Class 10 Exam > Class 10 Notes > Social Studies (SST) Class 10 > Cheatsheet: Globalisation and the Indian Economy
Cheatsheet: Globalisation and the Indian Economy | Social Studies (SST) Class 10 PDF Download

Consumer Choices
Consumers enjoy a wide range of goods (e.g., cameras, phones, cars) due to recent market transformations.
- Past: Limited choices (e.g., Ambassador, Fiat cars in India).
- Present: Diverse brands for shirts, TVs, fruit juices, etc.
- Impact: Increased competition, better quality, lower prices for consumers.
Production Across Countries
Multinational Corporations (MNCs):
- Companies managing production in multiple countries.
- Set up factories in regions with cheap labor/resources to minimize costs.
- Proximity to markets.
- Availability of skilled/unskilled labor at low costs.
- Access to production resources.
- Government policies protecting MNC interests.
Interlinking Production:
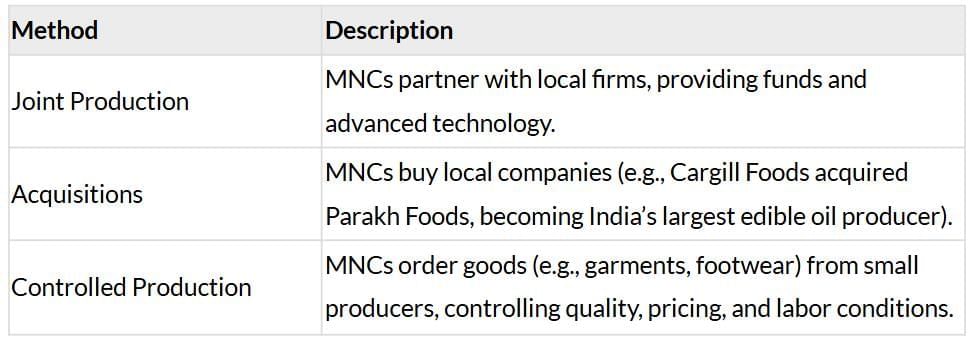
Benefits to Local Firms: Access to funds, advanced technology, and modern production methods.
Foreign Trade and Market Integration
- Role: Connects markets across nations, increasing product variety and competition.
- Historical Context: Trade routes (e.g., East India Company) linked nations.
- Producers reach global markets.
- Prices align across markets.
- Consumers get more choices at lower prices (e.g., Chinese toys in India).
- Example: Chinese toys flooded Indian markets, reducing prices but challenging local toy makers.
What is Globalisation?
Rapid integration of countries through trade and investment by MNCs.
Examples:
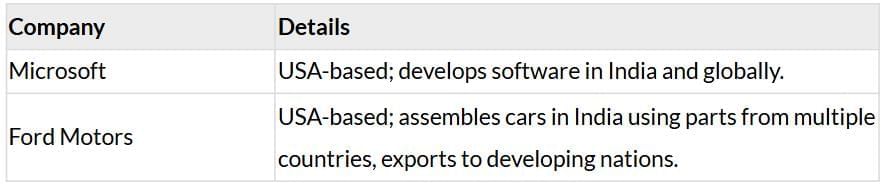
Impact: Creates jobs, boosts global economic interdependence.
Factors Enabling Globalisation

Trade Barriers Example: Tax on Chinese toys raises prices, protecting Indian toy makers.
Role of MNCs in Globalisation
- Market Expansion: Facilitate trade of goods, services, and technology.
- Technology Transfer: Introduce advanced tech and management practices.
- Investment: Fund local firms, boosting growth and jobs.
- Competition: Improve product quality, lower prices.
- Cultural Exchange: Introduce new products and practices globally.
World Trade Organisation (WTO)
- Role: Promotes free trade, sets international trade rules (161 member countries, India joined in 1995).
- Criticism: Developing nations argue developed countries maintain unfair subsidies (e.g., agriculture).
Impact of Globalisation in India

Note: Small/medium industries employ 11 crore people, second only to agriculture.
Steps to Attract Foreign Investment
Government Initiatives:
- Special Economic Zones (SEZs): Offer tax exemptions, world-class facilities (electricity, water, roads).
- Flexible Labour Laws: Allow temporary hiring to reduce costs.
- Benefits to Local Firms: Supply raw materials to SEZs.
- Opposition: Concerns about displacement and prioritizing corporate interests.
Struggle for Fair Globalisation
Unequal Benefits: Educated, wealthy gain more; others miss out.
- Government protection of all citizens.
- Enforce labour laws.
- Support small producers.
- Use trade barriers if needed.
- Negotiate fairer WTO rules.
People’s Role: Public campaigns and organisations (e.g., ILO) influence trade decisions.
The document Cheatsheet: Globalisation and the Indian Economy | Social Studies (SST) Class 10 is a part of the Class 10 Course Social Studies (SST) Class 10.
All you need of Class 10 at this link: Class 10
|
66 videos|614 docs|79 tests
|
FAQs on Cheatsheet: Globalisation and the Indian Economy - Social Studies (SST) Class 10
| 1. What are the main features of globalisation? |  |
Ans.Globalisation is characterized by the increased interconnectedness of economies, cultures, and populations across the world. Key features include the expansion of international trade, the rise of multinational corporations (MNCs), advancements in technology and communication, and the flow of capital and labor across borders. These elements contribute to a more integrated global economy, facilitating the exchange of goods, services, and ideas.
| 2. What role do MNCs play in the process of globalisation? |  |
Ans.Multinational corporations play a crucial role in globalisation by establishing operations in multiple countries, which helps in spreading technology, capital, and managerial expertise. MNCs contribute to economic growth in host countries by creating jobs, increasing production, and enhancing competitiveness. They often influence local markets and can drive policy changes to facilitate their operations, thereby shaping the global economic landscape.
| 3. How does the World Trade Organisation (WTO) influence global trade? |  |
Ans.The World Trade Organisation (WTO) influences global trade by providing a framework for negotiating and formalizing trade agreements among member countries. It aims to ensure that trade flows as smoothly, predictably, and freely as possible. The WTO also resolves trade disputes and monitors national trade policies, promoting fairness and reducing trade barriers to enhance global economic cooperation.
| 4. What are the impacts of globalisation on the Indian economy? |  |
Ans.Globalisation has had significant impacts on the Indian economy, including increased foreign investment, enhanced access to international markets, and accelerated economic growth. It has led to the emergence of a competitive environment, promoting efficiency and innovation in various sectors. However, globalisation has also led to challenges such as income inequality and environmental concerns, necessitating policies to address these issues.
| 5. What steps can be taken to attract foreign investment in a country? |  |
Ans.To attract foreign investment, countries can implement several strategies, including creating a favorable regulatory environment, offering tax incentives, improving infrastructure, and ensuring political stability. Transparency in governance and protecting investors' rights are also crucial. Additionally, promoting skilled labor and fostering innovation can make a country more appealing to foreign investors looking for growth opportunities.
Related Searches
















