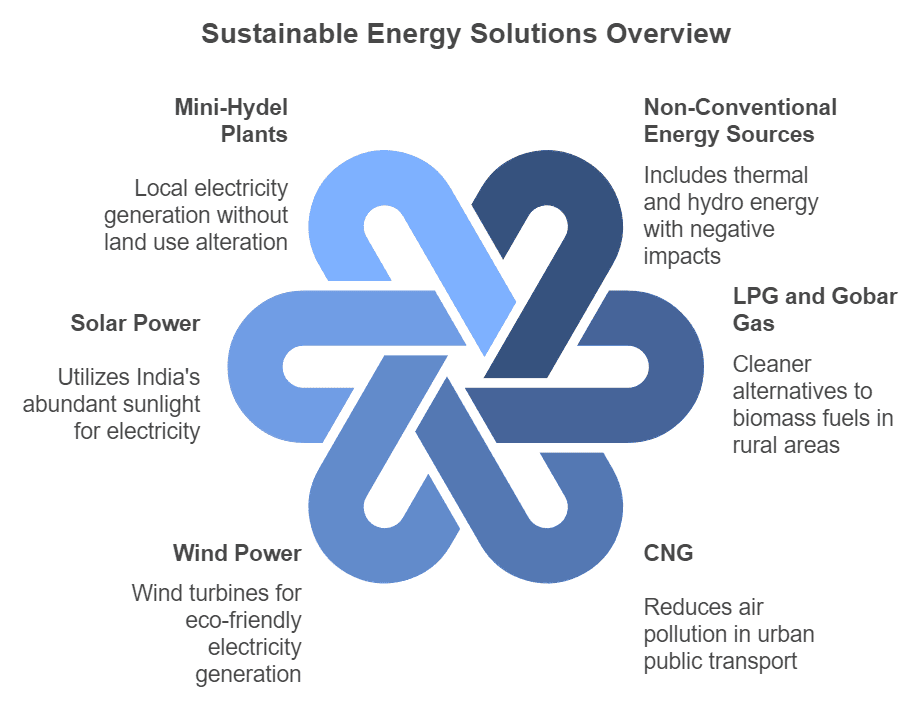
Use of Non-conventional Sources of Energy
- India mostly relies on thermal and hydropower plants for its energy needs. However, these sources harm the environment.
- Thermal power plants release large amounts of carbon dioxide, a greenhouse gas, and produce fly ash, which can pollute water and land if not managed properly.
- Hydroelectric projects can flood forests and disrupt natural water flow in rivers and catchment areas.
- Efforts are being made to use clean energy sources like wind and solar power.
- For example, in Tamil Nadu, the Muppandal Wind Farm is one of the largest wind farms in India, providing clean electricity to thousands of homes.
LPG and Gobar Gas in Rural Areas
- Rural households often use wood, dung cake, and biomass as fuel, which leads to deforestation, air pollution, and wasted resources.
- To address this, the government provides subsidized LPG, which is a clean fuel and reduces household pollution.
- Additionally, Gobar Gas plants are promoted with easy loans and subsidies.
- These plants convert cattle dung into biogas for cooking and the leftover slurry acts as an excellent organic fertilizer.
CNG in Urban Areas
- In cities like Delhi, the use of Compressed Natural Gas (CNG) in public transport has significantly reduced air pollution, making the air much cleaner.
- Other cities are also gradually adopting CNG for public transportation.
Wind Power
- Regions with high wind speeds use windmills to generate electricity.
- Wind turbines move with the wind to produce power.
- Though initial costs are high, the long-term benefits make it a worthwhile investment.
- For instance, the Jaisalmer Wind Park in Rajasthan is one of the largest wind power projects in India, producing clean energy for several regions.
Solar Power through Photovoltaic Cells
- India receives plenty of sunlight, which can be used to generate electricity through photovoltaic cells.
- These cells use special materials to capture sunlight and convert it into power.
- This technology is particularly helpful in remote areas where regular power supply is difficult.
- India is actively working to boost its solar power capacity and leads the International Solar Alliance (ISA) to promote solar energy worldwide.
Mini-hydel Plants
- In mountainous areas, perennial streams are used to operate small turbines that produce electricity.
- These mini-hydel plants are environment-friendly, meeting local power needs without disrupting land use or causing transmission losses.
- For example, the Chhattisgarh Mini-Hydel Plant is a successful initiative providing clean energy to nearby villages.
Traditional Knowledge and Practices
- India has a rich history of environment-friendly practices in agriculture, healthcare, housing, and transportation.
- However, with modern industrialization, we moved away from these practices, causing environmental damage.
- One good example is Ayurveda and other traditional healthcare systems like Unani and Tibetan medicine, which are making a comeback for treating chronic health issues.
- Today, many herbal products like toothpaste, hair oil, and creams are popular because they are eco-friendly, free from harmful side effects, and don’t require large-scale chemical processing.
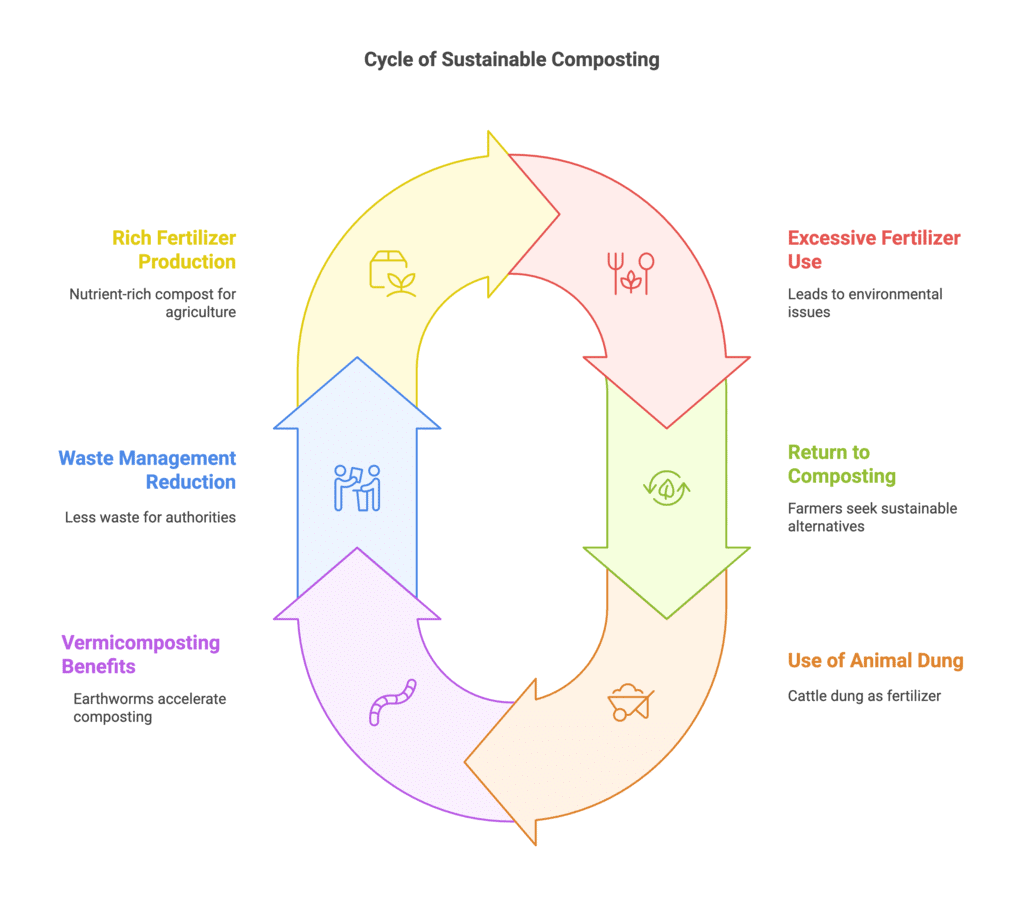
Biocomposting
- Over the past five decades, the excessive use of chemical fertilizers to boost agricultural production has led to soil degradation, contamination of water bodies, and increased irrigation demands.
- As a result, many farmers are returning to using compost made from organic wastes.
- In some areas, cattle are kept specifically for their dung, which serves as an excellent fertilizer and soil conditioner.
- A great example of eco-friendly composting is vermicomposting, where earthworms convert organic matter into compost much faster than normal methods.
- This process also benefits civic authorities as they have to manage less waste.
- In Kerala, many households and farms now use vermicomposting pits to turn kitchen waste into rich, natural fertilizer.
Biopest Control
- The Green Revolution led to the widespread use of chemical pesticides, which contaminated food, soil, water bodies, and even groundwater. Harmful chemicals were found even in milk, meat, and fish.
- To tackle this, farmers are increasingly turning to pesticides derived from plants, especially the Neem tree, which provides various natural pest-controlling chemicals. For example, farmers in Maharashtra are now using Neem oil sprays to protect crops from pests.
- Additionally, techniques like mixed cropping and crop rotation have helped control pests effectively. Wildlife also plays a crucial role in natural pest control. For instance, snakes prey on rats and mice, while birds like owls and peacocks feed on harmful insects and pests. Even lizards, which often roam agricultural lands, contribute to pest control by feeding on insects.
Conclusion
- The goal of economic development to fulfil the needs of a growing population by increasing the production of goods and services, results in greater strain on the environment.
- Initially, during the early stages of development, the demand for environmental resources was lower than their supply.
- However, the world is currently dealing with an elevated demand for environmental resources, while their supply is limited due to overuse and misuse.
- The objective of sustainable development is to promote a type of development that minimizes environmental problems and fulfils the present generation's requirements, without compromising the future generation's ability to meet their own needs.
|
64 videos|308 docs|51 tests
|
FAQs on Environment & Sustainable Development Class 12 Economics
| 1. What are the main functions of the environment? |  |
| 2. What is the carrying capacity of the environment? |  |
| 3. What is the current state of India’s environment? |  |
| 4. What is sustainable development and why is it important? |  |
| 5. How can individuals contribute to sustainable development? |  |





















