UPSC Exam > UPSC Notes > History Optional for UPSC > Charter Act of 1793 & 1813
Charter Act of 1793 & 1813 | History Optional for UPSC PDF Download
Introduction
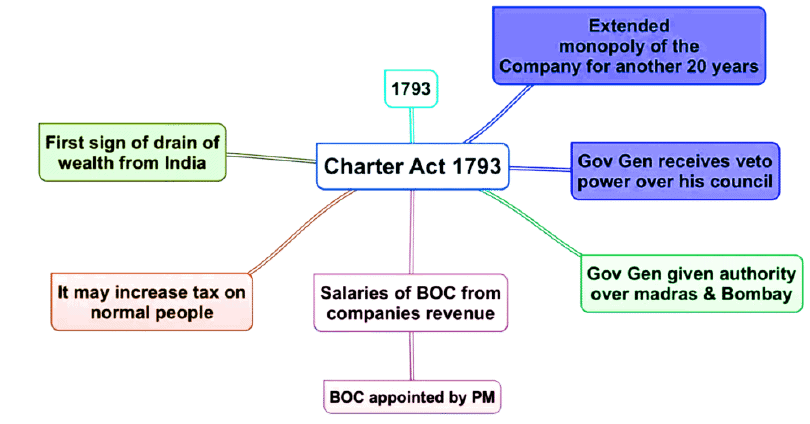
- The East India Company Act 1793, also known as the Charter Act of 1793, was enacted by the Parliament of Great Britain to renew the charter of the British East India Company (EIC) for another twenty years. This act solidified the Company’s control over all territories in India during this period and extended its rule in India.
- Unlike previous legislation concerning British India, the 1793 Act faced minimal opposition and passed smoothly.
- The Act introduced only slight modifications to the governance system in India and British oversight of the Company’s activities.
- The Company’s trade monopoly was extended for an additional 20 years, with the charter set to be renewed again by the Charter Act of 1813.
Provisions of the Act
- The Act acknowledged the political role of the Company and clarified that the “acquisition of sovereignty by the subjects of the Crown is on behalf of the Crown and not in its own right.”
- The Company was permitted to raise its dividend to 10%.
- A stipulation in the Charter Act of 1793 mandated that the Company would pay £5 Lakh annually to the British Government from the surplus revenue after covering necessary expenses, interest, dividends, and salaries from Indian revenues.
- Indian Administration:
- The Act granted the Governor-General extensive powers over the subordinate presidencies of Madras and Bombay, bringing the governors of these presidencies more firmly under his control.
- The Governor-General was empowered to override the majority in the Council under special circumstances, enhancing his authority.
- The power to override the respective councils, initially granted to Lord Cornwallis, was extended to all future Governor-Generals and Governors.
- The Commander-in-Chief was no longer a member of the Governor-General’s council unless specially appointed by the Court of Directors.
Question for Charter Act of 1793 & 1813Try yourself: Which provision of the East India Company Act of 1793 allowed the Company to pay an annual amount to the British Government?View Solution
Regular Code of Regulations for Bengal Territories:
- A comprehensive code of regulations was established for the internal governance of British territories in Bengal.
- This code applied to the rights, persons, and properties of Indian people, binding courts to make decisions based on its rules and directives.
- All laws were required to be printed with translations in Indian languages, ensuring that people were aware of their rights, privileges, and immunities.
- The Act introduced the concept of civil law in India, enacted by a secular human agency and applied universally.
Reorganization of Courts and Revenue Administration:
- The Act reorganized the courts and redefined their jurisdictions.
- It separated revenue administration from judicial functions, leading to the disappearance of the Maal Adalats.
Home Government Reforms:
- The President of the Board of Control was now the first-named Commissioner.
- The two junior members of the Board of Control no longer needed to be members of the Privy Council.
- Staff salaries and those of paid members of the Board of Control were charged to the Company, not the State Exchequer, using Indian revenues until 1919.
- Royal approval was required for appointing the Governor-General, governors, and the Commander-in-Chief.
- Senior officials were prohibited from leaving India without permission, and unauthorized departure was considered resignation.
- The East India Company (EIC) was given the power to grant trade licenses to individuals and Company employees, facilitating opium shipments to China.
Wilberforce's Proposed Clauses:
- William Wilberforce proposed two additional clauses for the Act.
- One clause aimed to declare that British rule in India would focus on the moral and spiritual uplift of Indians, allowing entry of appropriate individuals such as teachers and missionaries to achieve this goal.
The Charter Act of 1813
East India Company Act 1813 (Charter Act of 1813):
- Renewed the British East India Company's charter, allowing its rule in India for another 20 years.
- Company's trade monopoly was extended, but the charter was revised again in 1833.
Background of the Charter Act of 1813:
- The Company's vast territories made it difficult to manage both commercial and political roles.
- Demands for ending the Company's trade monopoly grew due to new economic theories and Napoleon's Continental System, which restricted British trade in Europe.
- Free traders in Britain wanted unrestricted access to Indian trade, believing it would lead to development in India.
- The Company insisted on the inseparability of its political authority and commercial privileges.
- After investigations and political influences, British policy towards India began to change, leading to the Charter Act of 1813.
Provisions of the Charter Act of 1813:
- Renewed the Company's charter for 20 years, asserting the British Crown's sovereignty over Indian territories.
- Regulated the Company's territorial revenues and commercial profits, fixing dividends at 10.5% per annum.
- Opened Indian trade to all Englishmen, ending the Company's monopoly in Indian trade.
- Strengthened the Board of Control's power and provincial governments' authority over European British subjects in India.
- Allocated funds for encouraging literature, science, and moral improvements in India, including allowing Christian missionaries to enter India.
- Signified a step towards the westernization of India.
Key Highlights:
- Renewed the East India Company's charter and trade monopoly.
- Asserted British Crown's sovereignty over Indian territories.
- Opened Indian trade to all Englishmen.
- Strengthened the Board of Control and provincial governments' powers.
- Allocated funds for literature, science, and moral improvements.
- Allowed Christian missionaries to enter India.
- Marked a step towards the westernization of India.
Question for Charter Act of 1793 & 1813Try yourself: Which Act extended the East India Company's trade monopoly for an additional 20 years and introduced the concept of civil law in India?View Solution
The document Charter Act of 1793 & 1813 | History Optional for UPSC is a part of the UPSC Course History Optional for UPSC.
All you need of UPSC at this link: UPSC
|
367 videos|995 docs
|
FAQs on Charter Act of 1793 & 1813 - History Optional for UPSC
| 1. What were the main objectives of the Charter Act of 1813? |  |
Ans. The main objectives of the Charter Act of 1813 were to renew the East India Company's charter for another 20 years, to promote education and spread of Christianity in India, and to allow the British government to exercise greater control over the Company’s administration in India. It also aimed at regulating the trade of the Company, particularly the trade of opium and other commodities.
| 2. How did the Charter Act of 1813 differ from the Charter Act of 1793? |  |
Ans. The Charter Act of 1793 primarily focused on the renewal of the Company's charter and the expansion of its trade privileges without significant changes in governance. In contrast, the Charter Act of 1813 introduced important reforms, including the end of the Company's monopoly over trade in India (except for tea and trade with China), the promotion of education, and the establishment of a more direct government oversight of the Company's activities.
| 3. What impact did the Charter Act of 1813 have on Indian society? |  |
Ans. The Charter Act of 1813 had a significant impact on Indian society as it encouraged the spread of Western education and Christianity, which led to the emergence of a new educated middle class in India. It also initiated discussions about social reforms and contributed to the rise of nationalistic sentiments among Indians, as they began to demand more rights and representation.
| 4. Did the Charter Act of 1813 introduce any provisions for the administration of India? |  |
Ans. Yes, the Charter Act of 1813 included provisions for the administration of India by allowing the British Crown to appoint a Governor-General and regulate the administration of justice. It also mandated the separation of the executive and judicial functions to ensure better governance and legal processes in the territories under British control.
| 5. What role did the Charter Act of 1813 play in the evolution of British colonial policy in India? |  |
Ans. The Charter Act of 1813 marked a significant shift in British colonial policy by indicating a move toward greater government control and accountability over the East India Company. It laid the groundwork for future reforms and policies that would lead to more direct British governance in India, ultimately culminating in the Government of India Act of 1858, which transferred power from the Company to the British Crown.
Related Searches
















