Revisiting AI Project Cycle & Ethical Frameworks for AI Chapter Notes - Class 10 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| AI Project Cycle |

|
| Introduction to AI Domains |

|
| Ethical Frameworks for AI |

|
| Case Study |

|
AI Project Cycle
The AI Project Cycle is a structured framework consisting of six stages that guide the development of AI projects, ensuring a systematic approach to problem-solving and model implementation.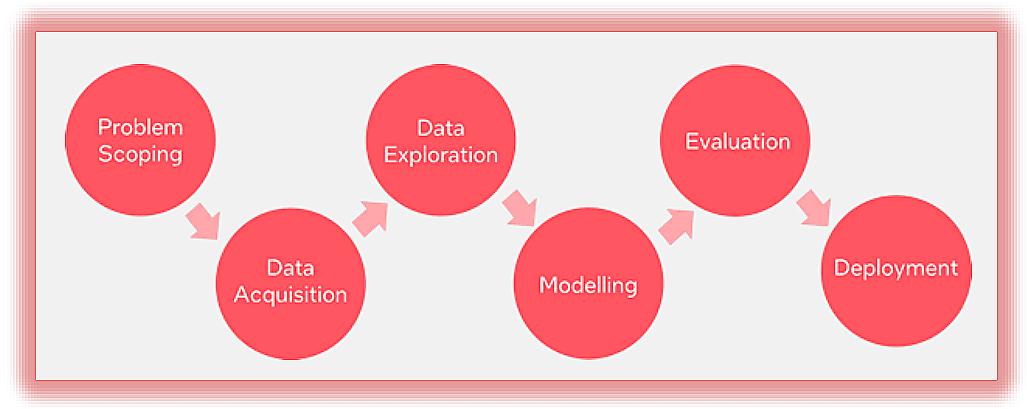
1. Problem Scoping
- Clearly define the objective of your AI project by identifying the specific problem you aim to solve.
- Analyze the context and influencing factors to develop a comprehensive understanding of the issue
2. Data Collection
- Acquire data from reliable sources that will form the foundation of your project.
- Represent the data visually through graphs, databases, flow charts, or maps to identify patterns more easily.
3. Model Selection
- Analyze the patterns in your data and decide on the type of model you will build to achieve your goal.
- Research online to find models that provide suitable outputs for your project.
4. Model Testing
- Test the selected models to determine which one performs best for your project.
- The most effective model will be the basis of your AI project.
5. Model Development
- Develop your algorithm around the chosen model.
- Test your model using new data to assess and refine its performance.
6. Deployment
- The deployment stage is crucial for ensuring the successful integration and operation of AI solutions in real-world situations, providing value and impact to users and stakeholders.
Introduction to AI Domains
Artificial Intelligence (AI) gains its intelligence through training, which involves providing it with datasets. The type of data used for training varies based on the specific applications for which the AI algorithm is designed. Generally, AI can be categorized into three main domains based on the data fed into the AI model.
Statistical Data
- Statistical Data focuses on the collection and analysis of data systems and processes.
- In this domain, the AI system gathers a large number of data points and maintains datasets for analysis.
- The primary goal is to extract valuable insights from the collected data.
- These insights play a crucial role in informing decisions related to the AI model's development and application.
Statistical Data Example
- Price comparison websites make use of large amounts of data.

- These platforms enable users to easily compare product prices from different sellers all in one place.
- Some examples of price comparison websites include PriceGrabber, PriceRunner, Junglee, Shopzilla, and DealTime.
- Price comparison websites are now commonly found in various sectors, such as:
- Technology
- Hospitality
- Automobiles
- Electronics
- Apparel
- Furniture
Computer Vision
Computer Vision (CV) is a branch of AI that focuses on enabling machines to interpret and understand visual information from the world, similar to how humans do. This involves making predictions and decisions based on visual data.
The process of computer vision involves several key steps:
- Image Acquisition: Capturing images or video from various sources, such as cameras, sensors, or other devices.
- Screening: Filtering and processing the acquired images to prepare them for analysis.
- Analysis: Examining the images to extract relevant features and information.
- Identification: Recognizing and identifying objects, patterns, or anomalies within the images.
- Information Extraction: Pulling out specific data and insights from the analyzed images.
- Visual Content Understanding: Through this extensive processing, computers can understand and interpret visual content, enabling them to respond appropriately to various scenarios.
Input Sources: Machines can take visual inputs from various sources, including:
- Photographs
- Videos
- Images from thermal or infrared sensors
- Other specialized sources
Feature Extraction and Interpretation: Projects in computer vision focus on processing visual data to extract features and make interpretations. This involves converting visual data into a format that computers can understand, facilitating the decision-making process.
Pixel Information Gathering: The primary goal of computer vision is to teach machines to gather and interpret information from individual pixels in an image, enabling detailed analysis and understanding of visual data.
Applications of Computer Vision:
1. Agricultural Monitoring
Computer vision plays a crucial role in agriculture by enabling:
- Crop monitoring
- Pest detection
- Yield estimation
- Drones equipped with cameras capture aerial images of farmland.
- These images are then analysed to assess crop health and improve farming practices.
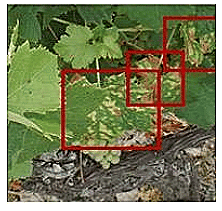 Agriculture Monitoring
Agriculture Monitoring
2. Surveillance Systems
Computer vision enhances surveillance systems for monitoring:
- Public spaces
- Buildings
- Borders
- It can identify suspicious activities and track individuals or vehicles.
- Real-time alerts are generated for security personnel.
- However, it is important to note that computer vision does not replace human oversight, and ethical considerations regarding privacy must be taken into account.
Understanding Natural Language Processing (NLP)
- Natural Language Processing, commonly known as NLP, is a branch of artificial intelligence that focuses on the interaction between computers and humans through natural language.
- Natural language refers to the language that people use in everyday speech and writing.
- NLP involves the use of algorithms to extract meaningful information from this data.
- The primary objective of NLP is to read, understand, and interpret human languages in a manner that is both useful and practical.
Instances of Natural Language Processing:
Email Filters
- Email filtering originated with spam filters, which identify specific words or phrases that are indicative of a spam message.

Machine Translation
- Natural Language Processing (NLP) is utilized in machine translation systems such as Google Translate and Microsoft Translator to facilitate automated language translation.
- These systems rely on statistical models and deep learning techniques to analyze the structure and meaning of sentences in the source language.
- Subsequently, they generate equivalent translations in the target language.
Ethical Frameworks for AI
Frameworks are like step-by-step guides that help us solve problems in a clear and organized way. They make sure we consider all the important parts of a problem and help us communicate and work together better by using the same approach.
Ethics is about what we believe is right and wrong. Frameworks give us a structured way to think about and resolve ethical issues.
What Are Ethical Frameworks?
Ethical frameworks are tools that help us make sure our decisions don’t accidentally cause harm. They offer a methodical approach to tackling tricky ethical situations by looking at different ethical principles and perspectives. By using these frameworks, people and organizations can make choices that reflect their values and lead to positive results for everyone involved.
The Importance of Ethical Frameworks for AI
- Bias in AI can lead to negative consequences, such as in the case of a hiring algorithm that discriminated against women applicants.
- As AI becomes more involved in decision-making and influencing people, it is crucial to ensure that its recommendations are morally acceptable.
- Ethical frameworks are essential for ensuring that AI makes morally sound choices. By implementing these frameworks during the development of AI solutions, we can prevent unintended outcomes before they happen.
- Having established the need for ethical frameworks, let’s take a look at what such a framework might include.
Activity: 1 My Goodness
Purpose: To understand how our decisions are shaped by our personal morals, values, and ethics.
Overview of the Activity
- Players make 10 decisions about how to donate to charities.
- Most of the time, players get details about the recipients and how the money will be used.
- Sometimes, this information is hidden, but players can choose to reveal it.
- The goal is to understand a person’s judgment and find potential biases in their decisions.
- Data is collected anonymously.
Exploring Your Decision-Making
- If you want to explore your decision-making further, click “yes.”
- After clicking “yes,” you’ll go to a short survey.
- After completing the survey, you’ll see interesting insights about your decisions.
- Did you find any internal biases in your decisions?
- Do you agree with the results shared by the game?
Factors That Might Influence Your Decisions
- Identity of the charity recipient.
- Location of the recipient.
- Bias towards relatives.
- Uncovering information available.
Purpose of the Exercise
- To reveal our biases and the thought processes that influence our decision-making.
- To create a framework for making ethically sounder decisions.
Let’s list at least 3 factors that knowingly or unknowingly influence our decision-making:
- Value of humans
- Value of non-humans
- Is the decision I am taking aligned with my religious views ?
- Religion
- Intuition & Values
- Does what I am thinking sound correct?
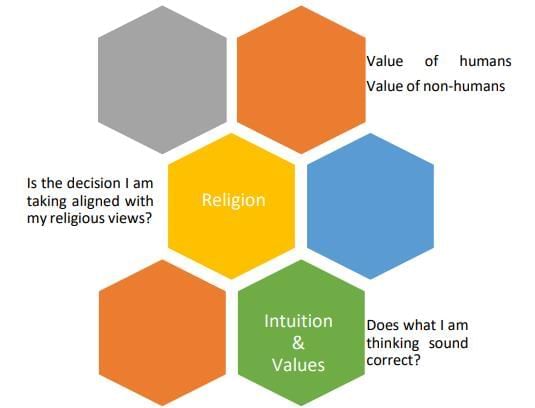
Types of Ethical Frameworks
Ethical frameworks for AI can be categorized into two main types: sector-based and value-based frameworks.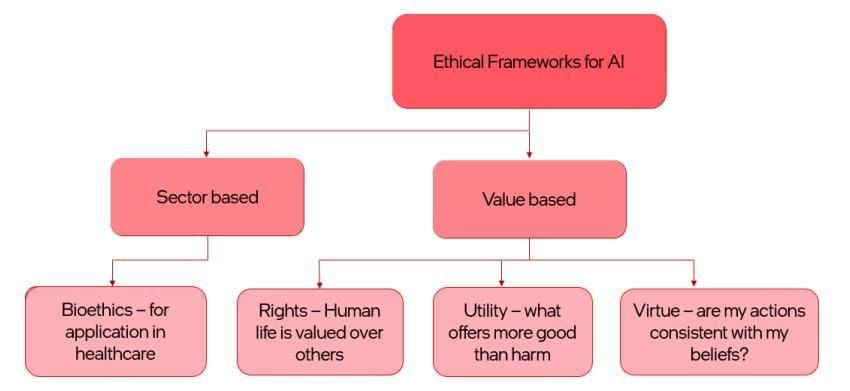
1. Sector-based Frameworks:
- Sector-based frameworks are tailored for specific sectors or industries.
- For instance, in the realm of AI, Bioethics is a prominent sector-based framework that addresses ethical issues in healthcare.
- Bioethics deals with concerns such as patient privacy, data security, and the ethical use of AI in medical decision-making.
- Beyond healthcare, sector-based ethical frameworks can be applied to various fields, including:
- Finance
- Education
- Transportation
- Agriculture
- Governance
- Law enforcement
2. Value-based Frameworks
These frameworks center on fundamental ethical principles and values that guide decision-making, reflecting various moral philosophies that shape ethical reasoning. They assess the moral worth of actions and direct ethical behaviour.
Rights-based
- Prioritises the protection of human rights and dignity, valuing human life above all else.
- Emphasises individual autonomy, dignity, and freedoms.
- In AI, it ensures systems do not breach human rights or discriminate against groups.
Utility-based
- Assesses actions based on maximising utility or overall good.
- Strives for outcomes that provide the greatest benefit while minimising harm.
- Involves balancing AI advantages against societal risks, such as job loss or privacy issues.
Virtue-based
- Emphasises the character and intentions of decision-makers.
- Questions whether actions align with virtuous traits like honesty, compassion, and integrity.
- Considers whether developers, users, and regulators maintain ethical values throughout the AI lifecycle.
These categories provide a structured approach to addressing ethical issues in AI development and deployment, ensuring sector-specific concerns are adequately met. Bioethics is a notable framework in the healthcare sector, addressing ethical challenges related to health, medicine, and biological sciences, ensuring AI applications in healthcare comply with ethical standards.
Principles of Bioethics
- Respect for Autonomy.
- Do not harm.
- Ensure maximum benefit for all.
- Ensure justice is served.
- Non-maleficence is about avoiding harm or negative impacts. It emphasizes the responsibility to minimize harm as much as possible.
- It centers on actions that prevent harm to individuals, communities, or the environment.
- Maleficence involves intentionally causing harm or doing something wrong.
- Beneficence is about promoting and maximizing the well-being of individuals and society.
- It focuses on actions that lead to positive outcomes and contribute to the overall good.
- The aim is to achieve the greatest benefit for everyone involved.
Case Study
- A company set out to assist hospitals in improving patient care by developing an AI algorithm aimed at identifying individuals at high risk.
- The goal was to equip healthcare providers with valuable insights for effective resource allocation, ensuring that those in greatest need receive the appropriate attention.
- However, there are potential unintended consequences that could lead to issues within the model. For instance, the algorithm might inadvertently amplify existing biases or inaccuracies present in the data.
- This could lead to the misclassification of patients or the oversight of critical cases.
- Therefore, addressing concerns regarding the algorithm's accuracy and reliability is crucial.
- Any shortcomings in its design or the training data could jeopardize patient care and outcomes.
The problem it caused:
- Patients from the Western region of a specific area, assessed at the same risk level by the algorithm, exhibited more severe health issues compared to patients from other regions.

Why the problem happened:
- The algorithm was trained using healthcare expense data as a proxy for health metrics instead of actual physical illness.
- This algorithm was developed in the United States, where healthcare funding for Western region patients is lower compared to other ethnic groups.
- Consequently, the algorithm may not accurately reflect the health needs of all patients.
- Applying principles from the Bioethics framework can aid in creating an ethical AI solution.
- The four principles of bioethics are crucial for developing an ethical AI solution to address this healthcare issue.
- Respect for autonomy: Users should have a clear understanding of how the AI system makes decisions.
- The data used for training models must be reproducible and accessible to patients.
- If there are concerns about performance, model predictions and data labels should be transparent.
- Do not harm: Avoid causing harm to anyone, whether human or non-human, at all costs.
- When options are limited, always choose the path of least harm.
- Promote well-being, reduce harm, and ensure a fair distribution of benefits and harms among stakeholders.
- The AI algorithm should be trained on data sets that minimize harm for everyone, not just specific groups.
- In this scenario, patients from regions outside the Western part who are less ill would receive more intensive care than those who actually need it.
- Implementing this algorithm could harm Western region patients by misallocating healthcare resources.
- Maximum benefit: Focus not only on avoiding harm but also on providing maximum benefits.
- The solution should meet clinical practice standards, not just technological ethics standards.
- Aim for beneficence, not merely avoiding harm.
- The AI algorithm should benefit patients from the Western region as well as those from other regions and of all races.
- Consider if there is a better data set for training that accurately reflects the healthcare needs and outcomes of patients of all races.
- The training data must be unbiased.
- Justice: Distribute all benefits and burdens of a decision fairly among people, regardless of their background.
- Developing solutions requires a deep understanding of social structures that lead to issues like racism and sexism.
- The solution must acknowledge social determinants of healthcare and actively work against these inequities.
- Adhering to bioethical principles could have prevented the unintended consequences of the AI solution.
FAQs on Revisiting AI Project Cycle & Ethical Frameworks for AI Chapter Notes - Class 10
| 1. What is statistical data and how is it used in research? |  |
| 2. What are price comparison websites and how do they function? |  |
| 3. Can you provide examples of computer vision applications? |  |
| 4. What role does natural language processing play in technology today? |  |
| 5. What are the ethical considerations in AI project development? |  |


















