Cheatsheet: Life Lines of National Economy | Social Studies (SST) Class 10 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| Why Do We Need Political Parties? |

|
| How Many Parties Should We Have? |

|
| National and State Parties in India |

|
| Challenges to Political Parties |

|
| Reforms for Political Parties |

|
Introduction
Political parties are groups with shared beliefs aiming to influence government policy. They are vital for democracy, shaping policies, representing interests, and ensuring governance. This cheatsheet covers their role, number, types in India, challenges, and reforms.
Why Do We Need Political Parties?
Parties represent diverse groups, form policies, contest elections, govern, act as opposition, shape public opinion, and connect citizens to government schemes. They ensure structured governance, accountability, and representation in complex societies.
Role of Political Parties
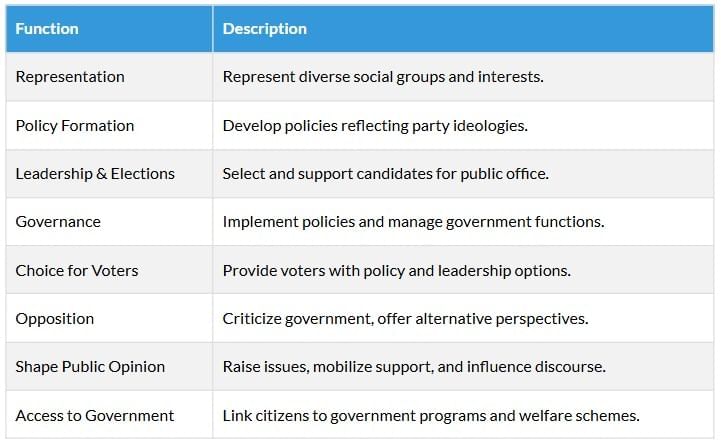
Necessity
- Coordination: Provide structured policy platforms and accountability.
- Government Formation: Ensure stable governance and national focus.
- Representation: Aggregate diverse views in complex societies.
- Checks and Balances: Support or restrain government policies.
How Many Parties Should We Have?
India has over 750 registered parties, but only a few are major contenders. The ideal number depends on the system: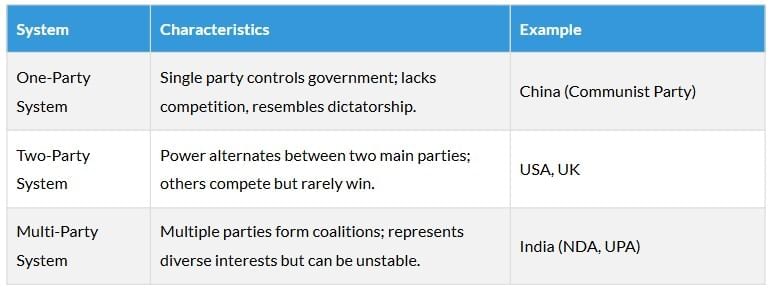
Note: No universal ideal system; evolves based on societal, regional, and historical factors.
National and State Parties in India
India’s political landscape includes national parties (active across states) and state parties (regional focus). National parties follow unified policies, while state parties enhance federalism.
National Parties
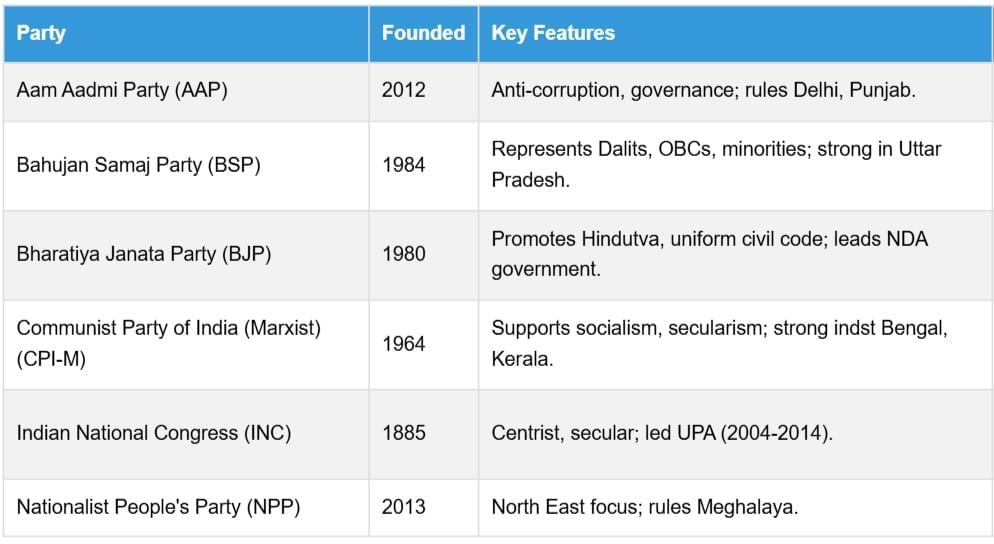
State Parties
- Operate within specific states (e.g., Samajwadi Party, Biju Janata Dal).
- Increasing influence since 1990s; strengthen federalism.
- No single national party won Lok Sabha majority without state party alliances until 2014.
Challenges to Political Parties
Political parties face significant issues that undermine democracy:
Reforms for Political Parties
Reforms aim to address challenges and strengthen democracy, but require willingness and external pressure: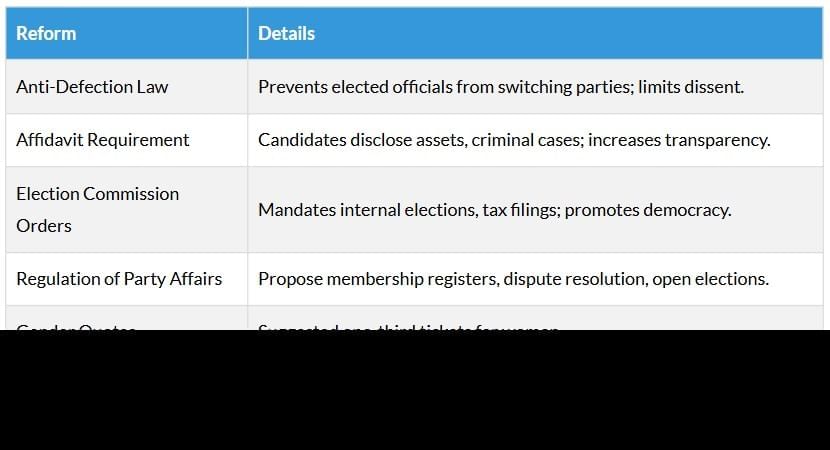
Alternative Approaches
- Public Pressure: Citizens, media, and movements can push for reforms.
- Public Participation: Active citizen involvement strengthens democracy.
|
66 videos|614 docs|79 tests
|
FAQs on Cheatsheet: Life Lines of National Economy - Social Studies (SST) Class 10
| 1. Why are political parties essential for a democratic system? |  |
| 2. How many political parties are typically considered ideal for a functioning democracy? |  |
| 3. What are the roles of national and state political parties in India? |  |
| 4. What challenges do political parties face in India? |  |
| 5. What reforms are suggested for improving the functioning of political parties? |  |















