Cheatsheet: Agriculture | Social Studies (SST) Class 10 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| Types of Farming |

|
| Cropping Pattern |

|
| Major Crops |

|
| Horticulture and Non-Food Crops |

|
| Technological and Institutional Reforms |

|
Introduction
Agriculture forms the backbone of India's economy, engaging approximately two-thirds of the population in various farming activities. India is not just a source of livelihood but a critical component of the nation's economic and social fabric.
- Food Production: Provides the majority of food consumed across India, including staple crops like rice and wheat.
- Raw Materials: Supplies essential inputs for industries, such as cotton for textiles and sugarcane for sugar production.
- Economic Role: Supports rural livelihoods and contributes significantly to India's GDP.
Types of Farming
Farming methods in India have evolved over time, adapting to local climates, soil types, and available technology. From primitive slash-and-burn techniques to intensive and commercial farming, these systems cater to both local consumption and market demands.
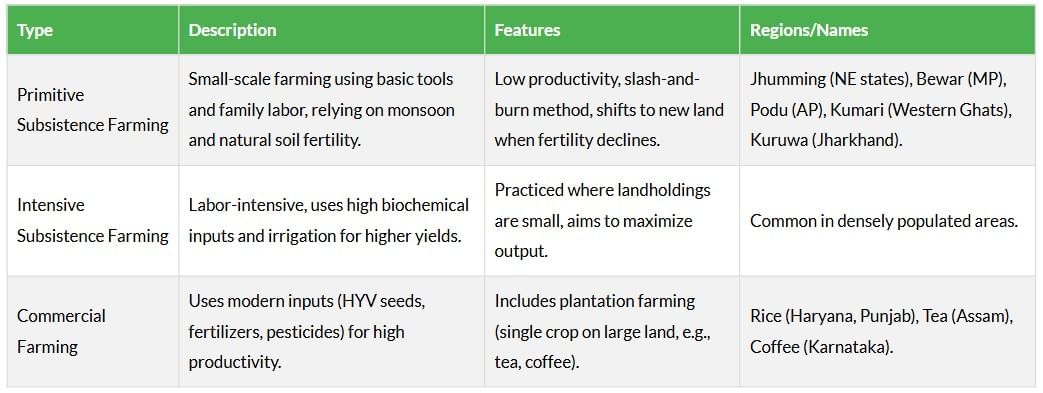
Cropping Pattern
The cropping pattern in India is shaped by monsoon cycles, soil types, and irrigation facilities. The three seasons allow farmers to grow a variety of crops, from food grains to fruits and vegetables, ensuring year-round agricultural activity. The Green Revolution and irrigation advancements have expanded crop cultivation to non-traditional areas.
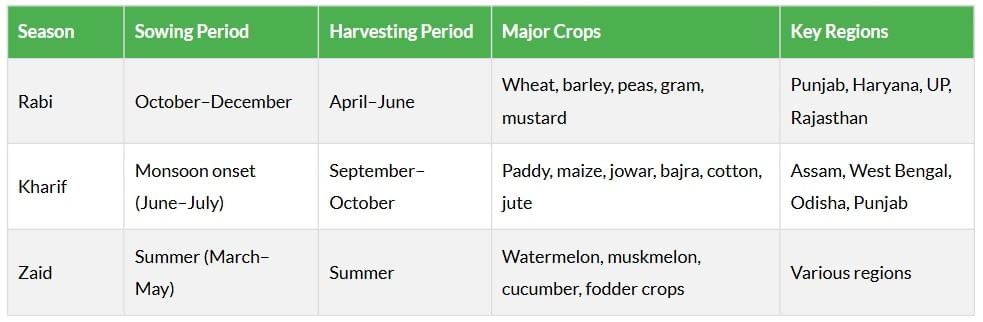
Major Crops
India’s diverse agro-climatic zones support the cultivation of major crops like rice, wheat, millets, pulses, and plantation crops. The country ranks high globally in the production of several crops, supported by irrigation advancements and modern farming techniques.
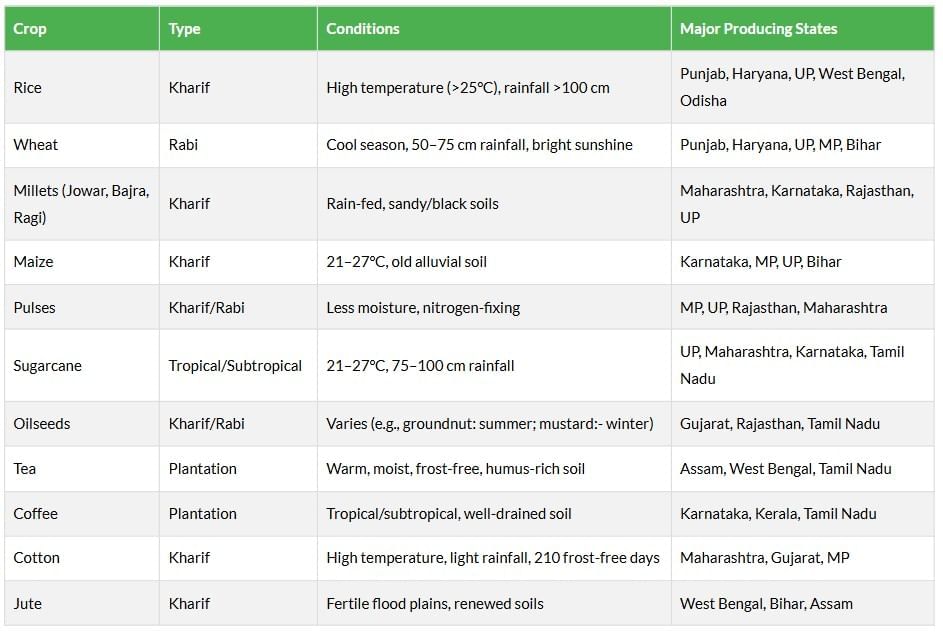
Horticulture and Non-Food Crops
India’s horticulture sector is a global leader, with diverse fruits and vegetables grown across tropical and temperate regions. Non-food crops like rubber and fibre crops (cotton, jute, silk) support industries and export markets, contributing significantly to the economy.
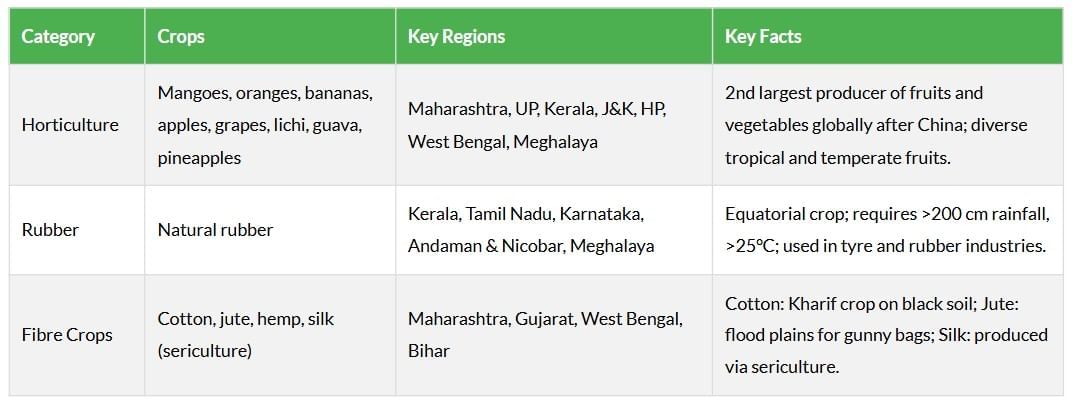
Technological and Institutional Reforms
Agriculture in India has a long history, but its development has been hindered by reliance on monsoons and lack of technological advancements. Post-Independence reforms and modern initiatives have aimed to improve productivity and farmer welfare, though challenges like inadequate implementation persist.
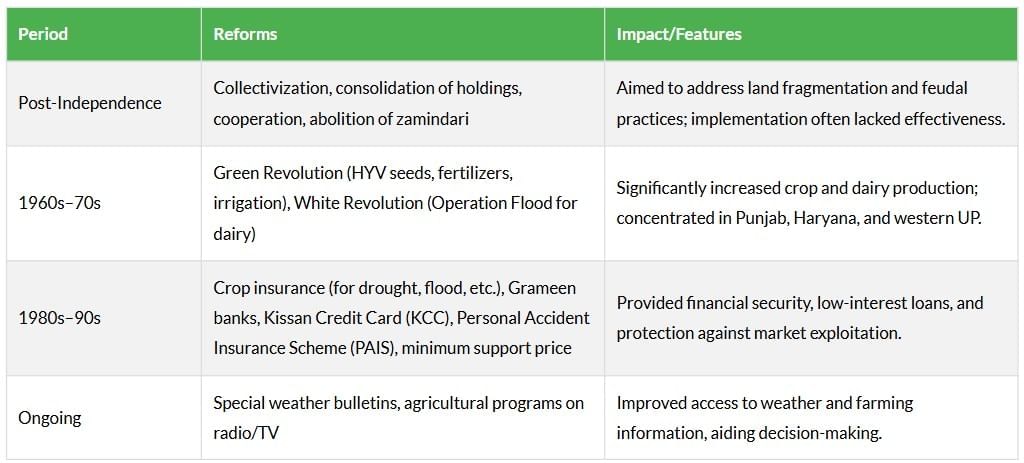
Challenges: Over 60% of India’s population depends on agriculture, yet many farmers rely on monsoons and natural soil fertility, making it difficult to meet the food demands of a growing population. Continued reforms focus on improving irrigation, technology adoption, and financial support.
|
66 videos|614 docs|79 tests
|
FAQs on Cheatsheet: Agriculture - Social Studies (SST) Class 10
| 1. What are the main types of farming practiced globally? |  |
| 2. How do cropping patterns affect agricultural productivity? |  |
| 3. What are the major crops cultivated in different regions? |  |
| 4. What is the significance of horticulture and non-food crops in agriculture? |  |
| 5. What are some technological and institutional reforms that have impacted agriculture? |  |















