Cheatsheet: Nationalism in India | Social Studies (SST) Class 10 PDF Download
Timeline and Key Events
This timeline highlights the significant events in the Indian nationalist movement, focusing on how different groups and leaders contributed to India's struggle for independence from British rule.
Nationalism in India developed as a response to British rule, with various leaders and movements emerging to fight for independence. The struggle spanned decades, incorporating diverse groups and ideologies. Major events in Indian Nationalism as follows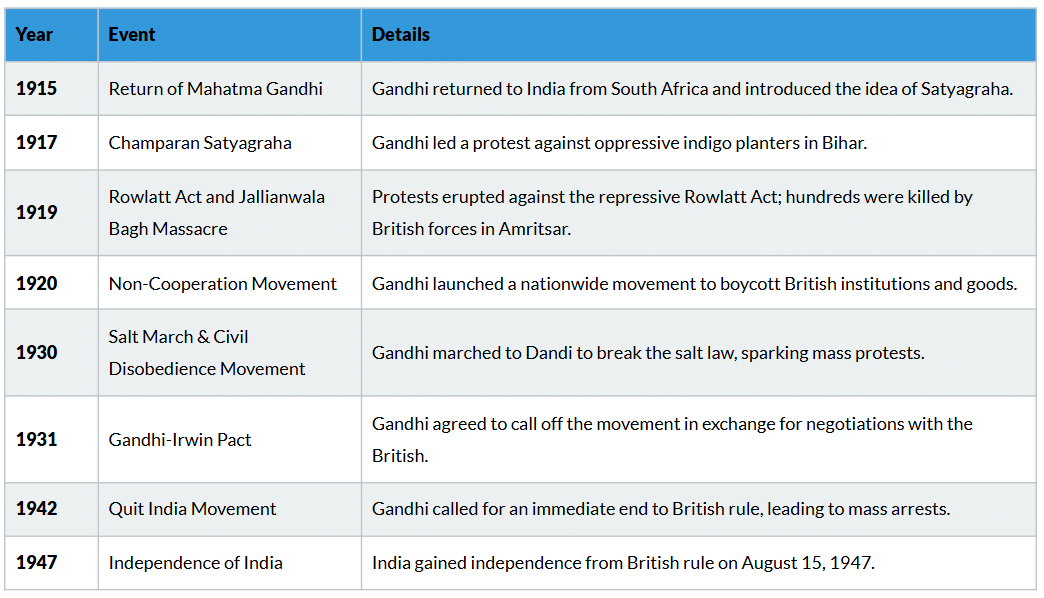
Nationalism: Europe vs. India
Compares how nationalism developed in Europe through state formation and in India via anti-colonial unity.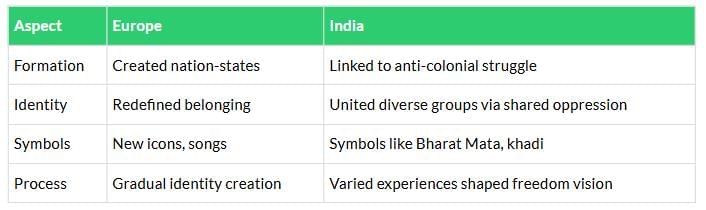
Congress & Gandhi’s Role
Gandhi and Congress unified diverse groups for India’s freedom struggle.

First World War & Khilafat
Details economic and social impacts of WWI and Gandhi’s use of Khilafat for unity.

Satyagraha
Explains Gandhi’s non-violent Satyagraha and its application in key early movements.
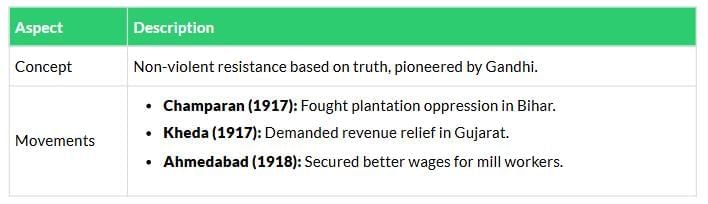
Rowlatt Act (1919)
Opposition to Rowlatt Act, Jallianwala Bagh massacre, and its aftermath.

Non-Cooperation Movement (1920–22)
Gandhi’s strategy, urban/rural impacts, and reasons for the movement’s end.
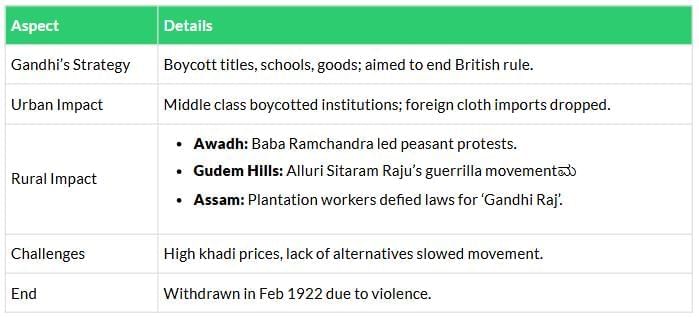
Civil Disobedience & Salt March
Details the Salt March, Civil Disobedience Movement, and Gandhi-Irwin Pact outcomes.

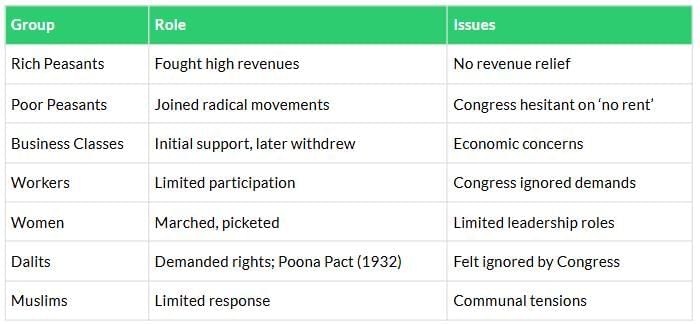
Participation in Movements
Different social groups participated and faced challenges in the freedom struggle.
Key Takeaways
- Nationalism in India was closely linked to the anti-colonial movement.
- Gandhi played a crucial role in uniting people through non-violent struggles.
- Different social groups had unique interpretations of nationalism, contributing in their own ways.
- The independence movement witnessed major events like the Non-Cooperation Movement, Civil Disobedience Movement, and Quit India Movement.
Conclusion
The Indian nationalist movement evolved over decades, with contributions from diverse social and political groups. Mahatma Gandhi and the Congress played a crucial role in uniting people under a common vision for independence. The movement's success was shaped by various mass struggles, ultimately leading to India's freedom in 1947.
|
66 videos|614 docs|79 tests
|
FAQs on Cheatsheet: Nationalism in India - Social Studies (SST) Class 10
| 1. What were the main causes of nationalism in India during the freedom struggle? |  |
| 2. Who were the key leaders in the Indian nationalist movement? |  |
| 3. What role did the Indian National Congress play in the nationalist movement? |  |
| 4. How did the partition of India impact nationalism? |  |
| 5. What were some significant movements that contributed to the rise of nationalism in India? |  |

















