Class 10 Exam > Class 10 Notes > Social Studies (SST) Class 10 > Cheatsheet: Life Lines of National Economy
Cheatsheet: Life Lines of National Economy | Social Studies (SST) Class 10 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Importance of Transport and Communication |

|
| Types of Transport |

|
| Roadways |

|
| Classification of Roads |

|
| Railways |

|
| Pipelines |

|
| Waterways |

|
| Major Sea Ports |

|
| Airways |

|
| Communication |

|
| International Trade |

|
Importance of Transport and Communication
- Essential for producing and moving goods and services across regions.
- Efficient transport and communication drive economic growth and global trade.
- Connects India globally, boosting trade and improving quality of life.
Types of Transport
- Land Transport: Roads, railways, pipelines.
- Water Transport: Inland waterways, sea ports.
- Air Transport: Domestic and international airways.
Expansion of Trade and Transport
- Early trade was local; science and technology made it global.
- Fast transport systems make the world a "global village."
- Transport and communication work together for smooth trade.
Roadways
India’s Road Network: Second largest globally.
Advantages Over Railways:
- Cheaper to build and maintain.
- Can navigate hilly, uneven terrains (e.g., Himalayas).
- Ideal for short distances and small loads.
- Door-to-door service; connects to railways, airports, and ports.
Classification of Roads
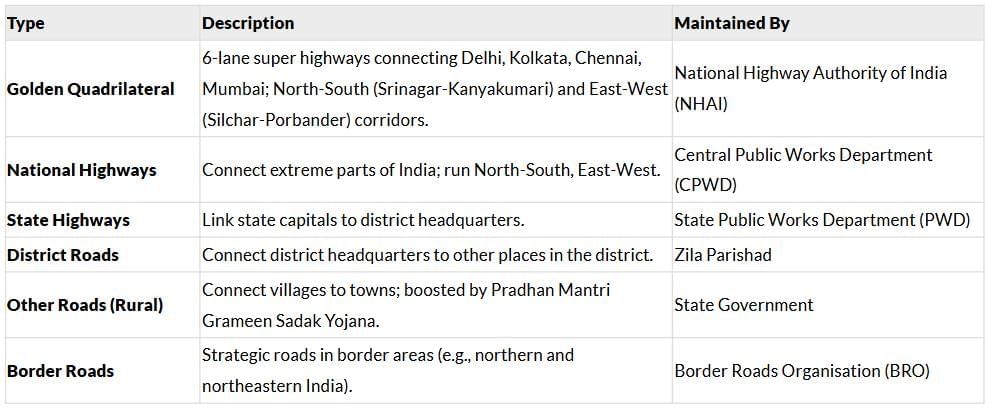
Challenges:
- Inadequate road network for traffic volume.
- Many roads are unmetalled, unusable in rainy seasons.
- Congested city roads; old, narrow bridges and culverts.
Railways
Significance:
- Principal mode for freight and passengers.
- Supports business, tourism, pilgrimage, and long-distance goods transport.
- Integrates India’s economy and boosts industry and agriculture.
- Network: 7,031 stations, 63,221 km route, 7,817 locomotives, 228,170 wagons (as of 31st March).
- Railway Zones: Organized into 16 zones for efficient management.
Factors Affecting Railway Distribution

Pipelines
Purpose: Transport crude oil, petroleum products, natural gas, and slurried solids.
Advantages:
- High initial cost but low running costs.
- No trans-shipment losses or delays.
Major Pipeline Networks
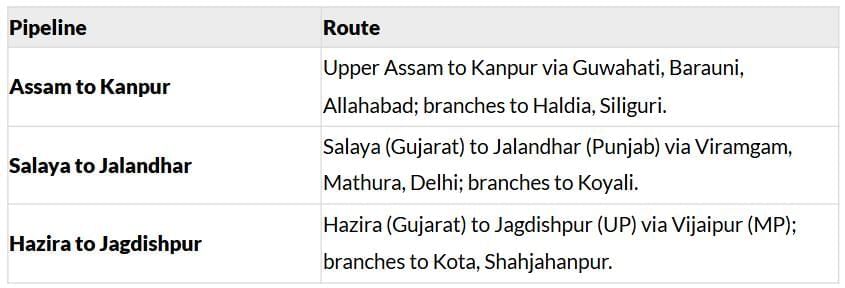
Waterways
- Advantages: Cheapest, fuel-efficient, eco-friendly; ideal for heavy, bulky goods.
- Inland Waterways: 14,500 km total, only 3,700 km navigable by mechanized boats.
National Waterways
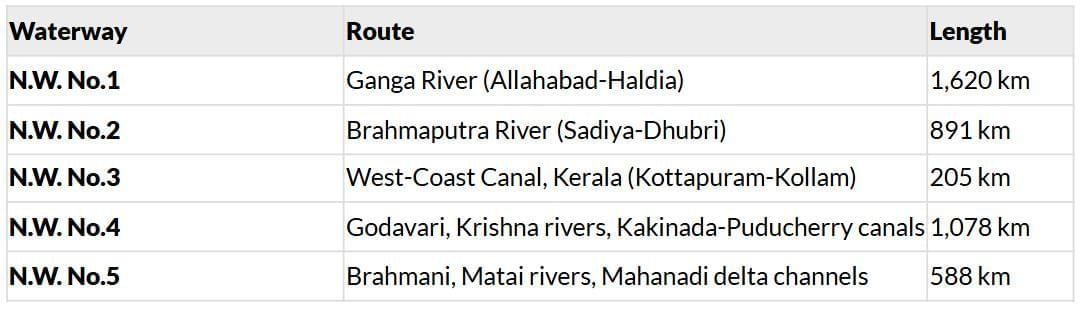
- Other Waterways: Mandavi, Zuari, Cumberjua, Sunderbans, Barak, Kerala backwaters.
Major Sea Ports
- India’s Coastline: 7,516.6 km; 12 major, 181 medium/minor ports.
- Role: Handle 95% of India’s foreign trade.

Airways
Significance:
- Fastest, most comfortable, prestigious mode.
- Covers difficult terrains (mountains, deserts, forests, oceans).
- Vital for northeastern India due to challenging geography.
- Nationalization: Air transport nationalized in 1953.
- Services: Indian Airlines, Alliance Air, private airlines, non-scheduled operators.
- Pawanhans Helicopters: Serves ONGC, northeastern states, and remote areas (J&K, HP, Uttarakhand).
Communication
Types:
- Personal: Postal services, telephones, mobile phones.
- Mass: Radio, TV, newspapers, films.
Indian Postal Network
Largest in the World:
- Handles parcels and written communication.
- First-Class Mail: Cards, envelopes (airlifted).
- Second-Class Mail: Book packets, newspapers (surface mail).
- Mail Channels: Rajdhani, Metro, Green, Business, Bulk, Periodical Channels for quick delivery.
Telephone and Mobile
- Telephone: One of Asia’s largest networks; 24-hour STD facility in every village.
- Mobile Phones: Fastest-growing network; empowers small businesses (e.g., vendors, plumbers).
Mass Communication
- All India Radio (Akashvani): Broadcasts in national, regional, local languages.
- Doordarshan: Largest terrestrial TV network; offers entertainment, education, sports.
- Newspapers: Published in ~100 languages; Hindi leads, followed by English, Urdu.
- Films: India is the largest producer of feature films; certified by Central Board of Film Certification.
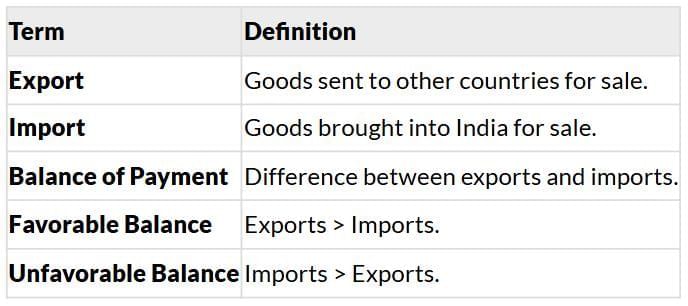
International Trade
- Definition: Trade between countries via sea, air, or land.
- Economic Barometer: Reflects a country’s prosperity.
Key Terms
The document Cheatsheet: Life Lines of National Economy | Social Studies (SST) Class 10 is a part of the Class 10 Course Social Studies (SST) Class 10.
All you need of Class 10 at this link: Class 10
|
66 videos|614 docs|79 tests
|
FAQs on Cheatsheet: Life Lines of National Economy - Social Studies (SST) Class 10
| 1. What is the significance of transport and communication in the national economy? |  |
Ans. Transport and communication are vital for the national economy as they facilitate the movement of goods and people, ensuring efficient trade and connectivity. They enhance economic growth by reducing transportation costs, increasing accessibility to markets, and enabling timely delivery of products. Additionally, effective communication systems support business operations and improve coordination between various sectors.
| 2. What are the main types of transport used in the economy? |  |
Ans. The main types of transport used in the economy include roadways, railways, waterways, airways, and pipelines. Each mode has its advantages: roadways provide flexibility and accessibility, railways are efficient for bulk transport, waterways are cost-effective for long-distance transportation, airways offer speed, and pipelines are essential for transporting liquids and gases.
| 3. How are roads classified in the context of transport? |  |
Ans. Roads are classified into several categories based on their functions and surface types. The primary classifications include national highways, state highways, district roads, and rural roads. Additionally, roads can be categorized as paved or unpaved, depending on their surface materials, which affects their durability and maintenance needs.
| 4. What role do major sea ports play in international trade? |  |
Ans. Major sea ports are crucial for international trade as they serve as gateways for importing and exporting goods. They facilitate the transfer of cargo between ships and land transport, allowing for efficient distribution of products globally. Well-equipped ports enhance a country's trade competitiveness by providing necessary infrastructure for handling large volumes of goods.
| 5. Why is effective communication important for transportation systems? |  |
Ans. Effective communication is essential for transportation systems as it ensures timely sharing of information regarding schedules, routes, and logistics. It helps in coordinating activities between various transport modes, enhancing safety, and improving operational efficiency. Additionally, effective communication facilitates better customer service by keeping users informed about delays or changes in transport services.
Related Searches




















