Cheatsheet: Minerals and Energy Resources | Social Studies (SST) Class 10 PDF Download
What is a Mineral?
Minerals are found in rocks, soil, and water, serving as nutrients for plants and animals, building blocks for rocks, and raw materials for industries like electronics, jewelry, and construction. 
Mode of Occurrence of Minerals
Minerals occur in various geological formations, affecting their extraction methods and costs. The geological formation determines the ease and cost of extraction, with sufficient mineral concentration being crucial for commercial viability. Different formations, such as veins, lodes, or placer deposits, influence mining techniques and economic feasibility.
Distribution of Mineral Resources in India
The distribution of minerals in India reflects its varied geological history. Peninsular rocks are rich in coal, metallic minerals, and mica, while sedimentary rocks in Gujarat and Assam hold petroleum deposits.
Ferrous Minerals
Ferrous minerals account for about three-fourths of India’s metallic mineral production, providing a strong foundation for metallurgical industries. India’s abundant iron ore and manganese resources support both domestic needs and exports, with major production concentrated in specific belts.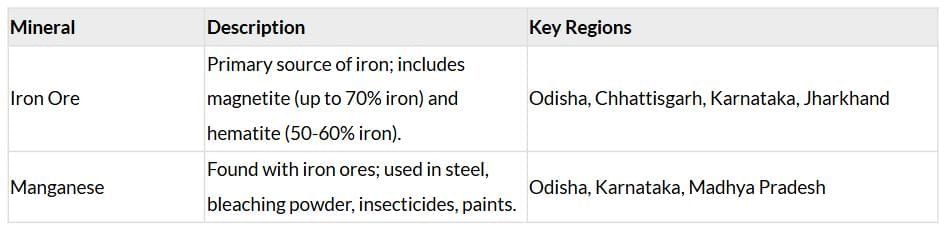
Major Iron Ore Belts:
- Odisha-Jharkhand: High-grade hematite in Badampahar, Gua, Noamundi.
- Durg-Bastar-Chandrapur: Bailadila (Chhattisgarh) exports to Japan, South Korea.
- Ballari-Chitradurga: Kudremukh (Karnataka) is a major export unit.
- Maharashtra-Goa: Moderate-quality ore exported via Marmagao port.
Non-Ferrous Minerals
Non-ferrous minerals, lacking iron, are vital for alloys, electronics, and other specialized industries. India’s non-ferrous mineral reserves are limited but crucial for applications like electrical wiring, construction, and aluminum production. Copper and bauxite are key examples, supporting industries with their unique properties like conductivity and lightness.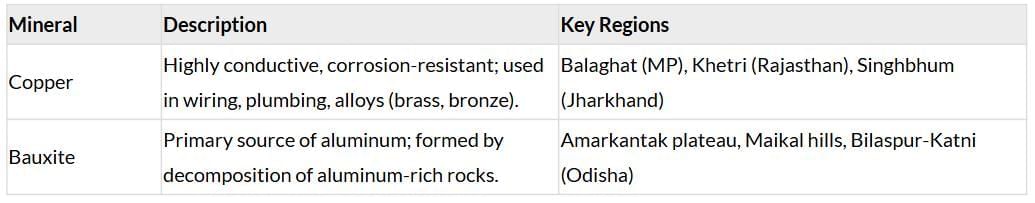
Non-Metallic Minerals
Non-metallic minerals, free of metal content, are essential for construction, electronics, and other sectors. Non-metallic minerals like mica and limestone support industries such as cement production, electronics, and construction. Their diverse applications make them critical to the economy, with significant deposits in specific regions of India.
Hazards of Mining
Mining activities expose workers to hazardous conditions like dust and noxious fumes, leading to health issues, while environmental impacts include land degradation and water pollution. These challenges necessitate safer practices and environmental safeguards to mitigate risks.
Conservation of Minerals
Mineral deposits, formed over millions of years, are depleting rapidly due to high consumption. As extraction moves to deeper, lower-quality ores, costs increase, making conservation essential through sustainable practices, improved technologies, and recycling.
Energy Resources
Energy resources are vital for agriculture, industry, transport, and domestic use. India’s growing energy demand underscores the need for sustainable sources. Conventional sources like coal and petroleum are non-renewable, while non-conventional sources like solar and wind offer renewable alternatives.
Conservation of Energy Resources
India’s low energy efficiency and increasing consumption highlight the need for conservation strategies. Promoting renewable energy sources and efficient practices ensures sustainable development, balancing economic growth with resource preservation.
|
66 videos|614 docs|79 tests
|
FAQs on Cheatsheet: Minerals and Energy Resources - Social Studies (SST) Class 10
| 1. What are the main types of minerals, and how are they categorized? |  |
| 2. How are mineral resources distributed across India? |  |
| 3. What are the hazards associated with mining activities? |  |
| 4. Why is the conservation of minerals important, and what measures can be taken? |  |
| 5. What are the different types of energy resources, and how do they relate to mineral resources? |  |
















