Population Composition Class 12 Geography
| Table of contents |

|
| Sex composition |

|
| Age Structure |

|
| Rural Urban Composition |

|
| Literacy |

|
| Occupational Structure |

|
| Frequently Asked Questions FAQs |

|
The degree of population density in a country doesn't necessarily correlate with its level of economic development. For instance, both Bangladesh and Japan have high population densities, but Japan is considerably more economically advanced than Bangladesh.
- To gain insights into the significance of people as a valuable resource, it's crucial to delve into their individual characteristics. People exhibit considerable diversity in terms of age, gender, literacy, health status, profession, and income. It's vital to comprehend these attributes of the population, which collectively constitute what is referred to as population composition.
- Population composition allows us to discern the distribution of males and females, their respective age groups, educational attainments, occupational profiles, income levels, and overall health conditions.
Sex composition
- The text explains that sex composition refers to the number of men and women in a country, and is expressed as a sex ratio, which is the ratio of the number of men to women.

- The global sex ratio is 990 females per 1000 males, with the highest sex ratio found in Latvia (1187 females per 1000 males) and the lowest in the UAE (468 females per 1000 males).
- The text goes on to mention that there is gender discrimination in 72 countries of the world, which leads to female foeticide, female infanticide, and low economic status of women, resulting in an unfavourable sex ratio.
- Specifically, Asian countries such as China and India have a low sex ratio, while European countries have a higher sex ratio.
Age Structure
The composition of a population based on different age groups is known as its age structure. It typically consists of three categories: children (aged 0-14 years), adults or the working-age population (aged 15-59 years), and the elderly or aging population (aged 60 years and above).
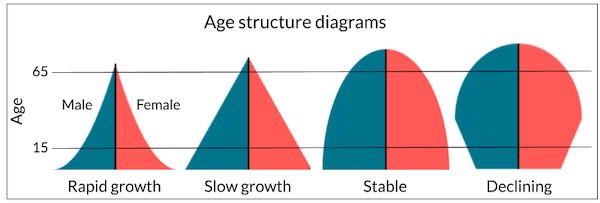
Age-sex Pyramid
The age-sex distribution of a population indicates the count of males and females across various age categories.
- To illustrate the age-sex structure of a population, a population pyramid is utilized.
- The form of the population pyramid signifies the distinctive features of the population.
- The vertical axis depicts the age groups while the horizontal axis represents the percentage of individuals in each group. The left side of the pyramid represents males, while the right side represents females.
Expanding Populations:
- This type of population pyramid exhibits a triangular shape with a broad base and is typically found in less developed nations. It reflects a greater proportion of individuals in the lower age groups, due to high fertility rates. Examples include Nigeria, Bangladesh, and Mexico.
Constant Population:
- This population pyramid has a bell-shaped curve and gradually narrows towards the top.
- It indicates that birth and death rates are nearly equal, leading to a stable population. An example of such a pyramid can be seen in Australia.
Declining Populations:
- This type of population pyramid has a narrow base and a tapering top, indicating low birth and death rates.
- In developed countries, population growth is usually zero or negative, resulting in a decrease in the population. An example of this can be found in Japan.
Rural Urban Composition
- The classification of a population into rural and urban categories is based on their place of residence. This categorization is important because rural and urban lifestyles differ significantly in terms of livelihood and social conditions.
- The criteria used to differentiate between rural and urban populations varies among different countries.
- In Western countries, males tend to outnumber females in rural areas while females tend to outnumber males in urban areas. However, the opposite is observed in countries such as Nepal, Pakistan, and India.
- The excess of females in urban areas of the USA, Canada, and Europe is due to the migration of females from rural areas to take advantage of the numerous job opportunities available in urban centers.
- The shortage of housing, high cost of living, limited job opportunities, and lack of security in cities often discourage women from migrating from rural to urban areas.
Literacy
- The proportion of literate individuals in a country is a significant indicator of its standard of living, the social status of women, and the availability of educational resources.
- In India, the literacy rate is determined by calculating the percentage of the population over the age of seven who can read, write, and perform arithmetic calculations.
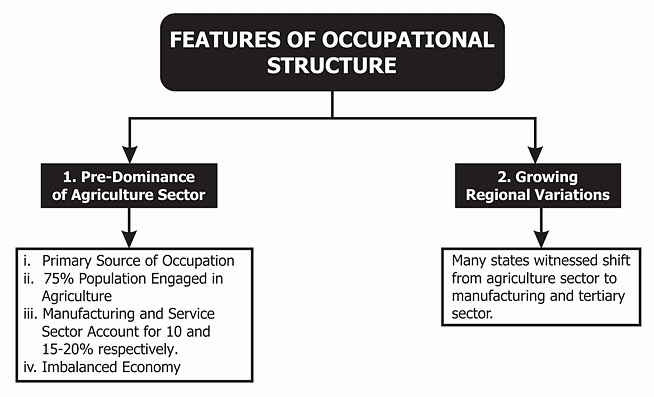
Occupational Structure
- The working-age population, consisting of individuals aged 15 to 59, participate in various occupations including agriculture, forestry, fishing, manufacturing, construction, commercial transport, services, communication, and other unclassified services.
- Activities such as agriculture, forestry, fishing, and mining are classified as primary activities, while manufacturing is considered a secondary activity. Trade, transport, communication, and other services are tertiary activities, and jobs related to research, information technology, and idea development are quaternary activities.
- If the economy is still in its early stages, a larger proportion of people would be engaged in primary activities, while more people are engaged in secondary, tertiary, and quaternary sectors if the economy is more developed.
Frequently Asked Questions FAQs
1. What is the sex composition of a population?
Ans: The sex composition of a population refers to the distribution of males and females within a specific population. It provides information on the ratio of males to females and can be expressed as a percentage or ratio. This composition is important for understanding various aspects of a population, such as reproductive patterns, gender dynamics, and potential imbalances between males and females.
2. How is the age structure of a population determined?
Ans: The age structure of a population is determined by analyzing the distribution of individuals across different age groups. This data is typically presented in the form of an age pyramid or age-sex pyramid, which displays the number or percentage of people in each age group, categorized by gender. By examining the age structure, we can gain insights into the population's demographic trends, such as population growth, aging, or youthfulness.
3. What is the rural-urban composition of a population?
Ans: The rural-urban composition of a population refers to the distribution of people living in rural and urban areas within a country or region. It provides information on the proportion of the population residing in rural areas, characterized by agricultural activities and lower population density, versus urban areas, characterized by non-agricultural economic activities and higher population density. Understanding the rural-urban composition helps in analyzing the spatial distribution of the population and planning for infrastructure and development.
4. What does literacy rate indicate about a population?
Ans: The literacy rate indicates the percentage of the population aged 15 and above who can read and write with understanding. It is often used as a measure of educational attainment and human development within a population. A high literacy rate suggests a higher level of education, intellectual development, and access to information. It is an important indicator for assessing the overall social and economic development of a country or region.
5. How does the occupational structure of a population impact its economy?
Ans: The occupational structure of a population refers to the distribution of individuals across different types of occupations or employment sectors. It provides insights into the workforce's composition and the relative importance of different economic activities within a country or region. The occupational structure impacts the economy by influencing productivity, income distribution, and economic growth. For example, a shift from agriculture-based occupations to manufacturing or service-based occupations can indicate economic development and diversification.
|
168 docs|32 tests
|
FAQs on Population Composition Class 12 Geography
| 1. What is the sex composition of the population? |  |
| 2. How does the age structure affect a population? |  |
| 3. What does the rural-urban composition indicate about a population? |  |
| 4. How is literacy measured in population composition studies? |  |
| 5. What is the occupational structure of a population? |  |