Class 10 Exam > Class 10 Notes > Social Studies (SST) Class 10 > Cheatsheet: Money and Credit
Cheatsheet: Money and Credit | Social Studies (SST) Class 10 PDF Download
What is Money?
Essential for daily needs and desires, acting as a solution to many challenges.
Functions of Money:
- Facilitates transactions.
- Common measure for valuing goods/services.
- Maintains purchasing power over time.
Money as a Medium of Exchange
Easily exchanged for any commodity or service, offering flexibility.
Barter System:
- Exchanging goods for goods (e.g., surplus vegetables for wheat).
- Double coincidence of wants—both parties must want what the other offers.
- Impractical to carry heavy goods, restricts economic activity.
Evolution of Money:
- Grains, cattle used as money in India.
- Gold, silver, copper coins introduced later.
- Paper notes and coins issued by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI).
- Eliminates double coincidence of wants, smoothens exchange.
Modern Forms of Money
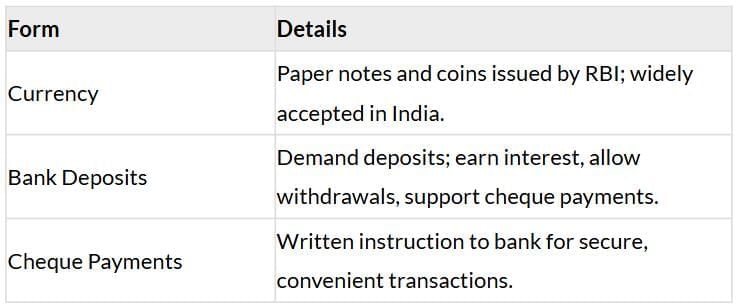
Note: Currency and deposits work together, managed by the banking system.
Loan Activities of Banks
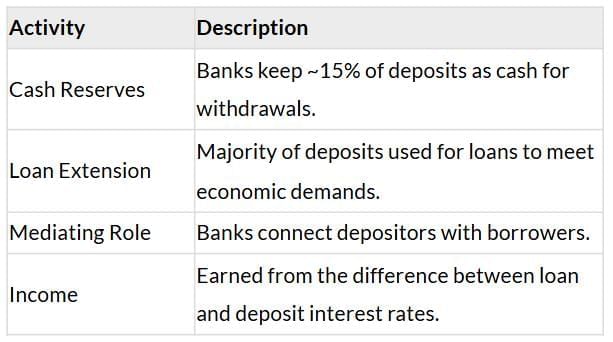
Two Credit Situations

Role of Credit: Can boost earnings (Salim) or lead to debt trap (Swapna).
Terms of Credit

Lender’s Right: Can sell collateral if loan isn’t repaid.
Formal vs. Informal Credit
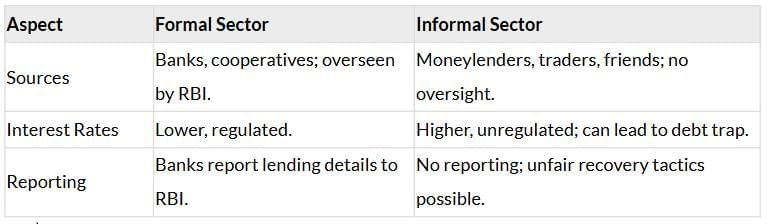
Need: Increase formal credit to reduce reliance on costly informal loans.
Self-Help Groups (SHGs)
- Structure: 15-20 members (often women) save regularly (Rs 25-100).
- Function: Members take small loans from group savings at low interest.
- Bank Loans: After 1-2 years of regular savings, SHGs can access bank loans for self-employment.
- No collateral needed.
- Timely, affordable loans.
- Empowers rural poor, especially women.
- Platform for discussing social issues (health, nutrition, domestic violence).
Example: Grameen Bank (Bangladesh)
- Overview: Provides microcredit to poor women; 9 million members by 2018.
- Impact: Reliable borrowers start small businesses, fostering economic growth.
Summary
- Role of Banks: Manage deposits and loans; mediate between depositors and borrowers.
- Credit Sources: Formal (banks, cooperatives) vs. informal (moneylenders); formal is cheaper but less accessible to poor.
- Reform Needed: Expand formal credit to rural areas and poor households to reduce debt traps and promote economic growth.
The document Cheatsheet: Money and Credit | Social Studies (SST) Class 10 is a part of the Class 10 Course Social Studies (SST) Class 10.
All you need of Class 10 at this link: Class 10
|
66 videos|614 docs|79 tests
|
FAQs on Cheatsheet: Money and Credit - Social Studies (SST) Class 10
| 1. What is the definition of money and its primary functions? |  |
Ans. Money is defined as a medium of exchange that facilitates transactions for goods and services. Its primary functions include acting as a medium of exchange, a unit of account, a store of value, and a standard of deferred payment.
| 2. What are the modern forms of money used today? |  |
Ans. Modern forms of money include physical currency such as coins and banknotes, digital currency, bank deposits, and electronic payment systems. These forms allow for easier and faster transactions compared to traditional barter systems.
| 3. How do banks conduct loan activities and what is their significance? |  |
Ans. Banks conduct loan activities by accepting deposits from savers and lending those funds to borrowers. This process is significant as it facilitates investment and spending in the economy, supporting growth and development.
| 4. What is the difference between formal and informal credit? |  |
Ans. Formal credit refers to loans provided by banks and financial institutions that follow regulated procedures and require documentation. In contrast, informal credit is provided by non-institutional sources, such as friends or local moneylenders, and often lacks formal agreements and regulations.
| 5. What are Self-Help Groups (SHGs) and their role in credit access? |  |
Ans. Self-Help Groups (SHGs) are small, voluntary associations of people who come together to save and lend money among themselves. They play a crucial role in providing credit access to marginalized communities, promoting financial inclusion and empowering members through collective savings and loans.
Related Searches
















