Rural Development Class 12 Economics
| Table of contents |

|
| Rural Credit in India |

|
| Agricultural Marketing System |

|
| Diversification of Agricultural Activity |

|
| Organic Farming |

|
| Operation Flood |

|
| Conclusion |

|
The term rural development refers to initiatives aimed at improving the economic and social conditions of rural areas. Key areas for improvement include enhancing employment opportunities and increasing agricultural productivity. Rural development is crucial for the overall growth of the country, with over two-thirds of the population relying on agriculture for their livelihood. Currently, one-fourth of rural India is living in severe poverty, necessitating proactive government support to improve living standards.
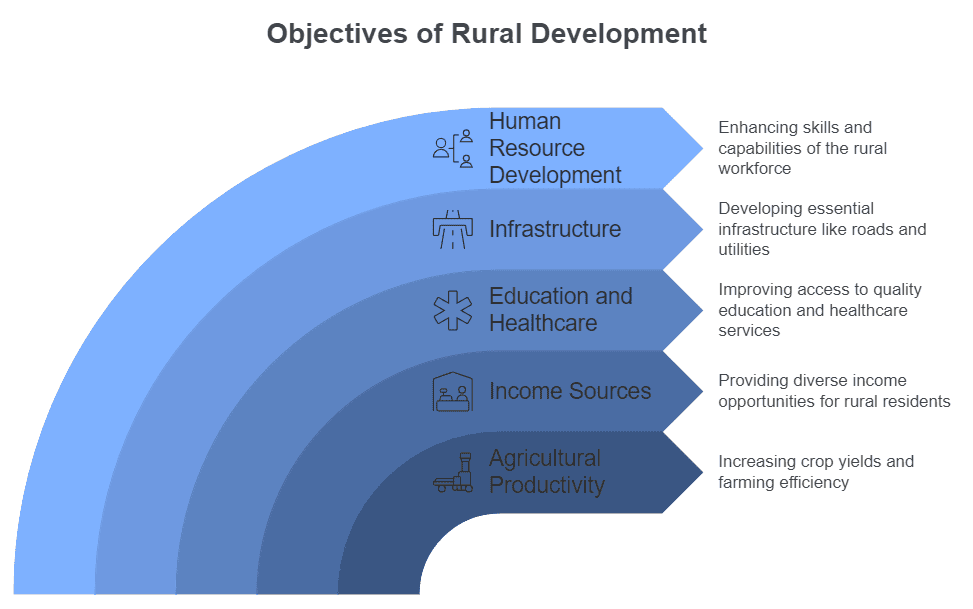
Objectives of Rural Development
- Enhancing agricultural sector productivity.
- Creating additional income sources in rural areas.
- Improving access to education and healthcare in rural communities.
- Developing infrastructure.
- Enhancing human resource development in rural regions.
- Reducing poverty.
- Implementing land reforms.
- Addressing health issues, including sanitation and public health.
Key Initiatives in Rural Development:
- Diversifying crops reduces production risks and promotes agricultural commercialisation.
- Promoting organic farming as a sustainable production method is increasingly important.
- Enhancing human resources.
- Improving healthcare by addressing cleanliness and public health issues.
- Expanding production activities to find sustainable alternatives to crop cultivation for livelihoods.
- Developing infrastructure such as electricity, irrigation, credit, and transport facilities, including village roads and feeder roads to nearby highways.
- Implementing special measures to alleviate poverty and significantly improve living conditions for the disadvantaged, focusing on access to productive employment opportunities.
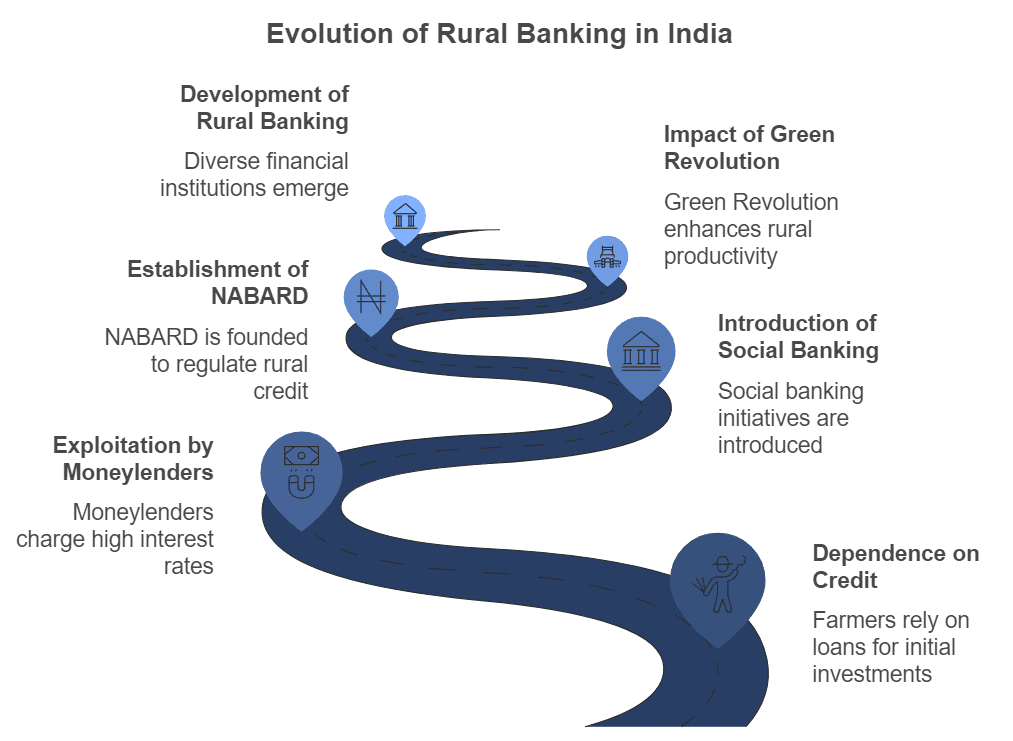
Rural Credit in India
- The growth of the rural economy relies heavily on funding from one period to the next to boost productivity in both agricultural and non-agricultural areas.
- Due to the long time between sowing crops and receiving income, farmers often need to borrow from various sources for initial investments like seeds and fertilisers and to cover family expenses for events such as marriages or funerals.
- After India's independence, small farmers and landless labourers faced exploitation from moneylenders and traders who charged high interest rates and manipulated accounts, trapping them in debt.
- A major shift occurred in 1969 when India adopted a social banking system and a multi-agency approach to address rural credit needs.
- In 1982, the National Bank for Agriculture and Rural Development (NABARD) was set up to oversee and organise all financial activities related to rural finance.
- The Green Revolution was pivotal in changing the credit system, steering it towards production-oriented lending.
- Today, the structure of rural banking includes various institutions such as commercial banks, regional rural banks (RRBs), cooperatives, and land development banks.
- Recently, Self-Help Groups (SHGs) have emerged to bridge gaps in the formal credit system, which has not fully integrated into rural social structures.
- SHGs have played a significant role in empowering women.
- However, agricultural loan default rates have remained chronically high.
Sources of Rural Credit:
The availability of rural credit can be divided into two categories:
- Informal Sources: These include traditional sources of agricultural credit in India, such as moneylenders, relatives, traders, commission agents, and landlords.
- Formal Sources: These consist of cooperative credit, commercial banks, regional rural banks, government institutions, land development banks, the National Bank for Agriculture and Rural Development (NABARD), self-help groups, and others.
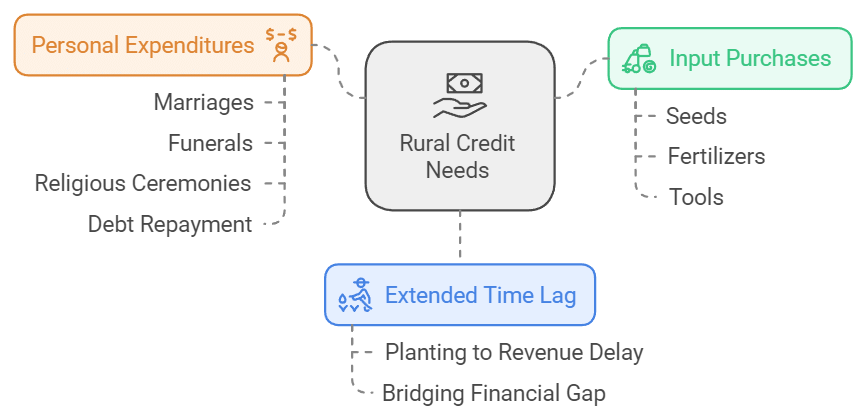
Rural Credit is needed for the following reasons:
- Extended time lag: The duration between planting crops and receiving revenue from their sale is very long. Consequently, farmers require credit to bridge this gap.
- Input purchases: Farmers require money to purchase seeds, fertilisers, tools, etc.
- Personal expenditures: They need funds for personal expenditures such as marriages, funerals, religious ceremonies, debt repayment, etc.
Agricultural Marketing System
Agricultural Marketing involves the integration of activities such as assembling, storing, processing, transporting, packaging, grading, and distributing different agricultural commodities across the country.
Measures to Improve Agricultural Marketing
After independence, the government has taken several initiatives to strengthen India's agricultural marketing system. The government has implemented the following measures to regulate the markets:
- Regulated Markets: The first step was to regulate the markets to ensure a transparent and organised marketing system. This was intended to protect farmers from the deceitful practices of sellers and brokers.
- Cooperative Marketing: Farmers formed marketing societies to sell their produce collectively and negotiate better prices through collective bargaining. However, cooperatives have struggled to operate effectively in recent years due to poor membership coverage and inefficient management.
- Infrastructural Facilities: The government also provided infrastructural facilities such as roads, railways, warehousing, cold storage, and processing units to promote rural development in India.
- Standardisation and Grading: Grading and quality control assist farmers in obtaining better prices for their high-quality produce. Proper segregation and categorisation of the output of different grades and standards enhance the efficiency of their work.
Policy Instruments:
- Minimum Support Price: The government sets a price, known as the Minimum Support Price, for products like wheat, rice, maize, cotton, sugarcane, and pulses to protect farmers' interests.
- Buffer Stock: The Food Corporation of India maintains stocks of crops like wheat and rice to manage price fluctuations caused by supply and demand or emergencies.
- Public Distribution System: This system distributes food grains and sugar, ensuring farmers' revenue while providing food to the poor at subsidised rates.
At the time of independence, moneylenders and traders took advantage of small and marginal farmers, as well as landless labourers, by charging high interest rates and manipulating accounts to keep them trapped in debt.
The National Bank for Agriculture and Rural Development (NABARD) was established in 1982 as a leading body to coordinate the activities of all institutions involved in rural financing.
Diversification of Agricultural Activity
The promotion of crop diversification involves shifting from a single cropping system to various cropping systems, including a shift from food grains to cash crops. This aims to encourage the transition from subsistence farming to commercial farming. Additionally, the agricultural sector is already overcrowded, so many labourers are seeking work in non-agricultural industries and related activities such as livestock, poultry, fisheries, etc. These options provide an alternative source of income while also promoting sustainable livelihoods. The diversification of productive activities includes animal husbandry, which involves breeding and caring for livestock to gain economic benefits. Fisheries have also made significant progress due to increased financial allocations and the adoption of new technologies. Horticulture is another branch of agriculture that involves growing plants for various purposes. Finally, IT has played a critical role in exploring alternative options for sustainable development beyond farming and agricultural activities.
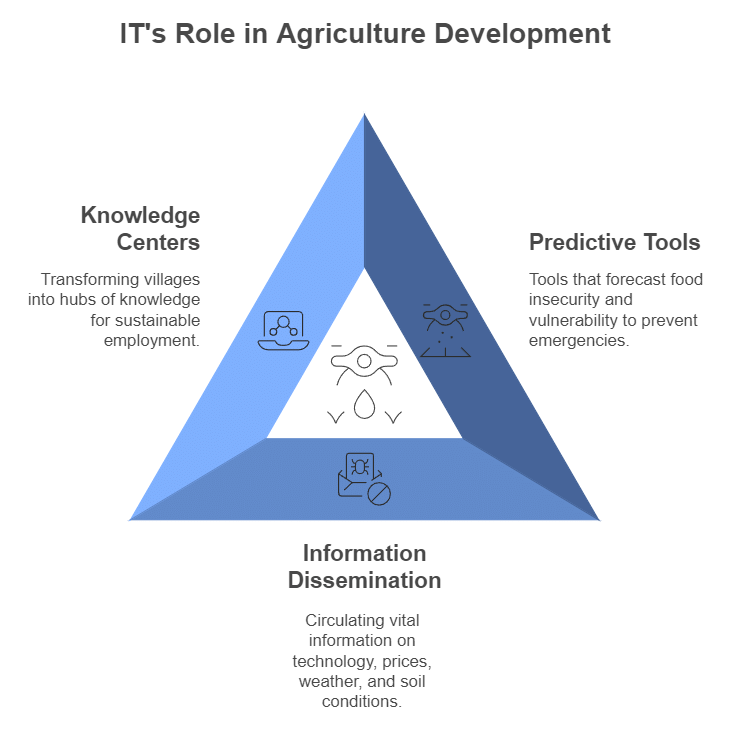
Role of IT Industries in Agriculture Development
- Information technology significantly influences various sectors of the Indian economy.
- It is recognised that IT will be vital for achieving sustainable development and food security in the 21st century.
- The government can identify areas prone to food insecurity using suitable information and software tools, allowing for timely actions to avert emergencies.
- IT positively impacts agriculture by sharing information on emerging technologies, prices, weather, and soil conditions for different crops.
- This enhances the understanding of agriculture and its various aspects.
- While IT is not a direct catalyst for change, it serves as a tool to unlock the creative potential and knowledge within society.
- It also holds the potential for employment generation in rural areas.
- Experiments with IT in rural development are being conducted across different parts of India.
Organic Farming
Organic farming involves the cultivation of food through natural methods without the use of synthetic chemical fertilisers or genetically modified organisms. It is an eco-friendly practice that is crucial for sustainable development and has minimal impact on the environment.
Advantages of Organic Farming
- Instead of relying on costly agricultural inputs like high-yield variety seeds, chemical fertilisers, herbicides, etc., organic farming employs locally sourced organic inputs that are affordable and yield favourable returns on investment.
- Organic farming can be a source of income through exporting crops due to the increasing demand for organically grown produce.
- By cultivating crops organically, we can ensure that the food we consume is more nutritious compared to chemically farmed food, since organic produce has a higher nutrient content.
- Organic farming has the potential to create more employment opportunities in India as it requires more labour-intensive work compared to conventional farming practices.
Disadvantages of Organic Farming
- Farmers' lack of awareness and education about organic farming is a significant challenge. However, by increasing their knowledge and willingness to adopt new methods, this situation can be improved.
- Insufficient infrastructure and marketing facilities hinder the growth of organic crops. An adequate agricultural policy that supports organic farming can help overcome this challenge.
- The high production costs associated with growing organic crops, as well as the absence of subsidies in this sector, also impede the development of organic farming.
Limitations of Organic farming:
- Initially, organic farming yields were lower than those of modern agricultural farming.
- Organic produce has a shorter shelf life compared to sprayed produce.
- The range of choices for off-season crop production is limited in organic farming.
- Due to the labour-intensive nature of organic farming, India has a comparative advantage in this sector.
Operation Flood
- Operation Flood is a network of milk cooperatives that was launched in 1966. This system focuses on the collection of milk from farmers through cooperative societies, which helps improve the quality and quantity of milk sales in the market.
- By pooling milk from farmers based on different grading and quality standards, Operation Flood has been successful in increasing both the volume and market value of the product.
- Thanks to Operation Flood, milk production has reportedly increased fourfold, as this system has encouraged farmers to adopt better milk production practices and management techniques.
Conclusion
- Until significant changes occur, the rural sector may continue to remain backwards.
- There is a greater need to make rural areas more vibrant through diversification into dairying, poultry, fisheries, vegetables, and fruits.
- Linking rural production centres with urban and foreign markets is essential for achieving higher returns.
- Infrastructure elements like credit, marketing, and farmer-friendly agricultural policies are crucial.
- A constant dialogue between farmers' groups and state agricultural departments is necessary to realise the full potential of the sector.
- Unless significant changes occur, it seems that the rural sector might continue to remain backwards.
- There is a pressing need to revitalise rural areas by diversifying into dairying, poultry, fisheries, and vegetables and fruits.
- Linking rural production centres with urban and foreign (export) markets will enable farmers to achieve higher returns on their investments.
- To fully realise the potential of the rural sector, it is essential to develop infrastructure elements like credit and marketing, farmer-friendly agricultural policies, and a constant dialogue between farmers' groups and state agricultural departments.
|
64 videos|308 docs|51 tests
|
FAQs on Rural Development Class 12 Economics
| 1. What is the concept of rural credit in India? |  |
| 2. How does the agricultural marketing system work? |  |
| 3. What is the significance of diversification of agricultural activity? |  |
| 4. What is organic farming? |  |
| 5. What is Operation Flood and its significance in rural development? |  |
















