Class 10 Economics Chapter 3 Previous Year Questions - Money and Credit
Previous Year Questions 2025
Q1: Why does it become difficult for farmers in rural areas to take loans from government banks? Read the following reasons and choose the most appropriate option: (1 Mark ) (CBSE 2025)
I. Lack of collateral
II. Complicated procedure
III. Higher cost of borrowing
IV. Lack of awareness
Options:
(a) Only I, II and III are correct.
(b) Only II, III and IV are correct.
(c) Only I, II and IV are correct.
(d) Only I, III and IV are correct.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c)
Farmers in rural areas face difficulties in obtaining loans from government banks due to:
- I. Lack of collateral: Many farmers do not have sufficient assets (like land titles or property) to offer as collateral, which banks require to secure loans.
- II. Complicated procedure: The loan application process in government banks often involves extensive paperwork and bureaucratic procedures, which can be challenging for farmers with limited literacy or resources.
- IV. Lack of awareness: Many rural farmers are unaware of government bank loan schemes or how to access them due to limited outreach and information.
III. Higher cost of borrowing is incorrect because government banks typically offer loans at lower interest rates compared to informal sources, making borrowing costs relatively affordable. Thus, option (c) is the most appropriate.
Q2: Which of the following groups in urban India depend on informal sources to meet their credit needs? (1 Mark ) (CBSE 2025)
(a) Poor households
(b) Households with few assets
(c) Both poor households and households with few assets
(d) Both well-off households and households with few assets
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c)
In urban India, informal sources of credit (like moneylenders, traders, or relatives) are often relied upon by:
- Poor households: These households lack the income or assets to access formal credit from banks or financial institutions, pushing them toward informal lenders.
- Households with few assets: These households may not have sufficient collateral or creditworthiness to qualify for formal loans, making informal sources their primary option.
Well-off households, on the other hand, typically have access to formal credit sources like banks due to their financial stability and assets. Thus, option (c) is correct.
Q3: Read the given source and answer the questions that follow :
Loans From Cooperatives
Besides banks, the other major source of cheap credit in rural areas are the cooperative societies (or cooperatives). Members of a cooperative pool their resources for cooperation in certain areas. There are several types of cooperatives possible such as farmers cooperatives, weavers cooperatives, industrial workers cooperatives, etc. Krishak Cooperative functions in a village not very far away from Sonpur. It has 2300 farmers as members. It accepts deposits from its members. With these deposits as collateral, the Cooperative has obtained a large loan from the bank. These funds are used to provide loans to members. Once these loans are repaid, another round of lending can take place.
Krishak Cooperative provides loans for the purchase of agricultural implements, loans for cultivation and agricultural trade, fishery loans, loans for construction of houses and for a variety of other expenses. (3 Mark ) (CBSE 2025)
(a) Cooperative societies come under which source of credit?
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Cooperative societies, like banks and other financial institutions, are part of the formal credit system. They are regulated, provide loans at reasonable interest rates, and operate with structured processes, as highlighted in the source where the Krishak Cooperative secures loans from banks and lends to its members.
(b) Mention any two sources of capital of cooperative societies.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans:
- Members’ deposits: Cooperative societies collect deposits from their members, which form a significant part of their capital, as mentioned in the source where Krishak Cooperative accepts deposits.
- Loans from banks: Cooperatives use members’ deposits as collateral to obtain large loans from banks, as described in the source, to fund their lending activities.
(c) Explain the role of cooperative societies in increasing the income of farmers.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans:
Cooperative societies play a crucial role in increasing the income of farmers by providing affordable credit and support services. Based on the source and the chapter, their role can be explained as follows:
- Access to Affordable Loans: Cooperatives like Krishak Cooperative offer low-interest loans for agricultural needs, such as purchasing implements, seeds, or fertilizers. This enables farmers to invest in better farming practices, leading to higher crop yields and income.
- Support for Diverse Activities: Cooperatives provide loans for cultivation, agricultural trade, fishery, and even non-agricultural expenses like house construction. This diversification of income sources (e.g., through fishing or trade) helps farmers increase their overall earnings.
- Collective Bargaining Power: By pooling resources, cooperatives enable farmers to access bulk inputs (like seeds or fertilizers) at lower costs and sell produce at better prices, reducing dependency on exploitative middlemen and boosting profits.
- Financial Stability and Reinvestment: The cooperative’s model of lending and repayment (as described in the source) ensures a continuous cycle of credit availability. Farmers can repay loans and borrow again, allowing sustained investment in farming activities, which enhances productivity and income over time.
In conclusion, cooperative societies empower farmers by providing accessible, low-cost credit and fostering collective economic activities, thereby improving agricultural productivity and increasing their income.
Q4: Arrange the following sources of credit in the most to least order to meet the credit requirement of rural households in India and choose the correct option:
I. Government,
II. Cooperative Banks and Societies,
III. Moneylenders,
IV. Relatives and friends.
(a) III, II, I, IV,
(b) III, II, IV, I,
(c) I, III, II, IV,
(d) I, III, IV, II.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (B) III, II, IV, I.
Explanation:
- Moneylenders (III): Most rural households rely on moneylenders due to easy access, despite high interest rates, as they require minimal documentation.
- Cooperative Banks and Societies (II): These provide affordable credit but are less accessible due to membership requirements and limited reach.
- Relatives and friends (IV): Borrowing from relatives or friends is common but limited by their financial capacity.
- Government (I): Government loans are least accessed due to complex procedures, collateral requirements, and lack of awareness.
Q5: Read the given source and answer the questions that follow:
Arun's Story
Arun supervises the work of one farm labourer. Arun has seven acres of land. He is one of the few persons in Sonpur to receive bank loan for cultivation. The interest rate on the loan is 8.5 per cent per annum, and can be repaid anytime in the next three years. Arun plans to repay the loan after harvest by selling a part of the crop. He then intends to store the rest of the potatoes in a cold storage and apply for a fresh loan from the bank against the cold storage receipt. The bank offers this facility to farmers who have taken crop loan from them.
Arun’s Story case-based questions:
(i) Under which source does Arun’s loan come?
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Formal sector (Bank).
Explanation:
- Arun’s loan is from a bank, which is a formal source of credit, characterized by regulated interest rates and structured repayment terms.
(ii) Mention one important term of credit for taking a loan from the bank.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Interest rate of 8.5% per annum.
Explanation:
- The interest rate is a key term of credit, determining the cost of borrowing. In Arun’s case, the bank loan has an interest rate of 8.5% per annum, which is reasonable for formal credit.
(iii) How is Arun’s loan beneficial? Explain any two reasons.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Arun’s loan supports his agricultural activities and financial planning.
Explanation:
- Flexible repayment: The loan can be repaid anytime within three years, allowing Arun to align repayment with his harvest cycle, reducing financial stress.
- Access to additional credit: After storing crops in cold storage, Arun can obtain another loan against the storage receipt, providing continuous financial support for his farming needs.
Q6: "Reserve Bank of India plays a crucial role in regulating the Indian banks." Justify the statement.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: The RBI ensures the stability and efficiency of the banking system.
Explanation:
- Monetary policy formulation: The RBI controls money supply and interest rates through policies like repo rate, influencing credit availability and economic stability.
- Regulation and supervision: It sets guidelines for banks, ensuring safe lending practices, capital adequacy, and consumer protection.
- Financial inclusion: The RBI promotes schemes like priority sector lending, ensuring banks provide credit to agriculture, small industries, and weaker sections.
Q7: Explain any three functions of money as a medium of exchange.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Money facilitates transactions by serving as a medium of exchange.
Explanation:
- Eliminates double coincidence of wants: Money allows people to buy goods or services without needing to barter, as it is universally accepted.
- Simplifies transactions: Money provides a common measure of value, making it easier to exchange goods and services efficiently.
- Facilitates trade: Money enables smooth buying and selling across markets, supporting economic activities and specialization.
Q8: Examine the importance of bank deposits.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Bank deposits are vital for financial stability and economic growth.
Explanation:
- Source of funds for lending: Deposits provide banks with capital to offer loans, supporting agriculture, industry, and individual needs.
- Safety and security: Banks offer a secure place for people to save money, protecting it from theft or loss compared to keeping cash at home.
- Interest earnings: Deposits earn interest, encouraging savings and providing depositors with additional income over time.
Q9: Read the following sources of loan carefully and choose the correct option related to formal sources of credit:
(i) Commercial Bank,
(ii) Landlords,
(iii) Government,
(iv) Money Lender.
(a) (i) and (iii) are correct.
(b) (ii) and (iv) are correct.
(c) (i) and (ii) are correct.
(d) (ii) and (iii) are correct.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a) (i) and (iii) are correct.
Explanation:
- Commercial Bank (i): Banks are formal sources, regulated by the RBI, offering loans with structured terms.
- Government (iii): Government institutions provide formal credit through schemes like Kisan Credit Cards or subsidies.
- Landlords (ii) and Money Lender (iv): These are informal sources, as they are unregulated and often charge high interest rates.
Q10: Imagine you are a part of a Self Help Group (SHG). Explain the working system of the Self Help Group (SHG) to the new member.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: SHGs are small groups that promote savings and credit among members.
Explanation:
- Group formation: SHGs consist of 10–20 members, usually from similar socio-economic backgrounds, who come together voluntarily.
- Savings collection: Members contribute small, regular savings to a common fund, fostering a habit of thrift.
- Internal lending: The collected savings are used to provide small loans to members for immediate needs, with low interest rates.
- Bank linkage: SHGs deposit savings in banks and use them as collateral to access larger bank loans for entrepreneurial activities.
- Decision-making: Members collectively decide loan disbursal, repayment terms, and group activities, promoting mutual trust and accountability.
Q11: Imagine that you are the Village Development Officer of a village. Explain the usefulness of formal sources of credit for the farmers.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Formal sources provide affordable and reliable credit for farmers.
Explanation:
- Low interest rates: Formal sources like banks and cooperatives charge lower interest rates compared to moneylenders, reducing the cost of borrowing.
- Structured repayment: Flexible repayment schedules, aligned with harvest cycles, ease the financial burden on farmers.
- Access to larger loans: Formal institutions offer substantial loans for purchasing inputs, equipment, or land improvement, boosting productivity.
- Government support: Schemes like Kisan Credit Cards ensure easy access to formal credit with minimal documentation.
- Financial discipline: Formal loans encourage timely repayment and savings, improving farmers’ financial management.
Q12: Analyse the role of credit in rural economy.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Credit is crucial for rural economic development.
Explanation:
- Agricultural investment: Credit enables farmers to buy seeds, fertilizers, and equipment, increasing crop yields and income.
- Income diversification: Loans support non-farm activities like poultry or small businesses, reducing dependency on agriculture.
- Poverty reduction: Access to credit helps rural households meet emergency needs, preventing distress sales or debt traps.
- Infrastructure development: Credit for housing or irrigation improves living standards and farm productivity.
- Economic empowerment: Affordable credit from formal sources like SHGs or cooperatives empowers rural communities to pursue entrepreneurial ventures.
Q13: Analyse the differences between formal and informal sectors of credit.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Formal and informal credit sectors differ significantly in structure and impact.
Explanation:
- Regulation: Formal sources (banks, cooperatives) are regulated by the RBI, ensuring transparency, while informal sources (moneylenders, landlords) are unregulated.
- Interest rates: Formal credit has lower, fixed interest rates; informal credit often involves exorbitant rates, leading to debt traps.
- Accessibility: Formal credit requires documentation and collateral, limiting access; informal credit is easily accessible but exploitative.
- Repayment terms: Formal sources offer flexible, structured repayment; informal sources may demand immediate or harsh repayment terms.
- Purpose: Formal credit supports productive investments (e.g., agriculture); informal credit often meets urgent personal needs.
Q14: Analyse the role of banks in the economy of the country.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Banks are pivotal to economic growth and stability.
Explanation:
- Mobilizing savings: Banks collect deposits, channeling public savings into productive investments.
- Credit provision: They provide loans to agriculture, industry, and individuals, driving economic activities and job creation.
- Financial inclusion: Banks implement schemes like Jan Dhan Yojana, ensuring credit access for underserved sections.
- Economic stability: Through monetary policy implementation, banks help control inflation and stabilize the economy.
- Infrastructure support: Bank loans fund infrastructure projects, contributing to national development.
Q15: Analyse the role of Self Help Groups in the development of rural areas in India.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: SHGs significantly contribute to rural development.
Explanation:
- Financial empowerment: SHGs provide access to credit for small-scale enterprises, empowering women and marginalized groups.
- Savings culture: Regular savings promote financial discipline and reduce reliance on exploitative moneylenders.
- Skill development: SHGs offer training in financial management and entrepreneurship, enhancing members’ capabilities.
- Social cohesion: Group activities foster community bonding, mutual support, and collective decision-making.
- Bank linkages: SHGs connect rural members to formal banking, enabling access to larger loans for income-generating activities.
Q16: Shyamal is a small farmer. Shyamal has got his 'Kisan Card' made. He needs a loan to grow new crops. Which of the following means will be easy and beneficial for this?
(a) Cooperative Bank,
(b) Agricultural Traders,
(c) Relatives,
(d) Friends.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (A) Cooperative Bank.
Explanation:
- Cooperative Bank (A): With a Kisan Credit Card, Shyamal can easily access loans from cooperative banks at low interest rates, designed specifically for farmers’ agricultural needs.
- Agricultural Traders (B): These are informal sources with high interest rates, unsuitable for sustainable borrowing.
- Relatives (C) and Friends (D): While accessible, they may not provide sufficient funds or structured repayment terms, making them less beneficial.
Q17: The problem of 'Double Coincidence of Wants' can be solved by which of the following?
(a) By increasing the circulation of currency,
(b) By expanding the scope of markets,
(c) By creating awareness amongst people,
(d) By registering the buyer and seller.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (B) By expanding the scope of markets.
Explanation:
- Expanding the scope of markets (B): Money as a medium of exchange eliminates the need for a double coincidence of wants by allowing goods and services to be traded through a common medium, facilitated by broader market access.
- Other options: Increasing currency circulation (A), creating awareness (C), or registering buyers and sellers (D) do not directly address the barter system’s limitation of requiring mutual wants.
Q18: Distinguish between formal and informal sources of credit in India with example.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Formal and informal sources differ in regulation, terms, and accessibility.
Explanation:
- Formal sources: Regulated by the RBI, e.g., banks (SBI) or cooperatives, offering low interest rates and structured repayment but requiring collateral and documentation.
- Informal sources: Unregulated, e.g., moneylenders or landlords, providing easy access but charging high interest rates, often leading to exploitation.
- Impact: Formal sources promote financial stability; informal sources may trap borrowers in debt cycles.
Q19: Why are formal sources more beneficial than informal sources of credit in India? Explain by giving any three arguments.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Formal sources are more beneficial due to their structure and affordability.
Explanation:
- Lower interest rates: Formal sources like banks charge regulated, lower interest rates, reducing the cost of borrowing compared to moneylenders’ exorbitant rates.
- Regulated terms: Formal credit offers clear, legally binding terms with flexible repayment schedules, ensuring borrower protection.
- Productive use: Formal loans support investments in agriculture or businesses, fostering economic growth, unlike informal loans often used for consumption.
Q20: Explain the role of credit in the economic development of the country with example.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Credit drives economic growth by enabling investment and consumption.
Explanation:
- Agricultural growth: Credit from banks (e.g., Kisan Credit Card) allows farmers to buy modern inputs, increasing productivity and food security.
- Industrial expansion: Loans to small businesses (e.g., MSMEs) create jobs and boost production, contributing to GDP.
- Infrastructure development: Bank loans fund projects like roads or power plants, enhancing economic connectivity and growth.
Q21: Rama is a farmer. She needs a loan for agriculture work. Which of the following sources of loan will be beneficial for Rama? Choose the most appropriate option:
I. Bank,
II. Agricultural Trader,
III. Self-Help Group,
IV. Government.
(a) Only I, III, and IV are correct.
(b) Only I, II, and III are correct.
(c) Only II, III, and IV are correct.
(d) Only I, II, and IV are correct.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (A) Only I, III, and IV are correct.
Explanation:
- Bank (I): Banks provide formal loans with low interest rates, ideal for agricultural needs.
- Self-Help Group (III): SHGs offer affordable credit with community support, suitable for small farmers like Rama.
- Government (IV): Government schemes provide subsidized loans for farmers, ensuring affordability.
- Agricultural Trader (II): Informal source with high interest rates, not beneficial for sustainable borrowing.
Q22: Two statements are given below. They are Assertion (A) and Reason (R).
Assertion (A): Rupees is accepted as medium of exchange in India.
Reason (R): The World Bank legalises the use of rupee as a medium of payment in India.
(a) Both (A) and (R) are correct and (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
(b) Both (A) and (R) are correct, but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
(c) (A) is correct, but (R) is incorrect.
(d) (A) is incorrect, but (R) is correct.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (C) (A) is correct, but (R) is incorrect.
Explanation:
- Assertion (A): The rupee is accepted as a medium of exchange in India, as it is the legal tender authorized by the government.
- Reason (R): The World Bank does not legalize the use of the rupee; this authority lies with the Reserve Bank of India and the Indian government, making (R) incorrect.
Previous Year Questions 2024
Q1: Read the image of the cheque. Identify the cheque number from the given options: (1 Mark ) (CBSE 2024)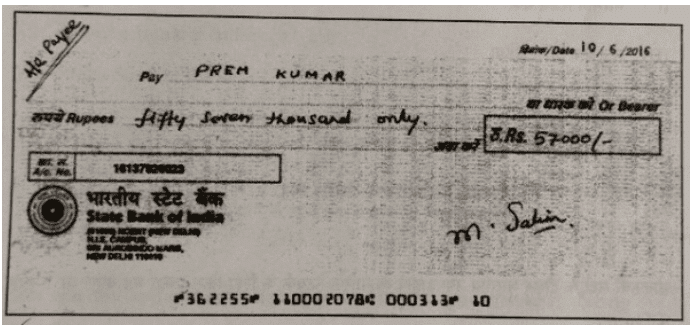 (a) 362255
(a) 362255(b) 110002078
(c) 000313
(d) 16137926023
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a)
The cheque number is a unique identifier for a specific cheque, typically found at the top right corner of the cheque. In the given options, the correct cheque number is (a) 362255, as it matches the format and position usually found on a cheque. The other options either have too many digits or do not fit the typical cheque numbering format.
Q2: Which one of the following banks in India controls the issuance of currency and regulates the credit system in the country?
(1 Mark ) (CBSE 2024)
(a) Punjab National Bank
(b) Indian Bank
(c) Reserve Bank of India
(d) State Bank of India
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c)
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) is the central bank of India, responsible for issuing currency and regulating the country's credit system. It manages monetary policy and ensures financial stability, making option (c) the correct answer. The other banks listed are commercial banks that operate under the regulations set by the RBI.
Q3: Explain the role of `Self Help Groups' in the rural society. (3 Marks ) (CBSE 2024)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: The role of self help groups in a rural society/ economyis as follows:
(1) They organise rural poor, in particular women, into small Self Help Groups to pool their savings.
(2) Self-help groups provide a platform for the rural poor to interchange thoughts, ideas and opinions about various domestic and regional issues.
(3) It inculcates the habit of saving and investing.
(4) It also becomes a medium to borrow cheap loans easily from local banks. Loan is sanctioned in the name of the group and is meant to create self-employment opportunities for the members.
(5) It develops the power of decision-making and develops political and social opinion among the members.
Q4: Why do lenders often require collateral before lending loan? Choose the most suitable option from the following. (1 Mark ) (CBSE 2024)
(a) To lower interest rates for borrowers.
(b) To establish personal relations.
(c) To increase their profit margins.
(d) To mitigate the risk of loan default.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (d) To mitigate the risk of loan default.
Lenders require collateral before lending a loan to ensure that if the borrower fails to repay the loan (defaults), the lender can recover the loan amount by selling the collateral. This reduces the financial risk for the lender, as collateral provides security for the loan.
Q5: Look at the given picture carefully and infer the income of the bank. (1 Mark ) (CBSE 2024)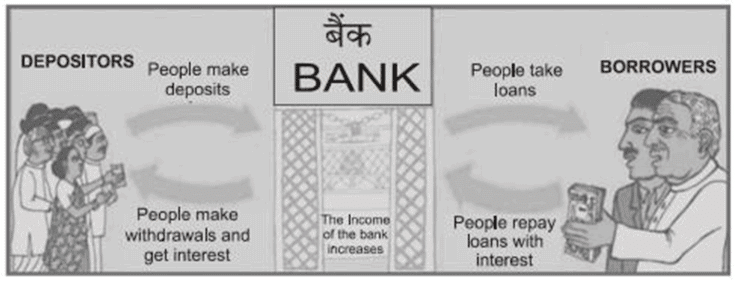
Choose the correct option from the following.
(a) The difference between the amount deposited and borrowed by the bank to Reserve Bank of India.
(b) The difference of amount of interest between what is charged from borrowers and what is paid to depositors.
(c) The difference of interest rate between what is charged from borrowers and what is charged from depositor.
(d) The difference between the amount deposited by the depositor and borrowed by the borrower.
Note: The following question is for Visually Impaired Candidates only in lieu of Q. No. 20. Which one of the following supervise the functioning of formal sources of loan in India?
(a) Reserve Bank of India
(b) State Bank of India
(c) National Development Council
(d) National Finance Commission
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b) The difference of amount of interest between what is charged from borrowers and what is paid to depositors.
For visually impaired Students only
(a) Reserve Bank of India
Q6: How is credit essential for economic activities? Explain with examples. (3 Marks ) (CBSE 2024)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Credit is essential for economic activities because it provides the necessary financial resources for individuals, businesses, and governments to invest, grow, and expand.
Here’s how credit plays a key role:
- Boosting Business Investments: Businesses often need credit to invest in machinery, technology, or expansion. For example, a company might take a loan to buy new equipment or expand its operations. This helps the business grow, increase production, and create more jobs, which boosts the economy.
- Supporting Consumption: Consumers rely on credit to make purchases that they might not be able to afford immediately, such as buying a house, car, or even paying for education. For instance, a person may use a home loan (mortgage) to buy a house, which contributes to the housing market and the overall economy.
- Encouraging Innovation: Entrepreneurs use credit to fund new projects or startups. For example, someone may take a loan to launch a tech startup, creating new products or services that could lead to job creation and new markets.
- Enabling Government Spending: Governments often use credit (through bonds and loans) to fund large infrastructure projects like building roads, schools, and hospitals. These projects not only improve public welfare but also stimulate economic activity and create jobs.
- Facilitating International Trade: Credit is essential for international trade. Businesses use credit (such as trade credit or letters of credit) to import and export goods. This allows companies to expand their markets and engage in cross-border business, boosting global economic activity.
In summary, credit provides the financial means for individuals, businesses, and governments to invest, spend, and grow, all of which are crucial for a thriving economy.
Previous Year Questions 2023
Q7: Explain the role of banks with regard to money which they accept from the public. (3 Marks) (2023) View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Banks play an important role regarding the money they accept from the public
- They keep the money of the public in their safe custody.
- They give interest on the deposited money to the public.
- Banks use the major portion of deposits to extend loans. These loans are then recovered with interest.
- It is easy for individuals to get credit who have savings and a current account in the banks.
Q8: Explain any three functions of the Reserve Bank of India. (3 Marks) (2023, Al 2019)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: The Reserve Bank of India has many important roles that affect the common public:
- RBI monitors the balance kept by the bank for day to day transactions.
- RBI monitors the banking activity, particularly the loan-giving activity of the banks. It ensures that the banks give loans to the priority sector like agriculture and not just to profit-making sectors.
- The RBI undertakes the responsibility of controlling credit created by the commercial banks. RBI uses quantitative and qualitative techniques to control and regulate the credit flow. This includes interest rates and the percentage of loans to a sector.
- The RBI gives guidelines to the bank about setting up the terms of credit that the bank may decide upon for the borrowers.
Q9: "Cheap and affordable credit is crucial for the country’s development’.” Justify the statement. (5 Marks) (CBSE 2023)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Cheap and affordable credit is crucial for a country's development due to the following factors:
- Increased lending leads to higher incomes, encouraging people to invest in agriculture, business, and small-scale industries.
- Cheap credit leaves more income with borrowers for reinvestment, accelerating economic activity.
- Affordable credit allows weaker sections of society to access formal lending, reducing exploitation by informal moneylenders.
- It helps break the cycle of debt and promotes sustainable economic activity, enabling borrowers to invest in better technology and become more competitive.
Q10: Justify the role of 'Self Help Groups’ in the rural economy. (5 Marks) (CBSE 2023)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (i) SHGs have emerged as building blocks of the rural poor as it is the group as a whole which is responsible of the repayment of the loan. In case of non-repayment, it is taken up in a serious manner by the group members.
(ii) The SHGs are organisations of the rural poor people especially women. They provide small loans on reasonable rates.
(iii) The members of SHGs pool their savings and take loans at nominal rates of interests.
(iv) This creates self employment opportunities for the members particularly rural poor women.
(v) The SHGs help poor borrov/ers to overcome the problem of lack of collateral.
Previous Year Questions 2022
Q11: Why are transactions made in money? Explain. (Term-II,2021-22 C) View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: A person holding money can easily exchange it for any commodity or service that he or she might want. Thus, everyone prefers to receive payments in money and then exchange the money for things that they want.
Q12: How does a bank work as a key component of the financial system? Explain. (Term-II, 2021-22)
 View Answer
View Answer 
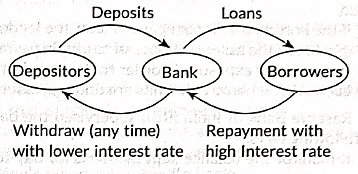
Ans: Banks mediate between those v/ho have surplus funds (the depositors) and those who are in need of these funds (the borrowers). People need small amount of money for their day-to-day needs and deposit the surplus amount in the bank. Bank accepts the deposit and also pay an amount of interest on the deposits. In this way people’s money is safe and earns an amount as an interest.
Bank use the major portion of the deposits to meet the loan requirements of the people.
Q13: Analyse the situation in which credit pushes the borrower into a situation from which recovery is painful. (Term-II, 2021-22)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Bank usually refered as a formal source of credit and in some situations the borrower would not able to repay loan. This pushes them in the situation of dept trap. Example:
(i) In case of rural areas if crop fails due to natural factors it will be difficult for the farmers to pay loan.
(ii) In case of failure of a business. It will be difficult for the businessman to repay the credit.
(iii) In case of informal sector, rate of interest is very high. If due to crop failure previous loan is not repaid interest rate further mounts.
(iv) In case of high risk activities failure without some support can push borrower in painful situation.
(v) In many cases people has to sell their land and fixed assets to repay loan.
Q14: Explain with an example the role of credit for development. (Term-ll, 2021-22)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: ‘Credit’ refers to an agreement in which the lender supplies the borrowers with money, goods or services in return for the promise of future payment. Credit plays vital role for development in different ways as:
(i) Credit helps people from all walks of life in setting up their business, increase their income and support their families.
(ii) To some people loan helps a lot in constructing their houses and get relief from monthly rent, to others it helps a lot in raising their standards of living.
(iii) Example of Salim: The credit helps him and he is able to meet the ongoing expenses of production, complete production on time and thereby increase his earning. 38. Banks play an important role in the economic development of the country.
(i) Capital formation : Banks offer very attractive schemes to attract the people to save their money with them and organised money market.
(ii) They mobilize the small savings of the people through their branches and make it available for productive purposes.
(iii) Credit creation leads to increased production, employment and caused faster economic development.
(iv) The banks help in the development of different type of industries by extending loans to concern persons.
(v) It ensures full utilisation of resources.
Q15: Read the following source and answer the questions that follow: (Term-II,2021-22)
A House Loan
Megha has taken a loan of Rs. 5 lakhs from the bank to purchase a house. The annual interest rate on the loan is 12 per cent and the loan is to be repaid in 10 years in monthly installments. Megha had to submit to the bank, documents showing her employment records and salary before the bank agreed to give her the loan. The bank retained as collateral the papers of the new house, which will be returned to Megha only when she repays the entire loan with interest.
(i) From which source of credit Megha has taken loan?
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Formal source
(ii) Explain the terms of credit given in the source.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Terms of credit given in the source are
Document required - Salary slip and employment record.
Interest rate - 2% per annum
Mode of repayment - Monthly instalment
Collateral - New house papers
Q16: Dhananjay is a government employee and belongs to a rich household, whereas Raju is a construction worker and comes from a poor rural household. Both are in need and wish to take a loan. Create a list of argument explaining who between the two would successfully be able to arrange money from a formal source. Why? (Term-II,2021-22 C, 2016)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Dhananjay will be able to get a loan from a formal source.
Arguments:
- Banks are not present everywhere in rural India. Even when they are present, getting a loan from a bank is much more difficult than taking a loan from informal sources.
- Bank loans require proper documents and collateral. Absence of collateral is one of the major reasons which prevent the poor from getting bank loans.
- Informal lenders such as moneylenders, on the other hand, know the borrowers personally and hence, are often willing to give a loan without collateral.
Previous Year Questions 2021
Q17: The exchange of goods with a commodity is known as: (2021 C)(a) Double coincidence of wants
(b) Local trade
(c) Domestic trade
(d) Foreign trade
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a)
The exchange of goods with a commodity is known as "double coincidence of wants." This term means that for a trade to happen, each party must want what the other has to offer at the same time. Therefore, option (a) is the correct answer, as it specifically describes this type of barter system. The other options refer to different types of trade but do not capture this specific concept.
Q18: Which of the following authorities of India issues currency notes on behalf of the Central Government? (2021 C)
(a) The State Bank of India
(b) The Reserve Bank of India
(c) The Allahabad Bank
(d) The Punjab National Bank
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b)
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) is the authority responsible for issuing currency notes on behalf of the Central Government. It manages the country's monetary policy and ensures the supply of currency in the economy. Therefore, option (b) is the correct answer, while the other banks listed are commercial banks that do not have this authority.
Q19: "The use of money spans a very large part of our everyday life". Support the statement. (2021 C)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: In everyday lives, we use money to fulfill our requirement in different ways:
(i) To buy goods and services like in market, money can be used to buy clothes, vegetables etc.
(ii) To deposit in banks so that money can be saved and used for future use. For example : If a labourer deposits his monthly salary in his bank account, then, he can use it in installments during the entire month.
(iii) As a store value. For instance, we cannot store perishable goods like milk, grain etc. to exchange; but v/e can keep money for future use.
Previous Year Questions 2020
Q20: How do demand deposits have the essential features of money? Explain. (2020) View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Demand deposits are considered as money because:
- The facility of cheques against demand deposits makes it possible to directly settle payments without the use of cash. Since demand deposits are accepted widely as a means of payment, along with currency, they constitute money in the modern economy.
- Banks accept the deposits and also pay an interest rate on the deposits.
- In this way, people’s money is safe with the banks and it earns an interest.
Q21: Read the information given below and select the correct option. (2020 C)
Rohan has taken a loan of Rs.5 lakhs from the bank to purchase a house on 12% rate of interest. He has to submit papers of new house and salary record to the bank. What is this process called as?
(a) Interest Rate
(b) Collateral
(c) Principal Amount
(d) Installments
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b)
The process described is called "collateral," which refers to the assets (like the house Rohan is purchasing) that a borrower offers to the bank as security for a loan. If Rohan fails to repay the loan, the bank can take possession of the collateral. Therefore, option (b) is the correct answer, while the other options refer to different aspects of loans and interest.
Q22: Krishna is working in a neighbouring field with very less wages. Expenses on sudden illnesses or functions in the family are also met through loans. The landowner charges an interest rate of 5 per cent per month. At present she owes the landowner Rs. 5,000.
Analyse the credit arrangements given above. (CBSE 2020)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Credit arrangement-informal sources of credit / No intervention of government in controlling the credit activities carried out by informal sources.
Q23: Why do lenders ask for collateral while lending? Explain. (CBSE 2020)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Lenders ask for collateral while lending because:
- It works as a guarantee to a lender until the loan is repaid.
- If the borrower fails to repay the loan, the lender has the right to sell the asset or collateral to obtain payment.
- It reduces exposure in order to do more business with each other when credit limits are under pressure.
Q24: "The Reserve Bank of India supervises the functioning of formal sources of loans." Support the statement with examples. (2020)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) supervises the functioning of formal sources of loans in the following ways:
- It monitors the balance kept by banks for day-to-day transactions.
- It checks that the banks give loans not just to profit-making businesses and traders but also to small borrowers.
- Periodically, banks have to give details about lenders, borrowers, and interest rates to RBI. It is necessary for securing public welfare. It avoids the banks to run the business with a profit motive only. It also keeps a check on the interest rate of credit facilities provided by banks. RBI makes sure that the loans from the banks are affordable and cheap.
Q25: "Bank plays an important role in the economic development of the country”. Support the statement with an example. (2020)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Banks play an important role in the economic development of the country.
(i) Capital formation : Banks offer very attractive schemes to attract the people to save their money with them and organised money market.
(ii) They mobilize the small savings of the people through their branches and make it available for productive purposes.
(iii) Credit creation leads to increased production, employment and caused faster economic development.
(iv) The banks help in the development of different type of industries by extending loans to concern persons.
(v) It ensures full utilisation of resources.
Q26: “Credit sometimes pushes the borrower into a situation from which recovery is very painful”. Support the statement with examples. (2020)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (i) In rural areas, the main demand for credit is for crop production. Crop production involves considerable costs on seeds, fertilisers, pesticides, water, electricity, repair of equipment, etc.
(ii) There is a minimum stretch of three to four months between the time when the farmers buy these inputs and when they sell the crop.
(iii) Farmers usually take crop loans at the beginning of the season and repay the loan after harvest.
(iv) Repayment of the loan is crucially dependent on the income from farming.
(v) Example of credit which is painful for a borrower: A farmer picks up the loan from a money lender to meet the expenses of cultivation. But unfortunately crops hit by the pests and fails. So, he is unable to repay the loan and ; debt grows larger with interest. Next year, he picks up a fresh loan and is able to have a normal crop that year. But earnings are not enough to pay the earlier loan. He can repay the loan, only after selling a part of the land. So we can say that "Credit sometimes pushes the borrower into a situation from which recovery is very painful”.
Q27: Self-Help Groups are the building blocks of organisation of the rural poor. Suggest any three ways to make them popular for social issues. (2020 C)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Ways to make SHGs popular for social issues:
- Government should make proper provisions to provide funding to SHGs for various social programs.
- SHG members can resolve family's internal issues like domestic violence faced by women and provide financial assistance for marriages.
- SHGs can be given a separate fund for pregnant women's health, which can provide proper diet and medical requirements.
Previous Year Questions 2019
Q28: Why are demand deposits considered as money? (AI2019) View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Demand deposits are considered as money, because they can be withdrawn when required and the money withdrawn can be used for making payments. So, they are also considered as money in the modern economy.
Q29: How is 'double coincidence of wants' not appreciable in the contemporary scenario? (CBSE 2019)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: For double coincidence of wants to work out, an individual must require what the other person is willing to give away and vice-versa. If this situation is not reached exchange of goods does not happen. This problem is eliminated by the use of money.
Q30: Why is money called a medium of exchange? (AI2019)
OR
How does money act as medium of exchange? (2015)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Money acts as an intermediate in the transaction and the exchange process . We can buy things with the help of money.
Q31: Describe the bad effects of informal sources of credit on borrowers. (Delhi 2019)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: The informal sector consists of money lenders, traders, employers, friends, relatives, merchants, and landlords. There is no organization that supervises the credit activities of lenders in the informal sector.
- The informal lenders usually charge a very high rate of interest. A higher cost of borrowing is often detrimental to the borrower. It usually results in a debt trap for the borrower. The borrower is seldom able to escape the never-ending cycle of loan repayment.
- Most loans from informal lenders carry a very high-interest rate and have other stringent conditions. They do little to increase the income of the borrowers.
- It has been observed that the loan recovery mechanics in the informal sector are particularly harsh in cases of loan repayment default. There have been cases of selling of properties at throwaway prices and total loss of belongings and even suicides.
Q32: Explain the three important terms of credit. (CBSE 2019)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: The three important terms of credit are:
- Interest Rate: It is the interest that the borrower pays to the bank. An interest component is added to the principal that the borrower pays to the bank as loan payment in installments.
- Collateral: An asset which is owned by the borrower and is used as a guarantee to a lender until the loan is repaid is called collateral. Land, house, vehicle, livestock, deposits with banks, insurance policy, gold, etc., are examples of assets that can be kept as collateral. If the borrower fails to repay the loan, the lender reserves the right to sell the collateral to obtain payment.
- Documentation: The transaction between the lender and the borrower is put on record by documenting it. It includes the rate of interest, tenure, collateral, and mode of repayment. The terms of credit vary from one loan agreement to another and also on the nature of the lender and the borrower.
Q33: Describe the vital and positive role of credit with examples. (2019, Delhi 2016)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: 'Credit' refers to an agreement in which the lender supplies the borrower with money to buy, goods or services in return for the promise of future payment. Credit plays a vital and positive role a s :
(i) Credit helps people from all walks of life in setting up their busiess, increases their income and support their families.
(ii) To some people loan helps in constructing their houses and get relief from monthly rent.
(iii) To other it helps in raising their living standards,
(iv) Example :Sheela has joined a job. She has taken a loan to buy a scooty that she can attend office conveniently and build a career. Without the loan she would have to travel in bus which takes more time. Thus she would not be able to attend evening classes.
Q34: Describe the importance of formal sources of credit in economic development. (Delhi 2019)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: The formal source of credit comprises of banks and cooperative societies. The Reserve Bank of India supervises the functioning of formal sources of loans.
The importance of formal sources of credit in economic development are:
- Even though collateral and paperwork are needed to secure a loan from banks, the interest rates here are lesser than informal sources.
- The formal sources of credit are part of the greater national economy. Hence even small borrowers should try to avail this facility and not go for informal sources of borrowing.
- The role of formal sources of credit has been very great, particularly for financing large developmental projects and various business projects in the private sector and the public sector.
Q35: Give one example each of modern currency and older currency. (CBSE 2019)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Examples of modern currency are paper bills/notes, coins, credit cards etc., whereas examples of older currency are coins made of precious metals like gold or silver, terracotta coins, etc.
Q36: Examine any three situations in which credit helps in the development of agriculturists. (CBSE 2019)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Credit helps in the development of agriculturists:
(1) The credit helps him to meet the ongoing expenses of production.
(2) It helps in purchasing raw material and equipment.
(3) It helps in irrigation.
Q37: Examine any three situations in which credit pushes the borrower into a debt-trap. (CBSE 2019)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Credit leads borrowers into debt traps in these situations:
(1) Loans from informal sector could lead to debt trap.
(2) Lack of planning results in debt.
(3) Difficulty in repaying loans due to certain circumstances.
Q38: Why do banks and cooperative societies need to lend more? Explain. (CBSE 2019)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Banks and cooperatives should increase their lending in rural areas because:
(1) India largely depends on agriculture for export revenues. Farmers and agricultural workers in rural areas deserve special attention as they lack capital and resources to invest in their work.
(2) Most of the people in rural areas are illiterate and informal money lenders exploit and cheat them for their benefit. People need a reliable source for credit.
(3) Most loans from informal lenders carry a very high interest rate and do little to increase the income of the borrowers.
(4) Banks and co-operative societies provide loans to the rural households at cheap rates and are backed by the government, which helps them boost their income. Incentives are also given to farmers for quick repayment.
(5) Most of the people in urban areas depend upon the rural people for their food and raw material requirements. For better production and to boost their income sources, easy credit is required.
Previous Year Questions 2018
Q39: Give any two examples of informal sector of credit. (2018) View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Two examples of the informal sector of credit are moneylenders and relatives/friends who provide loans.
Previous Year Questions 2017
Q40: Explain any three loan activities of banks in India. (Al 2017) View Answer
View Answer 
Ans:
- Banks provide loans for various economic activities to people or organizations.
- Banks keep only a small proportion of the deposits with them as cash, to meet daily payment demands. The deposits are used to meet the loan requirements of the people.
- Banks intermediates between those who have surplus funds and those who are in need of these funds. Banks offer less interest on deposits than what they charge on loans.
Q41: "Banks are an efficient medium of exchange." Support the statement with arguments. (Delhi 2017)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans:
- People deposit their money with banks by opening a bank account. Banks keep the money safe and provide interest on the deposited amount.
- The deposited money can be withdrawn from banks as and when required on demand.
- Banks also facilitate easy transfer of money through cheques, demand drafts, and internet banking from one account to another in the same or any other bank.
- Banks keep only 15% of their total cash deposits to meet the everyday withdrawal demands of their customers. The major portion of the remaining deposits is used to give loans to people at a specific rate of interest. Thus, we see that money is very efficiently exchanged between various people.
Q42: Illustrate with examples the role of 'loan' in 'business'. (Foreign 2017)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Loan or credit plays a crucial role in business. By sanctioning loans to developing industries and trade, banks provide them with the necessary aid for functioning, developing, and expanding business. This leads to an increase in production, profits, and employment.
For this reason, it is important that the formal sector gives out more loans so that borrowers are not duped by money lenders and can ultimately contribute to national development.
Q43: Review any three merits and any two demerits of 'Formal sector of credit' in India. (Foreign 2017)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Merits of the formal sector of credit in India:
- Regulation: The formal sector is regulated by the Reserve Bank of India, ensuring fair practices and protection for borrowers.
- Lower Interest Rates: Formal sources generally offer loans at lower interest rates compared to informal sources, reducing the burden on borrowers.
- Accessibility: The formal sector provides credit to a wide range of individuals, including both big businessmen and small borrowers.
Demerits of the formal sector of credit in India:
- Lengthy Process: Getting a loan from formal sources often involves a lengthy and bureaucratic process, leading to delays in loan disbursement.
- Collateral Requirement: Formal sources may require collateral for loans, which can be a barrier for individuals who do not possess valuable assets.
Q44: How is money beneficial in transactions? (Foreign 2017)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Money is beneficial in transactions because it eliminates the inconvenience of the double coincidence of wants. In a barter system, individuals would have to find someone who has what they want and is willing to accept what they have to offer in exchange. This can be inefficient and time-consuming. However, with the introduction of money, people can simply exchange their goods or services for money and then use that money to purchase whatever they desire from anyone willing to accept it. Money provides a common medium of exchange that simplifies and accelerates transactions.
Q45: Explain the inherent problem of the ‘barter system’. (CBSE 2017, 15)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: The inherent problem of the barter system is that it is not necessary that when one person is willing to exchange his/her goods, the person he/she wants to exchange with is also willing to do the same.
Q46: Why is it necessary that banks and cooperatives increase their lending in rural areas? Explain. (CBSE 2017)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Banks and cooperatives should increase their lending in rural areas because:
(1) India largely depends on agriculture for export revenues. Farmers and agricultural workers in rural areas deserve special attention as they lack capital and resources to invest in their work.
(2) Most of the people in rural areas are illiterate and informal money lenders exploit and cheat them for their benefit. People need a reliable source for credit.
(3) Most loans from informal lenders carry a very high interest rate and do little to increase the income of the borrowers.
(4) Banks and co-operative societies provide loans to the rural households at cheap rates and are backed by the government, which helps them boost their income. Incentives are also given to farmers for quick repayment.
(5) Most of the people in urban areas depend upon the rural people for their food and raw material requirements. For better production and to boost their income sources, easy credit is required
Previous Year Questions 2016
Q47: Why one cannot refuse a payment made in rupees in India? (2016) View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: One cannot refuse a payment made in rupees in India because the Indian rupee is the authorized and accepted medium of exchange in the country. The Government of India has established the Indian rupee as the official currency, and it is legally recognized as a valid form of payment. Therefore, individuals and businesses are required to accept payments made in rupees, and refusal to do so would be in violation of the accepted legal tender.
Q48: How does money eliminate the need for double coincidence? (2016)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Money eliminates the need for double coincidence by providing a crucial intermediate step in transactions. In a barter system, individuals would have to find someone who not only wants what they have to offer but also has what they desire in return. This double coincidence can be challenging to achieve. However, with the introduction of money, individuals can simply sell their goods or services for money and then use that money to purchase any other desired commodity available in the market. Money acts as a universally accepted medium of exchange, allowing individuals to acquire what they need without the requirement of a direct match between their wants and the wants of others.
Q49: How do the deposits with banks become their source of income? (CBSE 2016)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: When we deposit our money in the bank we get an interest on it. However the bank uses that money to give loan to people. The bank charges an interest on its loan at a higher rate than what is paid to the depositors. Thus, the banks earn money from the deposits.
Q50: Why do banks maintain cash reserve? (2016)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Banks maintain cash reserve to ensure smooth daily withdrawal by depositors.
Q51: Prove with an argument that there is a great need to expand formal sources of credit in rural India. (2016)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: The expansion of formal sources of credit in rural India is crucial because it ensures that the rural poor have access to credit at reasonable interest rates. This helps them meet their financial needs without falling into the trap of high-interest informal loans. Additionally, formal sources of credit provide better regulation and supervision, ensuring fair lending practices.
Q52: Why is the supervision of the functioning of formal sources of loans necessary? (2016)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: The supervision of formal sources of loans is necessary to ensure that these institutions provide loans not only to the rich but also to the poor. It helps in preventing exploitation and ensures that the banks follow the proper procedures and regulations set by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI).
Q53: Why do farmers require credit? (CBSE 2016)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Farmers require credit to finance their agricultural activities. This credit is used to purchase agricultural inputs such as seeds, fertilizers, pesticides, and machinery. It helps farmers to manage their expenses and invest in their farming operations for better productivity.
Q54: How can money be used to easily exchange it for goods or services? Give examples to explain. (Delhi 2016)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Money acts as a medium of exchange itself for goods and services. A person holding money can easily exchange it for any commodity or service that he or she might want. Everyone prefers to receive payments in money and exchange the money for things they want.
For example, a shoemaker wants to sell shoes in the market and buy wheat. The shoemaker will first exchange shoes for money and then exchange the money for wheat. If the shoemaker had to directly exchange shoes for wheat without the use of money, he would have to look for a wheat-growing farmer who not only wants to sell wheat but also wants to buy the shoe in exchange. Both the parties have to agree to sell and buy each other's commodities. This process is very difficult, time-consuming, and unhealthy.
Q55: How is money transferred from one bank account to another bank account? Explain with an example. (Foreign 2016)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: If a person has to make a payment to his or her friend and writes a cheque for a specific amount, this means that the person instructs his bank to pay this amount to his friend. His friend takes this cheque and deposits it in his account in the bank. This said amount is transferred from one bank account to another bank account.
Q56: Mention three points of difference between formal sector and informal sector loans. (2016)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Formal sector loans:
- Loans from banks and cooperatives need collateral.
- Under the supervision of the Reserve Bank of India.
- Reasonable rates of interest.
Informal sector loans:
- Loans from moneylenders, relatives, friends, traders, etc., do not need collateral.
- No supervision of any institution.
- Very high rates of interest.
Q57: How is the concept of Self Help Groups important for poor people? Give your viewpoint. (Foreign 2016)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Self Help Groups are known as SHGs:
- These are mainly created by the poor, often females of rural areas, for their own benefits.
- In this, all members deposit their monthly savings to the leader.
- This creates self-employment for the members.
- If any member needs money for domestic work such as renovation of a house, buying fertilizers, or agricultural equipment, he/she can borrow it from the group.
- Members can get timely loans at reasonable interest and without any collateral and documentation. It operates on mutual trust.
Q58: Poor households still depend on informal sources of credit". Support the statement with examples. (2016)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans:
- Banks are not present everywhere in rural India, whereas informal sources are easily available everywhere.
- Getting a loan from a bank is difficult for poor people than taking a loan from informal resources because bank loans require proper documents and collateral.
- Moneylenders provide loans to poor people without any collateral.
- Formal sources provide loans only for productive purposes, whereas informal sources provide credit for productive and non-productive purposes.
- Other informal sources of credit are friends and relatives, or traders and landlords, who know the borrowers personally and therefore do not demand collateral.
Q59: "The credit activities of the informal sector should be discouraged." Support the statement with arguments. (CBSE 2016)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans:
- 85% of loans taken by poor households in urban areas are from informal sources.
- Informal lenders charge very high interest on their loans.
- There are no boundaries and restrictions.
- The higher cost of borrowing means a larger part of the earnings of the borrowers is used to repay the loans.
- In certain cases, the high interest rate for borrowing can mean that the amount to be repaid is greater than the income of the borrower.
- This could lead to increasing debt and debt trap, therefore the credit activities of the informal sector should be discouraged.
Q60: What are demand deposits? Explain any three features of it. (2016)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Demand deposits refer to the deposits made by individuals in banks that can be withdrawn on demand.
Three features of demand deposits are:
- Banks pay interest on these deposits, providing a safe place for people to keep their money.
- Cheques can be issued against demand deposits, allowing for easy and convenient transactions without the need for cash.
- Demand deposits, along with currency, constitute the money supply in the modern economy.
Q61: How can formal sector loans be made beneficial for poor farmers and workers? Suggest any five measures. (AI 2016)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Formal sector loans can be made beneficial for poor farmers and workers through the following measures:
- Creating awareness: Educating farmers and workers about the availability and benefits of formal sector loans can encourage them to utilize these resources.
- Simplifying the loan process: Streamlining loan application procedures and reducing paperwork can make it easier for farmers and workers to access formal sector loans.
- Expanding banking services: Opening more branches of nationalized banks and cooperatives in rural areas can increase the accessibility of formal sector loans to farmers and workers.
- Increasing loan facilities: Banks and cooperatives should increase the availability of loans to cater to the demand of poor farmers and workers.
- Reducing interest rates: Lowering the interest rates for formal sector loans can make them more affordable for poor farmers and workers, reducing their financial burden.
Q62: Dhananjay is a Government employee and belongs to a rich household whereas Raju is a construction worker and comes from a poor rural household. Both are in need and wish to take loans. Create a list of arguments explaining who between the two will successfully be able to reach money from a formal source. Why? (CBSE 2016)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Out of the two, Dhananjay is more likely to lend money from formal sources.
(1) Dhananjay is more educated and rich and hence, he can understand the nuances of credit.
(2) He must have the required documentation.
(3) He must have assets to be submitted as the collateral.
(4) Raju is a poor construction worker. He is not educated enough.
(5) He might not have the required documentation.
(6) He might not have the required asset to be used as a collateral.
|
66 videos|614 docs|79 tests
|
FAQs on Class 10 Economics Chapter 3 Previous Year Questions - Money and Credit
| 1. What are the key components of money in the context of an economy? |  |
| 2. How does credit impact economic growth? |  |
| 3. What are the different types of credit available to consumers? |  |
| 4. What role does the central bank play in managing money and credit in an economy? |  |
| 5. What are the risks associated with excessive borrowing and credit use? |  |






















