Class 10 History Chapter 3 Previous Year Questions - The Making of Global World
Previous Year Questions 2025
Q1: Read the following reasons of migration of people from Europe to America till the 19th century and choose the correct option:
I. Poverty and hunger,
II. Slaves for sale,
III. Wide spread of diseases,
IV. Religious conflicts and persecution.
(a) Only I, II, and III are correct.
(b) Only II, III, and IV are correct
(c) Only I, III, and IV are correct.
(d) Only I, II, and IV are correct.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (C) Only I, III, and IV are correct.
Explanation:
Several factors led Europeans to migrate to America before the 19th century.- Poverty and hunger (I): Many Europeans faced extreme poverty and lacked sufficient food due to unemployment and famines. America offered opportunities for better jobs and a chance to improve their lives through farming or trade.
- Widespread diseases (III): Europe suffered from frequent disease outbreaks, worsened by crowded and unsanitary living conditions. This prompted many to seek healthier environments in America, where they could live free from such threats.
- Religious conflicts and persecution (IV): Groups like the Puritans faced discrimination or punishment for their religious beliefs in Europe. America provided a safe haven where they could practice their faith without fear.
- Slaves for sale (II): This option is incorrect as it refers to the forced migration of Africans in the slave trade, not the voluntary migration of Europeans seeking better lives. Thus, poverty, diseases, and religious persecution were key reasons for European migration, making option C the correct choice.
Q2: The author of 'Book of Marvels' is:
(a) Marco Polo,
(b) Columbus,
(c) Vasco da Gama,
(d) Alfred Crosby
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (A) Marco Polo
Explanation:
- Marco Polo authored the Book of Marvels, a detailed account of his travels across Asia. His writings described vibrant trade and cultures, inspiring Europeans to explore Asia further.
- The book highlighted the exchange of goods like silk and spices, making it significant in understanding early global trade.
- Other Options: Christopher Columbus discovered the Americas, Vasco da Gama pioneered sea routes to India, and Alfred Crosby is a modern historian, none of whom wrote the Book of Marvels. Therefore, Marco Polo is the correct answer.
Q3: Two statements are given below. Read both the statements carefully and choose the correct option:
Statement I: Rapid improvement in technology has been one major factor to stimulate the globalisation process.
Statement II: This has made much faster delivery of goods across long distances possible at lower costs.
(a) Both statements I and II are correct and statement II is the correct explanation of statement I.
(b) Both statements I and II are correct, but statement II is not the correct explanation of statement I.
(c) Statement I is correct, but statement II is incorrect.
(d) Statement I is incorrect, but statement II is correct.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (A) Both statements I and II are correct and statement II is the correct explanation of statement I.
Explanation:
- Statement I: Advancements in technology significantly boosted global trade and connectivity. Inventions like steamships, railways, and telegraphs enabled faster and more efficient exchange of goods and information across countries, fostering a connected global economy.
- Statement II: These technological improvements allowed goods, such as perishable items like meat, to be transported quickly and at lower costs. For instance, refrigerated ships made it possible to ship meat from America to Europe without spoilage, increasing trade and affordability.
- Explanation Link: Statement II explains how technology facilitated faster and cheaper transport, which directly supported the growth of global trade described in Statement I. Both statements are accurate, and Statement II clarifies the role of technology in driving globalisation.
Q4: 'Potato famine' was related to which of the following countries?
(a) England,
(b) Ireland,
(c) Finland,
(d) Scotland
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (B) Ireland
Explanation:
- The Great Potato Famine (1845–1849) occurred in Ireland, where potatoes were a vital food source for the population.
- A disease called potato blight destroyed crops, leading to widespread starvation and prompting many to emigrate to countries like America in search of survival. This tragic event significantly impacted Ireland’s people and economy.
- Other Options: England, Finland, and Scotland were not primarily affected by this specific famine, as their populations relied less on potatoes. Ireland is the correct answer due to its historical association with the potato famine.
Q5: In the mid-16th century, diseases like smallpox reached America through which of the following?
(a) Spanish soldiers,
(b) French merchants,
(c) Portuguese sailors,
(d) British tourists
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (A) Spanish soldiers
Explanation:
- In the mid-16th century, Spanish soldiers, including conquistadors like those led by Cortés, introduced smallpox to the Americas.
- This disease was unfamiliar to Native Americans, who had no immunity, resulting in devastating epidemics that killed many.
- This weakened local populations, aiding European conquests.
- Other Options: French merchants, Portuguese sailors, and British tourists were not primarily responsible for spreading smallpox during this period. Spanish soldiers were the key carriers, making them the correct answer.
Q6: The germs of which disease paved the way for Europe's conquest of America in the later half of the sixteenth century?
(a) Cholera,
(b) Smallpox,
(c) Jaundice,
(d) Malaria
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (B) Smallpox
Explanation:
- Smallpox played a critical role in Europe’s conquest of the Americas during the late 16th century. Brought by European explorers and soldiers, this disease spread rapidly among Native Americans, who lacked immunity.
- The resulting epidemics caused massive loss of life, weakening communities and making it easier for Europeans to establish control over regions like Mexico and Peru.
- Others: Cholera, jaundice, and malaria existed but did not have the same widespread impact on Native American populations during this period. Smallpox was the primary disease that facilitated European conquests.
Q7: "Globalisation is the process of rapid integration and interconnection between countries." Explain the statement with examples.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans:
Globalisation refers to the process of countries becoming closely connected through trade and cultural exchanges. Globalisation involves countries linking their economies and cultures through the exchange of goods and ideas. Two clear examples illustrate this:
- Trade Integration: In the 19th century, Britain’s growing cities needed more food. America responded by exporting large quantities of corn to Europe, connecting farmers across the ocean to European markets. This trade helped feed industrializing nations and strengthened global economic ties.
- Cultural Exchange: Long before modern times, Indian spices like pepper traveled along the Silk Route to Europe, where they were highly valued for cooking. This trade also spread ideas, such as Buddhism moving from India to China, creating cultural connections across continents. These examples show how globalisation links countries through shared goods and ideas, building a more interconnected world.
Q8: Why was the silk route considered a good example of vibrant pre-modern trade? Choose the most appropriate option from the following:
(a) Due to movement of silk cargoes,
(b) Due to flow of silver and gold,
(c) Due to linkage of China with Australia,
(d) Due to trade and cultural exchange
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (d) Due to trade and cultural exchange
Explanation:
- The Silk Route was a lively network of trade paths connecting Asia, Europe, and Africa, known for its role in exchanging goods and ideas.
- Traders carried valuable items like silk, spices, and textiles from places like India and China to Europe, creating bustling markets.
- Beyond goods, the route spread cultural ideas, such as Buddhism, which traveled from India to other parts of Asia, enriching societies along the way. This combination of trade and cultural exchange made the Silk Route a vibrant example of early global connections.
- Other Options: Silk cargoes (A) were important, but the route included many goods. Gold and silver (B) were traded but not the main focus. A China-Australia connection (C) did not exist in pre-modern times. Trade and cultural exchange (D) best captures the Silk Route’s significance.
Q9: Why was the Indian subcontinent significant to trade networks before European intervention? Explain.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: The Indian subcontinent was a hub for global trade due to its resources and location.
Explanation:
- Rich resources: India exported spices, textiles, and precious stones, attracting traders from Asia and Europe via the Silk Route.
- Strategic location: Its position between East Asia and the Mediterranean made it a key node in maritime and overland trade networks.
Q10: For which of the following markets were cotton and sugar primarily exported from America in the 18th Century?
(a) For American Market,
(b) For European Market,
(c) For Asian Market,
(d) For Australian Market
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (B) For European Market
Explanation:
- In the 18th century, American colonies, particularly in the Caribbean and southern regions, produced large quantities of cotton and sugar on plantations.
- These goods were primarily exported to Europe, where there was high demand for cotton to make textiles and sugar for food and drinks. This trade was a major part of the global economy, with Europe relying heavily on American supplies.
- Others: American markets consumed some of these goods locally, but the primary destination was Europe. Asian markets were not significant buyers of American cotton and sugar, and Australia was not a major market in the 18th century. Europe is the correct answer.
Q11: In the early years of the 19th century the production of which of the following food items brought about a fundamental change in the lives of poor people in Europe?
(a) Tomato,
(b) Potato,
(c) Soya,
(d) Groundnut
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (B) Potato
Explanation:
- In the early 19th century, the potato, introduced from the Americas, transformed the lives of Europe’s poor. It was affordable, easy to grow, and highly nutritious, becoming a staple food for many.
- The potato allowed poor families to eat better and stay healthier, significantly improving their living conditions. In places like Ireland, people depended so heavily on potatoes that a crop failure led to a devastating famine.
- Others: Tomatoes, soya, and groundnuts were also introduced from the Americas, but they had less impact on the diets and lives of Europe’s poor compared to the potato during this period.
Q12: In the 17th century the city El Dorado in South America became famous as which one of the following?
(a) City of Diversity,
(b) City of Gold,
(c) Smallpox City,
(d) Trading City
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (B) City of Gold
- In the 17th century, El Dorado was famous as a legendary “City of Gold” in South America. Stories of its immense wealth in gold sparked excitement among European explorers, who launched expeditions to find it, hoping to gain riches.
- Though El Dorado was more myth than reality, these tales drove exploration and shaped European interest in the Americas.
- Others: El Dorado was not known for diversity (A), smallpox (C), or being a trading hub (D). Its fame as a city of gold makes option B the correct choice.
Previous Year Questions 2024
Q1: “Buddhism emerged from eastern India and spread in several directions." Read the following reasons for its spread and choose the correct option.
(I) Due to Cultural exchange
(II) Due to Silk route
(III) Due to trade & travellers
(IV) Due to European efforts (CBSE 2024)
Options:
(a) Only (I) (II) and (IV ) are correct.
(b) Only (II) (III) and (IV ) are correct.
(c) Only (I) (II) and (III) are correct.
(d) Only (I) (III) and (IV ) are correct.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c)
- Buddhism spread due to cultural exchange, connecting with various cultures and belief systems.
- The Silk Route facilitated the sharing of ideas and practices across different regions.
- Trade and travellers played a significant role in propagating Buddhism, carrying its teachings to distant places.
Thus, the correct option is (c): Only (I), (II), and (III) are correct.
Q2: How did Europeans help in the expansion of trade, knowledge and customs across European countries during mid-sixteenth century? Explain. (CBSE 2024)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Europeans helped in the expansion of trade, knowledge and customs across European countries during mid-sixteenth century in the following ways:
(1) New wealth sources: In an effort to discover new wealth sources, nations engaged in mercantilism and colonialism.
(2) Discovery and colonisation: The 16thcentury discovery and colonisation of the Americas generated an era of economic growth known as the Commercial Revolution.
(3) Sea routes: European traders found a sea-route to Asia and an ocean-route to the Americas in the 16th century. South American mines producing silver and other precious metals made Europe's trade with Asia feasible.
(4) New trade routes: Trade shifted from the Mediterranean and Italy to the nations bordering Europe's Atlantic coast as trade routes between the colonies of the New World and Old World Europe expanded.
Previous Year Questions 2023
Q3: How did the ‘smallpox’ prove as the most powerful weapon of the Spanish conquerors in the mid-sixteenth century? Explain. (CBSE 2023)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Smallpox proved to be a deadly weapon for the Spanish conquerors in the mid-sixteenth century. This can be highlighted through the following points:
- Once introduced, smallpox spread rapidly across the continent.
- It decimated entire communities, making it easier for the Spanish to conquer.
Q4: There were three important developments that greatly shrank the pre-modern world. Identify the incorrect one from the following options: (2023)
(a) The flow of trade
(b) The flow of labour
(c) The flow of capital
(d) The flow of technology
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (d)
In the pre-modern world, the main factors that connected different regions were the flow of trade, labor, and capital. Technology was not yet a major global influence in shrinking distances and connecting the world at that time. Hence, the flow of technology is the incorrect option.
Q5: State the names and countries of the two hostile groups that turned against each other in the First World War. (2023)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: The two hostile groups in the First World War were:
- Allies: This group included Britain, France, and Russia.
- Central Powers: This group consisted of Germany, Austria-Hungary, and Ottoman Turkey.
Q6: Arrange the following in chronological order and choose the correct option.
I. The Bretton Woods conference established the International Monetary Fund.
II. The Second World War broke out between the Axis and Allied groups.
III. A car manufacturer Henry Ford adopted the 'Assembly Line Method’ for production.
IV. The Western economic organised themselves as a group - "The Group of 77". (2023)
(a) III, II, I and IV
(b) I, II, III and IV
(c) IV, III, II and I
(d) IV, II, III and I
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a)
1. Henry Ford adopted the Assembly Line Method for production in 1913.
2. The Second World War broke out in 1939.
3. The Bretton Woods Conference, which established the International Monetary Fund (IMF), was held in 1944.
4. The Group of 77 was formed by developing countries in 1964 to promote their economic interests.
Q7: Differentiate between Fixed and Floating exchange rate. (2023)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Fixed exchange rates mean that two currencies will always be exchanged at the same price, while floating exchange rates mean that the prices between each currency can change depending on market factors, primarily supply and demand.
Previous Year Questions 2020
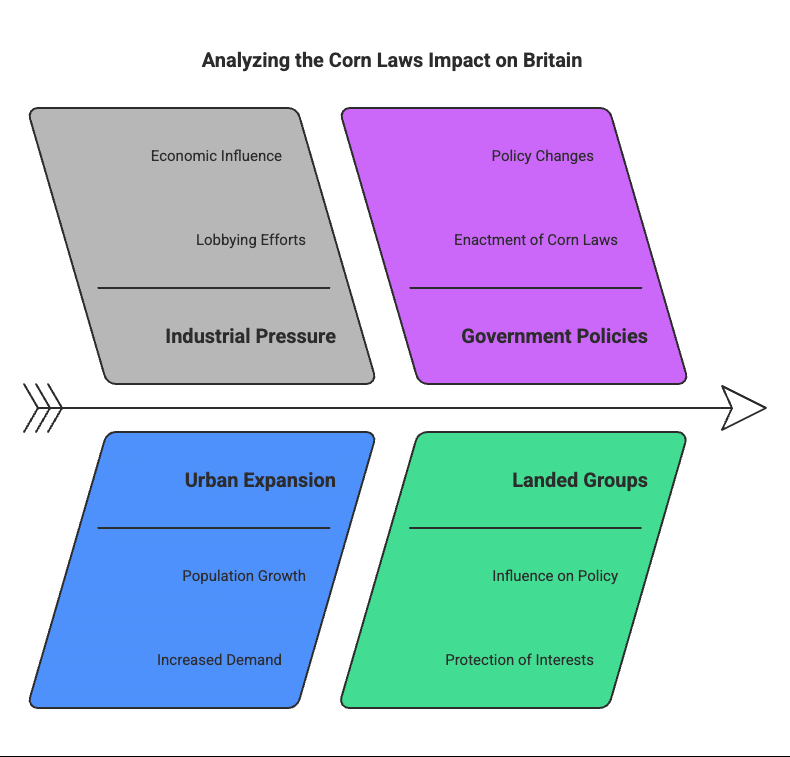
Q8: Explain any three effects of population growth in England in the later eighteenth century. (2020)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans:
- Due to pressure from industrialists, the government was forced to remove corn laws, leading to the import of food in Britain.
- The demand for food grains increased as urban centres expanded, putting pressure on the food supply.
- The government restricted the import of corn by enacting corn laws, due to pressure from landed groups.
Q9: Explain the impact of the Great Depression on Indian weavers during the early twentieth century. (2020)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: The Great Depression had a profound impact on Indian weavers in the early twentieth century.
Key effects included:
- Increased conflict between weavers and Gomasthas (agents of British companies), as weavers protested against unfair practices and sought improved working conditions.
- Weavers faced punishments for delays in delivering goods, which included fines and other penalties, worsening their financial struggles.
- They lost the ability to bargain for prices and sell to various buyers, becoming more reliant on British companies that exploited their situation by offering low prices.
- The prices paid by British companies for weavers' products were extremely low, leading to a significant decline in their income and worsening economic conditions.
- Many weavers, particularly in regions like Carnatic and Bengal, left their villages in search of better job opportunities.
- Some weavers, along with local traders, revolted against the exploitative practices of British companies.
- Due to these economic hardships, many weavers had to close their workshops, contributing to the decline of the traditional handloom industry.
Overall, the Great Depression severely impacted Indian weavers, intensifying their economic difficulties and leading to a decline in their industry.
Q10: Explain the role of Bretton Woods institutions in the post-Second World War settlement. (2020)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: The Bretton Woods institutions, including the International Monetary Fund (IMF) and the World Bank, played a crucial role in the post-Second World War settlement.
Some key roles of these institutions are:
- The Bretton Woods conference, held in 1944, aimed to establish a stable international monetary system after the war. The IMF and the World Bank were created as part of this effort.
- The IMF was tasked with promoting global monetary cooperation, exchange rate stability, and providing financial assistance to member countries facing balance of payment problems.
- The World Bank, officially known as the International Bank for Reconstruction and Development (IBRD), was established to provide financial and technical assistance for the reconstruction and development of war-torn countries.
- The IMF and the World Bank provided financial support to war-devastated countries, helping them rebuild their economies and infrastructure.
- These institutions played a crucial role in facilitating international trade and economic growth by providing financial stability and promoting cooperation among member countries.
- The IMF, through its surveillance and lending programs, helped stabilize exchange rates and provided financial assistance to member countries facing economic crises.
- The World Bank provided long-term loans and technical assistance for infrastructure development, agriculture, and industrial projects in developing countries, contributing to their economic development.
Overall, the Bretton Woods institutions played a vital role in post-World War II settlement, supporting economic reconstruction, stability, and development in member countries.
Previous Year Questions 2019
Q11: Explain any five effects of the abolition of the Corn Laws. (2019C)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: The abolition of the Corn Laws in Britain led to significant changes in the economy.
Here are five key effects:
- It resulted in cheaper grain imports, making food more affordable for consumers.
- British farmers struggled to compete with these low-cost imports, leading to large areas of land becoming uncultivated and many people losing their jobs.
- Increased industrialisation in Britain boosted food imports, with production rising in regions like Eastern Europe, Russia, America, and Australia.
- The demand for food imports enhanced revenues and political power associated with land ownership.
- As food prices fell, overall consumption in Britain increased, contributing to economic growth.
Q12: Indian trade had played a crucial role in the late nineteenth-century world economy.” Analyze the statement. (2019)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Indian trade indeed played a crucial role in the late nineteenth-century world economy. Some key points to consider are:
- India was a major exporter of raw materials to Britain, such as cotton, spices, and indigo. This trade helped fuel the British Industrial Revolution and supported the growth of British industries.
- British companies flooded the Indian markets with their manufactured goods, leading to huge profits for the British. This trade relationship created a trade surplus for Britain while trading with India.
- The trade surplus was used by Britain to pay for private remittances by British officials and to fund their colonial administration in India.
- India also had significant trade with China, mainly in opium. This trade contributed to the global economy and played a role in the Opium Wars between Britain and China.
- Additionally, thousands of Indian laborers migrated as indentured laborers to work on plantations, mines, and construction projects around the world. Their labor contributed to the economic development of various countries.
Overall, Indian trade had a significant impact on the global economy during the late nineteenth century, benefiting Britain and other countries involved in trade with India.
Q13: Describe the impact of ‘Rinderpest’ in Africa in the 1890s. (AI 2019)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Rinderpest, also known as cattle plague, had a devastating impact on Africa in the 1890s. Some key impacts of Rinderpest in Africa are:
- Rinderpest arrived in Africa in the late 1880s, carried by infected cattle imported from British Asia to feed Italian soldiers invading East Africa.
- The disease spread rapidly across Africa, moving from east to west like a forest fire. By 1892, it had reached Africa's Atlantic coast.
- Rinderpest killed approximately 90% of the cattle it infected. This led to a massive loss of cattle, which was a vital source of livelihood for many Africans.
- The loss of cattle destroyed African livelihoods, as people who relied on cattle for milk, meat, and transportation were left without these essential resources.
- As a result of the loss of their cattle-based livelihoods, many Africans were forced to work for wages in order to survive. This had a significant impact on the economy and labor dynamics in Africa.
- The colonial government took advantage of the situation and forced Africans into the labor market, providing cheap labor for colonial needs.
In summary, Rinderpest had a devastating impact on Africa, leading to the loss of cattle-based livelihoods and the forced entry of Africans into the labor market.
Q14: Describe the condition of indentured labour that migrated from India during the nineteenth century. (2019)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: The condition of indentured laborers who migrated from India during the nineteenth century was characterized by various hardships and exploitative practices. Some key aspects of their conditions are:
- Indentured laborers were often recruited through deceptive practices. Agents would provide false information about the nature of work, living conditions, final destinations, and modes of travel, tempting poor individuals into migrating.
- In some cases, less willing workers were forcibly abducted by the agents and taken to the plantations against their will.
- Once on the plantations, the working conditions were harsh, and the laborers had few legal rights. They were subjected to long working hours, physical labor, and poor living conditions.
- Punishments, including beatings and imprisonment, were common for laborers who failed to meet the demanding tasks or attempted to escape their jobs.
- Medical attention provided to the laborers was often nominal, and wages were deducted for absences or failure to fulfill tasks.
- The laborers faced various forms of exploitation, including low wages, debt bondage, and limited opportunities for social mobility.
Overall, the indentured laborers faced challenging conditions characterized by exploitation, deception, and harsh working and living conditions.
Previous Year Questions 2018
Q15: Why did big European powers meet in Berlin in 1885? (2018)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: They met in Berlin in 1885 to partition Africa among themselves.
Q16: “Food offers many examples of long-distance cultural exchange.” Support your answer with three examples. (CBSE 2016-17,2018)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans:
- Travellers and traders introduced new crops to the lands they travelled. For example, noodles travelled west from China to become spaghetti.
- Arab traders took pasta to fifth century Sicily (Italy). Similar foods were known to the Indians and Japanese people. Thus, there was long-distance cultural contact even in the premodern world.
- Potatoes, maize, tomatoes, chillies etc., were not known in India until about five centuries ago. These were introduced in Europe and Asia after the discovery of the Americas by Christopher Columbus.
Previous Year Questions 2017
Q17: Describe any three economic hardships faced by Europe in the 1830s. (2017)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans:
- A rise in food prices due to a year of bad harvest left the country poorer.
- The ratio of the rise in population was larger than that of employment generation, leading to overcrowded slums.
- Peasants suffered under the burden of feudal dues and obligations in some regions of Europe.
- Unhappy with high food prices, urban dwellers and industrialists forced the abolition of the Corn Laws.
Q18: Elucidate any three factors that led to the Great Depression. (2017, 2016)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans:
- Agricultural overproduction remained a problem, which was made worse by falling agricultural prices.
- As prices slumped and agricultural incomes declined, farmers tried to expand production, leading to a large volume of produce flooding the market and pushing down prices.
- Many countries financed their investments through loans from the US in the mid-1920s, but the withdrawal of these loans led to a crisis, including the failure of small major banks and the collapse of currencies such as the British Pound Sterling.
Q19: Describe the contribution of indentured labourers towards the cultural fusion in the emerging global world. (2017, 2014)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans:
Indentured laborers made significant contributions towards cultural fusion in the emerging global world. Their experiences and interactions with different cultures led to the blending of various cultural forms. Some examples of their contributions are:
- Indentured laborers lived and worked in harsh conditions, which forced them to seek avenues of comfort and relaxation. This resulted in the blending of different cultural forms, creating new cultural expressions.
- In Trinidad, for example, the annual Muharram procession was transformed into a riotous carnival called 'Hosay,' in which workers of all races and religions participated.
- The development of "Chutney music" in Trinidad and Guyana is another creative expression of the post-indenture experience, blending Indian musical traditions with Caribbean influences.
- The protest religion of Rastafarianism is also said to reflect social and cultural links with Indian migrants to the Caribbean, suggesting a fusion of Indian and Afro-Caribbean cultural elements.
These examples highlight how the indentured laborers' experiences and interactions contributed to the fusion of different cultural forms in the emerging global world.
Previous Year Questions 2016
Q20: Why did Europeans flee to America in the 19th century? Give three reasons. (CBSE 2016)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Europeans fled to America in the 19th century because:
(1) Europeans were facing problems of poverty and hunger. Economic opportunities were limited to a very high population. America had lesser competition.
(2) Hunger, deadly diseases and religious conflicts were causing a lot of deaths. Europeans fled to America to save their lives.
(3) Since America was not developed by the time, hungry Europeans fled to assert their power over Americans to earn more money.
Q21: Explain the three impacts of the First World War on the British economy. (2016)
 View Answer
View Answer 
- After the war, Britain found it difficult to recapture its earlier position of dominance in the colonial market.
- The war resulted in huge external debts for Britain as it had borrowed money from the US to finance its war expenditures.
- The increase in demand, production, and employment during the war was followed by a reduction in bloated war expenditures, leading to job losses. In 1921, one in every five British workers was unemployed.
Q22: Why do multinational companies (MNCs) choose China as an alternative location for investment? Explain the statement. (2016)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans:
- Since the revolution in 1949, China gradually emerged in the field of world economy and attracted foreign MNCs due to its economic structure.
- Wages in China are relatively low compared to other countries, making it an attractive location for investment.
- China has the largest population, providing a larger consumer base for multinational companies.
Q23: Why did the industrialists and people living in cities of Britain force the government to abolish Corn Laws in the 18th century? Give two reasons. (AI 2016)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans:
- Most industrialists and landlords did not support Corn Laws as they hindered free trade.
- The population in Britain was growing, leading to increased demand for food grains. The rising food prices caused social unrest and forced the government to abolish the Corn Laws.
Q24: "Trade and cultural exchange always went hand in hand." Explain the statement in the light of silk routes. (2016)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans:
- The silk routes are a good example of vibrant premodern trade and cultural links between distant parts of the world.
- The name 'silk routes' points to the importance of west-bound Chinese silk cargoes along this route, as well as the flow of precious metals from Europe to Asia.
- Chinese potteries, textiles from China, and spices from India were traded along the silk routes.
- Various food items also offer very good examples of long-distance cultural exchanges, as Christian missionaries, Muslim preachers, and Buddhist monks traveled through this route.
Q25: After the 19th century, how did the indentured labourers discover their own ways of survival? Explain. (2016)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: After the 19th century, indentured labourers found various ways to survive in difficult conditions.
Their adaptations included:
- Developing new forms of self-expression, blending traditional and modern cultural elements.
- Transforming the Muharram procession in Trinidad into a lively carnival known as 'Hosay', which included participants from all races and religions.
- Creating the protest religion of Rastafarianism, reflecting cultural connections between Indian migrants and Afro-Caribbean communities.
- Learning new skills and utilising their existing knowledge to adapt to their new environments and economic conditions.
- Establishing businesses or engaging in small-scale entrepreneurship to enhance their economic prospects.
- Forming close-knit communities that provided mutual support, fostering a sense of belonging and shared cultural identity.
These strategies enabled indentured labourers to navigate their challenging circumstances and create new opportunities in the post-indenture period.
Q26: Describe any five factors that led to the end of the Bretton Woods System and the beginning of globalisation. (2016)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Several factors contributed to the end of the Bretton Woods System and the beginning of globalization.
Here are five key factors:
- Decline in the economic power of the United States: The US dollar, which was central to the Bretton Woods System, lost its value in relation to gold. This decline eroded confidence in the US dollar and the fixed exchange rate system, leading to the collapse of fixed exchange rates and the shift towards floating exchange rates.
- Change in international finance: The creation of the International Monetary Fund (IMF) and the World Bank under the Bretton Woods System significantly transformed the international financial system. However, by the 1970s, the international financial landscape had changed, and developing countries were increasingly forced to borrow from western commercial banks rather than relying solely on the IMF and World Bank. This shift in international finance had implications for the Bretton Woods System.
- Unemployment in industrialized countries: Industrialized countries faced a rise in unemployment during the 1970s. This increased unemployment led to social and economic problems and contributed to a loss of confidence in the Bretton Woods System.
- Shifting production enterprises: Multinational corporations (MNCs) began shifting their production units to Asian countries, attracted by abundant labor and low wages. This shift in production contributed to the decline of industrialized countries' economies and the emergence of new economic centers in Asia.
- Changes in China: China's economic reforms and opening up to the global market had a profound impact on the global economy. China became an attractive destination for foreign investment, and its economic rise contributed to the transformation of the global economic landscape.
These factors, among others, led to the end of the Bretton Woods System and marked the beginning of globalization, characterized by a shift in economic power, changing financial dynamics, and the emergence of new global economic players.
Previous Year Questions 2015
Q27: The Spanish conquest and colonisation in America were decisively underway by the mid-sixteenth century. Explain with examples. (CBSE 2015)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: The Portuguese and the Spanish conquered America through the introduction of a lethal biological weapon in the form of germs of smallpox.
This can be explained as follows:
(1) Smallpox was carried to America on their person and introduced among the nonimmune Americans.
(2) The Americans caught the disease which led to the destruction of most of their community.
(3) The European and the Spanish invaders were both immune to this disease.
(4) Americans could not turn this weapon back upon their invaders unlike the conventional weapons.
|
66 videos|614 docs|79 tests
|
FAQs on Class 10 History Chapter 3 Previous Year Questions - The Making of Global World
| 1. What is the significance of globalization in the making of a global world? |  |
| 2. How did trade routes influence the development of global connections? |  |
| 3. What impact did colonialism have on global trade patterns? |  |
| 4. How did the Industrial Revolution contribute to the making of a global world? |  |
| 5. What role do international organizations play in a globalized world? |  |

















