Circles Class 10 Notes Maths Chapter 10
What is a Circle?
- A circle is a shape made up of all points in a flat area that are the same distance (called the radius) from a specific point (known as the centre).
- Any line that goes through the circle creates a line of symmetry, and it also has rotational symmetry around the centre for any angle.
Terms related to Circle
1. Centre
The fixed point is called the centre.
2. Radius
The constant distance from the centre is known as the radius.
3. Chord
A line segment connecting any two points on the circle is termed a chord.
4. Diameter
A chord that goes through the centre of the circle is called a diameter, which is the longest chord.
5. Secant
A straight line that intersects the circle at two points, also known as an extended chord.
6. Tangent
A line that touches the circle at exactly one point is referred to as a tangent.
The tangent to a circle is perpendicular to the radius through the point of contact.
⇒ OP ⊥ AB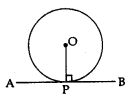
The lengths of the two tangents from an external point to a circle are equal.
⇒ AP = PB
7. Length of Tangent Segment
PB and PA are normally called the lengths of tangents from outside point P.
8. Arc
It is basically the connected curve of a circle.
Important Theorems related to Circle
Theorem 1: The tangent at any point of a circle is perpendicular to the radius through the point of contact.
Given: XY is a tangent at point P to the circle with centre O.
To prove: OP ⊥ XY
Construction: Take a point Q on XY other than P and join OQ
Proof: If point Q lies inside the circle, then XY will become a secant and not a tangent to the circle
OQ > OP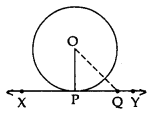
This happens with every point on line XY except point P. OP is the shortest of all the distances of point O the points of XY
OP ⊥ XY …[Shortest side is the perpendicular]
Example: A tangent PQ at a point P of a circle of radius 5 cm meets a line through the centre O at a point Q so that OQ = 12 cm. Then what is the length PQ?
Sol:
Given: Radius OP = 5 cm, OQ = 12 cm
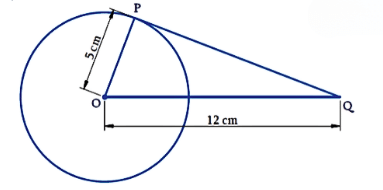
We have to find the length of the tangent PQ.
ΔOPQ is a right-angle triangle according to Theorem 10.1: The tangent at any point of a circle is perpendicular to the radius through the point of contact.
By Pythagoras theorem:
OQ² = OP² + PQ²
12² = 5² + PQ²
144 = 25 + PQ²
PQ² = 119
PQ = √119
Thus, the length of PQ is √119 cm.
Theorem 2: A line drawn through the endpoint of a radius and perpendicular to it, is tangent to the circle.
Given: A circle C(O, r) and a line APB is perpendicular to OP, where OP is the radius.
To prove: AB is tangent at P.
Construction: Take a point Q on line AB, different from P, and join OQ.
Proof: Since OP ⊥ AB
OP < OQ ⇒ OQ > OP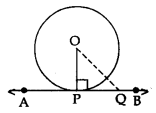
Point Q lies outside the circle.
Therefore, every point on AB, other than P, lies outside the circle.
This shows that AB meets the circle at point P.
Hence, AP is tangent to the circle at P.
Example: From a point Q, the length of the tangent to a circle is 24 cm and the distance of Q from the centre is 25 cm. What is the radius of circle?
Sol:
Let's draw a figure as per the given question.
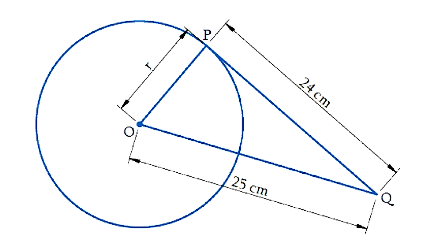
A tangent at any point of a circle is perpendicular to the radius at the point of contact.
Therefore, OPQ is a right-angled triangle.
By Pythagoras theorem,
OQ2 = OP2 + PQ2
252 = r2 + 242
r2 = 252 - 242
r2 = 625 - 576
r2 = 49
r = ± 7
Radius cannot be a negative value, hence, r = 7 cm.
Theorem 3: The lengths of tangents drawn from an external point to a circle are equal
Given: PT and PS are tangents from an external point P to the circle with centre O.
To prove: PT = PS
Construction: Join O to P, T and S. 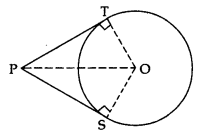
Proof: In ∆OTP and ∆OSP.
OT = OS …[radii of the same circle]
OP = OP …[common]
∠OTP = ∠OSP …[each 90°]
∆OTP = ∆OSP …[R.H.S.]
PT = PS …[c.p.c.t.]
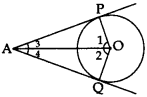
Note: If two tangents are drawn to a circle from an external point, then:
- They subtend equal angles at the centre i.e., ∠1 = ∠2.
- They are equally inclined to the segment joining the centre to that point i.e., ∠3 = ∠4.
- ∠OAP = ∠OAQ
Example: If tangents PA and PB from a point P to a circle with centre O are inclined to each other at angle of 80°, then what is the value of ∠POA?
Sol:
Let's draw a figure as per the question.
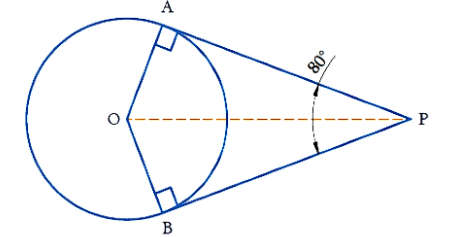
The lengths of tangents drawn from an external point to a circle are equal.
A tangent at any point of a circle is perpendicular to the radius at the point of contact.
In ΔOAP and in ΔOBP
OA = OB (radii of the circle are always equal)
AP = BP (length of the tangents)
OP = OP (common)
Therefore, by SSS congruency ΔOAP ≅ ΔOBP
SSS congruence rule: If three sides of one triangle are equal to the three sides of another triangle, then the two triangles are congruent.
If two triangles are congruent then their corresponding parts are equal.
Hence,
∠POA = ∠POB
∠OPA = ∠OPB
Therefore, OP is the angle bisector of ∠APB and ∠AOB
Hence, ∠OPA = ∠OPB = 1/2 (∠APB )
= 1/2 × 80°
= 40°
By angle sum property of a triangle,
In ΔOAP
∠A + ∠POA + ∠OPA = 180°
OA ⊥ AP (Theorem : The tangent at any point of a circle is perpendicular to the radius through the point of contact.)
Therefore, ∠A = 90°
90° + ∠POA + 40° = 180°
130° + ∠POA = 180°
∠POA = 180° - 130°
∠POA = 50°
|
127 videos|584 docs|79 tests
|
FAQs on Circles Class 10 Notes Maths Chapter 10
| 1. What is the definition of a circle in geometry? |  |
| 2. What are the key terms related to circles that students should know? |  |
| 3. What are some important theorems related to circles that are commonly taught in Class 10? |  |
| 4. How can the circumference of a circle be calculated? |  |
| 5. What is the relationship between the radius and diameter of a circle? |  |





















