Class 10 Exam > Class 10 Notes > Social Studies (SST) Class 10 > Cheatsheet: Gender, Religion and Caste
Cheatsheet: Gender, Religion and Caste | Social Studies (SST) Class 10 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| Gender and Politics |

|
| Religion, Communalism, and Politics |

|
| Caste and Politics |

|
| Social and Religious Diversity of India |

|
Introduction
Social diversity is a cornerstone of India's democratic identity, enriching political discourse and strengthening institutions. This cheatsheet covers three key social differences—gender, religion, and caste—and their impact on Indian politics.
Gender and Politics
Key Concepts
- Gender Division: Socially constructed roles based on expectations and stereotypes, not biology.
- Public/Private Division: Women are often expected to handle household chores and child-rearing, while men dominate public roles.
- Women's Work: Women contribute significantly outside the home (e.g., farming, domestic work), but their work is undervalued.
- Feminist Movements: Advocate for equality in education, employment, and family life, addressing issues like unequal pay and sex-selective abortions.
Women's Political Representation
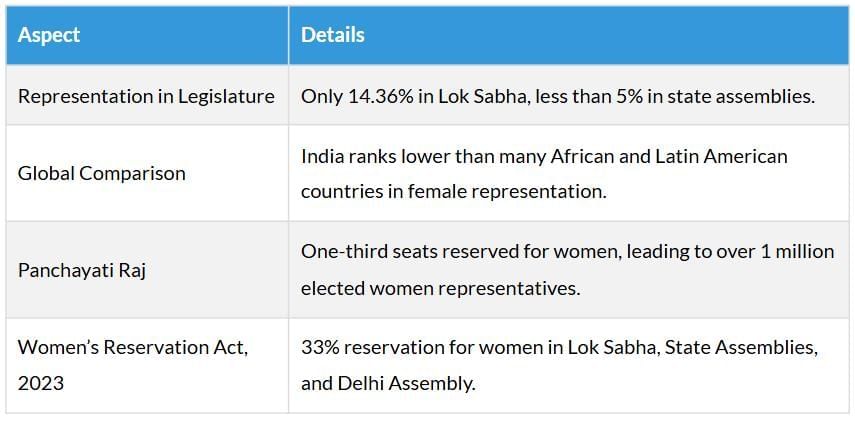
Religion, Communalism, and Politics
Key Concepts
- Religion in Politics: Ethical principles from religion can guide politics, but mixing them can lead to communalism.
- Communalism: When religion becomes the basis of social identity, often leading to conflict and dominance of one group.
- Forms of Communalism:
- Everyday biases and stereotypes about religions.
- Political mobilization using religious symbols and emotions.
- Communal violence, riots, and massacres (e.g., during Partition).
Secular State
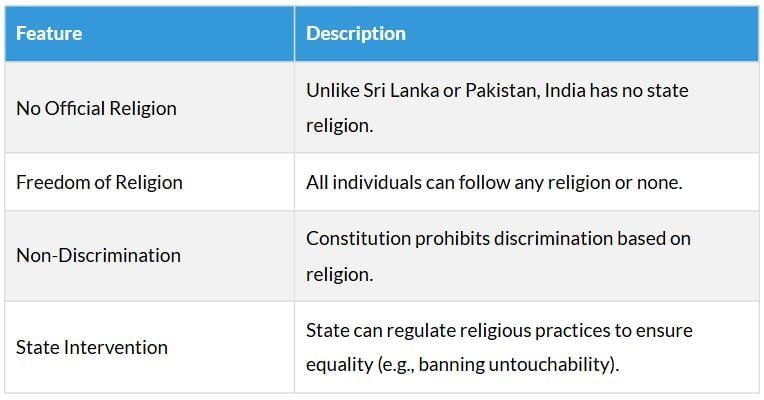
Note: Secularism is vital to combat communalism, but active efforts are needed to counter prejudices in everyday life and politics.
Caste and Politics
Key Concepts
- Caste System: Hereditary occupational division, historically rigid with exclusion and discrimination.
- Changes in Caste: Urbanization, literacy, and legal protections have weakened caste hierarchies, but issues like untouchability persist.
- Scheduled Castes (SCs) and Tribes (STs): SCs (16.6%) and STs (8.6%) face historical marginalization; together with OBCs, they form a significant population.
Caste in Politics
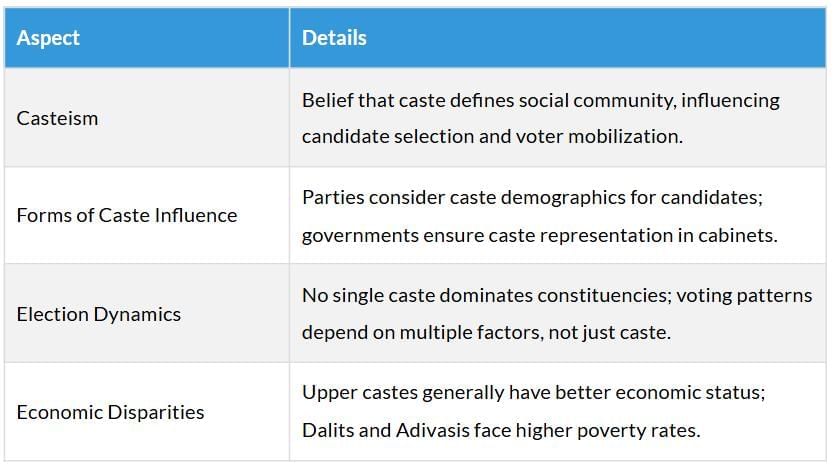
Politicization of Caste
- Caste groups expand by including neighboring castes.
- Coalitions form through dialogue and negotiation.
- New groups like 'backward' and 'forward' castes emerge in politics.
Social and Religious Diversity of India
Population Distribution (2011 Census)
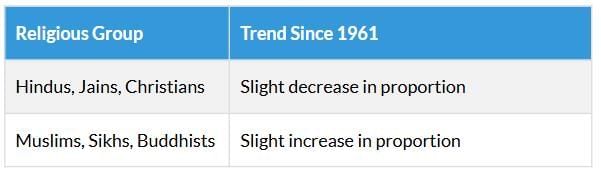
Note: Muslim population expected to rise by only 3-4% in the next 50 years, maintaining demographic balance.
The document Cheatsheet: Gender, Religion and Caste | Social Studies (SST) Class 10 is a part of the Class 10 Course Social Studies (SST) Class 10.
All you need of Class 10 at this link: Class 10
|
66 videos|614 docs|79 tests
|
FAQs on Cheatsheet: Gender, Religion and Caste - Social Studies (SST) Class 10
| 1. What is the significance of social diversity in Indian democracy? |  |
Ans. Social diversity is fundamental to Indian democracy as it reflects the country's varied cultural, religious, and ethnic backgrounds. This diversity ensures that multiple voices and perspectives are represented in governance, promoting inclusivity and social justice. It also encourages dialogue and understanding among different groups, which is essential for national unity and stability.
| 2. How does gender influence politics in India? |  |
Ans. Gender plays a crucial role in Indian politics, as women's participation has historically been limited. However, recent efforts have aimed at increasing women's representation through reservations in local governance and political parties. Women's issues such as health, education, and safety are gaining prominence, influencing policy decisions and political agendas.
| 3. What is the relationship between religion and politics in India? |  |
Ans. Religion significantly impacts Indian politics, often shaping party ideologies and electoral strategies. Communalism, or the politicization of religion, can lead to divisions and conflicts. Political parties may leverage religious identities to garner support, which can both mobilize communities and create tensions within society.
| 4. How does caste affect political dynamics in India? |  |
Ans. Caste remains a powerful factor in Indian politics, influencing voting behavior and party allegiance. Political parties often cater to specific caste groups to secure votes, leading to the emergence of caste-based parties. While affirmative action policies aim to uplift marginalized castes, caste-based politics can also perpetuate divisions and social stratification.
| 5. What steps are being taken to address social and religious diversity in Indian governance? |  |
Ans. To address social and religious diversity, the Indian government has implemented various policies, including affirmative action, reservations for marginalized communities, and laws protecting minority rights. Additionally, civil society organizations work to promote awareness and advocacy for inclusivity, aiming to ensure that all groups have a voice in the democratic process.
Related Searches




















