NEET Exam > NEET Notes > Chemistry Class 11 > Introduction to Organic Chemistry
Introduction to Organic Chemistry | Chemistry Class 11 - NEET PDF Download
General Introduction
- The branch of chemistry which deals with Carbon and its derivatives is called Organic chemistry.
- Organic chemistry began to emerge as a science about 200 years ago. By the late eighteenth century, substances were divided into two classes called organic and inorganic compounds.

Question for Introduction to Organic ChemistryTry yourself:What percent of our body is made up of carbon?
View Solution
- Organic compounds were obtained from plants and animals.
- Organic compounds were more difficult to work within the laboratory and decompose easily.
- The hydrides of carbon (hydrocarbons) and their derivatives are called organic compounds. The branch of chemistry which deals with these compounds is called organic chemistry.
- Berzelius (1808) defined organic chemistry as the chemistry of substances found in living matter and gave the vital force theory.
- The synthesis of urea, the first organic compound synthesised in the laboratory, by Wohler who gave the death blow to the vital force theory.

- Acetic acid is the first organic compound synthesized from its elements.
Tetravalency of Carbon: Shapes of Organic Compounds
(a) Catenation
- It is the tendency of self combination and is maximum in carbon.
- A carbon atom can combine with other carbon atoms by single, double, or triple bonds.

- Thus, Carbon forms more compounds than the other elements.
(b) Tetravalency and Small Size
- Carbon is tetravalent, is capable of bonding with four other C atoms or some other monovalent atoms.
- Carbon can form a compound with oxygen, hydrogen, chlorine, sulphur, nitrogen and phosphorus.
- These compounds have specific properties depending upon the nature of the element or group attached to the carbon.

- Furthermore, these compounds are exceptionally stable because of the small size of carbon.
General Characteristics of Organic Compounds
- These are the compounds of carbon with H, O, N, S, P, F, CI, Br and I.
- These are generally found in living organisms. e.g., carbohydrates, proteins etc.
- These may be gases, liquids or solids.
- Being covalent in nature, these have a low boiling point and melting point and soluble in organic solvents.
- These are generally volatile and inflammable.
- They do not conduct electricity because of the absence of free ions.
- They possess distinct colour and odour.

Question for Introduction to Organic Chemistry
Try yourself:Carbon is the _____ most abundant element in the universe
View Solution
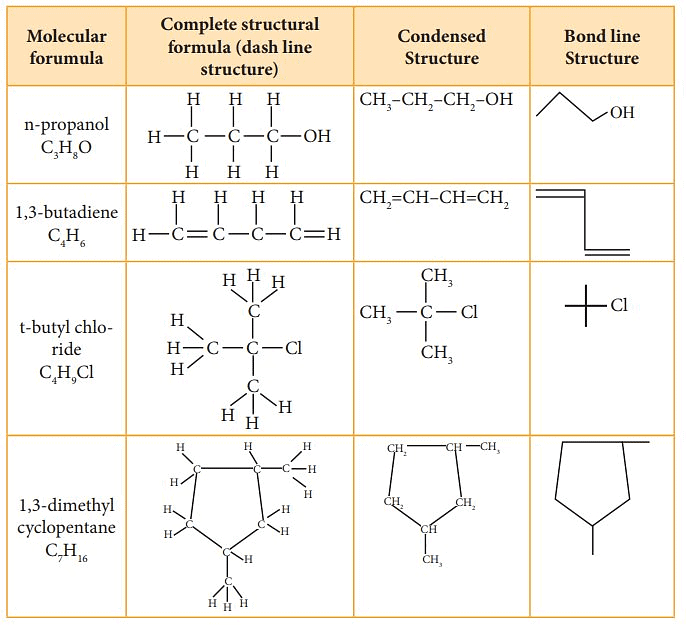
Structural Representations of Organic Compounds
- Complete Structural Formula – Full structural equations show all the atoms in a molecule, the types of bonds that bind them, and how they are interconnected.
- Condensed Structural Formula – The Condensed structural formula is used to save space, structural formulas are conveniently abbreviated as condensed structural formulas.

- Bond Line Structural Formula – A bond-line structure is a less cluttered drawing than a condensed structural formula. However, to understand the simplified bond-line structure, the reader has to mentally add many more features to comprehend the overall structure.
The document Introduction to Organic Chemistry | Chemistry Class 11 - NEET is a part of the NEET Course Chemistry Class 11.
All you need of NEET at this link: NEET
|
127 videos|244 docs|87 tests
|
FAQs on Introduction to Organic Chemistry - Chemistry Class 11 - NEET
| 1. What is tetravalency in carbon, and why is it important in organic chemistry? |  |
Ans. Tetravalency refers to the ability of a carbon atom to form four covalent bonds with other atoms. This property is crucial in organic chemistry because it allows carbon to serve as a versatile backbone for a vast array of complex molecules, enabling the formation of various structures such as chains, rings, and branched configurations. This versatility is fundamental to the diversity of organic compounds.
| 2. How do the shapes of organic compounds relate to their chemical properties? |  |
Ans. The shape of organic compounds, which is influenced by the arrangement of atoms and the types of bonds present, significantly affects their chemical properties and reactivity. For example, the three-dimensional arrangement of atoms can determine how a molecule interacts with other substances, including its boiling point, solubility, and biological activity. Thus, understanding molecular shapes is essential for predicting the behavior of organic compounds.
| 3. What are the different structural representations of organic compounds? |  |
Ans. There are several ways to represent organic compounds structurally, including Lewis structures, structural formulas, condensed formulas, and three-dimensional models. Lewis structures depict all atoms and bonds explicitly, while structural formulas often simplify these representations by omitting certain hydrogen atoms. Condensed formulas provide a more compact view, and three-dimensional models help visualize the spatial arrangement of atoms in a molecule.
| 4. Why is it necessary to learn about structural representations in organic chemistry? |  |
Ans. Learning about structural representations is essential in organic chemistry because it allows chemists to communicate complex information about molecular structures clearly and efficiently. Different representations can highlight various aspects of a molecule, such as functional groups, stereochemistry, or reactivity. This understanding aids in predicting the behavior of compounds in chemical reactions and enhances comprehension of organic synthesis.
| 5. How does the tetravalency of carbon contribute to the formation of isomers? |  |
Ans. The tetravalency of carbon allows it to bond with multiple atoms in various configurations, leading to the formation of isomers—molecules with the same molecular formula but different structures. This property is crucial in organic chemistry, as isomers can exhibit vastly different physical and chemical properties. The ability of carbon to form chains, branches, and rings contributes to the rich diversity of organic compounds.

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
Related Searches