Cheat Sheet: Jainism | History for UPSC CSE PDF Download
Introduction to Jainism
Jainism is an ancient religious philosophy centered on the principles of nonviolence and spiritual purity. Originating in the 6th century B.C., it gained prominence through Lord Mahavira, the 24th Tirthankara. The religion emphasizes liberation and enlightenment through adherence to principles such as Ahimsa, Satya, Asteya, Aparigraha, and Brahmacharya.
Chronology of Jainism

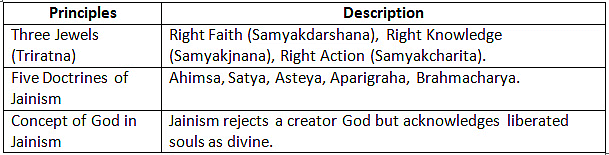
Tenets of Jainism
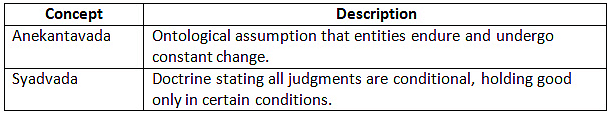
Anekantavada and Syadvada
Sects/Schools of Jainism

Spread of Jainism

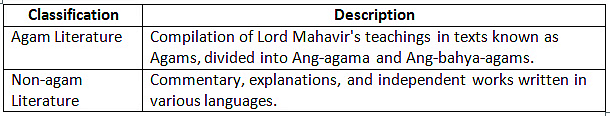
Jain Literature
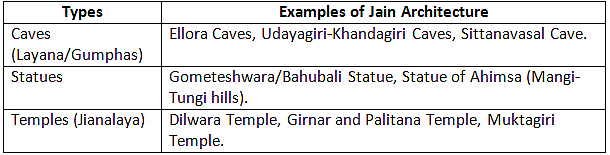
Jain Architecture
Jain Council

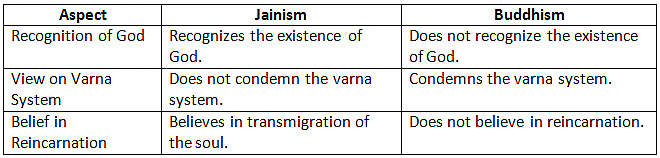
Differences from Buddhism
Relevance in Today’s World
Jainism's principles hold relevance today, advocating intellectual tolerance, non-violence, and minimalism in possessions. Concepts like Ahimsa can contribute to countering violence and terrorism, while Aparigraha can address consumerism and environmental concerns.
Conclusion
Jainism, with its ancient roots and timeless principles, offers a philosophy of peaceful coexistence and spiritual enlightenment. Its teachings continue to inspire ethical living, societal harmony, and environmental responsibility in the contemporary world.
|
111 videos|495 docs|173 tests
|
FAQs on Cheat Sheet: Jainism - History for UPSC CSE
| 1. What are the main beliefs of Jainism? |  |
| 2. Who is the founder of Jainism? |  |
| 3. How is Jainism different from other religions? |  |
| 4. How do Jains practice non-violence in their daily lives? |  |
| 5. What is the significance of the concept of karma in Jainism? |  |

|
Explore Courses for UPSC exam
|

|


















